Question: 1. Write sonic anemometer, thermal (hot wire) anemometer, cup anemometer, or pitot tube after the statement that best describes its basic principle of operation.
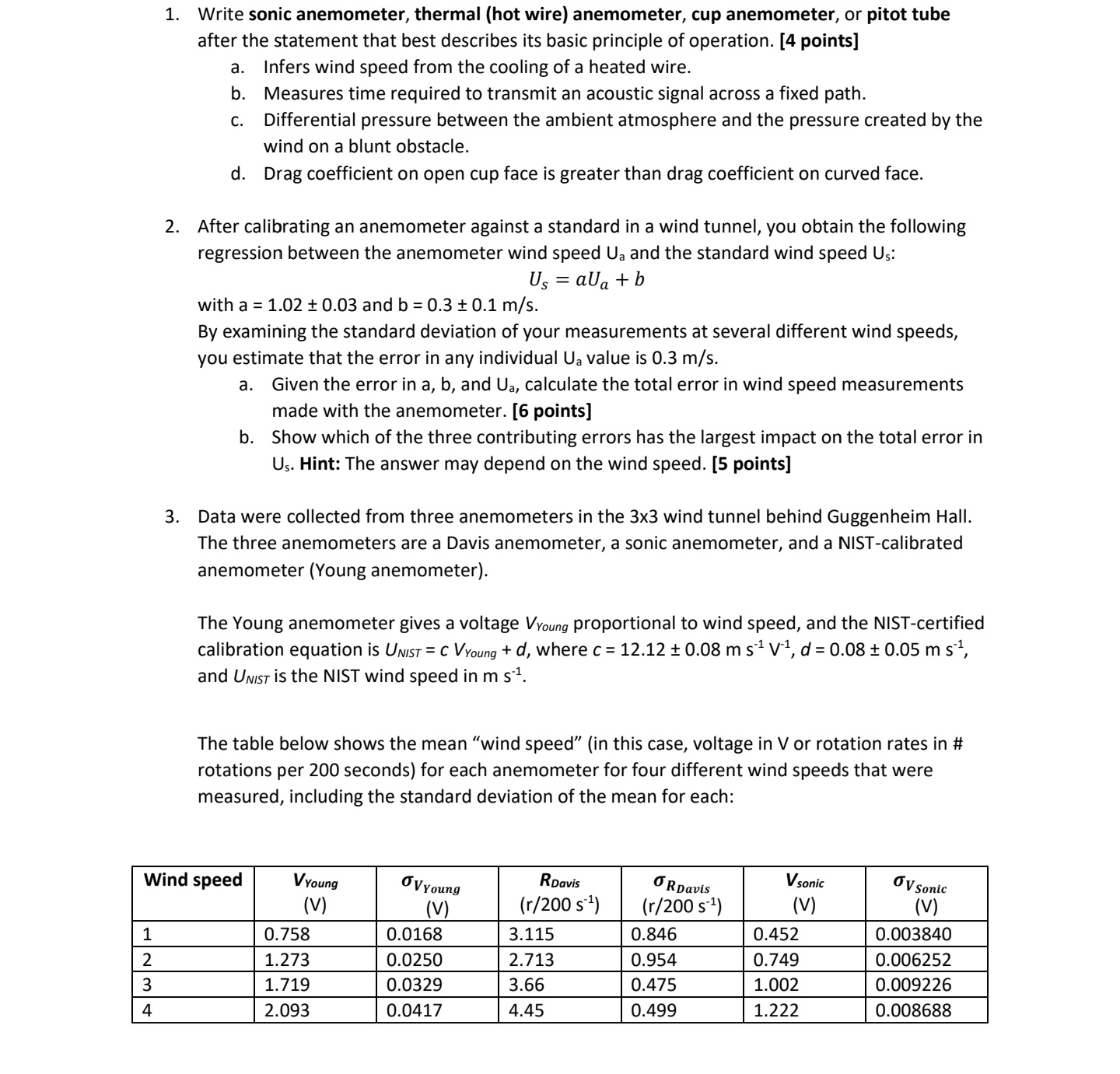
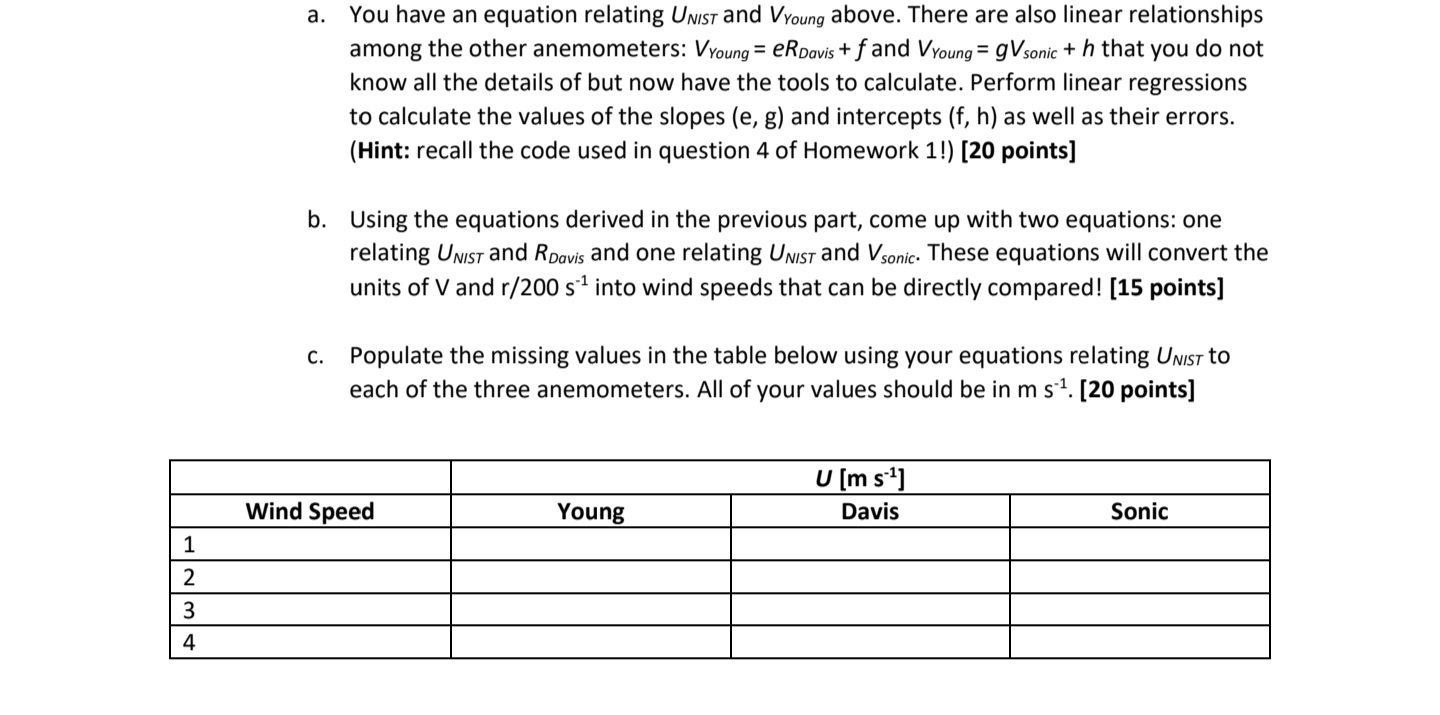
1. Write sonic anemometer, thermal (hot wire) anemometer, cup anemometer, or pitot tube after the statement that best describes its basic principle of operation. [4 points] a. Infers wind speed from the cooling of a heated wire. b. Measures time required to transmit an acoustic signal across a fixed path. C. Differential pressure between the ambient atmosphere and the pressure created by the wind on a blunt obstacle. d. Drag coefficient on open cup face is greater than drag coefficient on curved face. 2. After calibrating an anemometer against a standard in a wind tunnel, you obtain the following regression between the anemometer wind speed Ua and the standard wind speed Us: Us = aUa + b with a 1.02 0.03 and b = 0.3 0.1 m/s. By examining the standard deviation of your measurements at several different wind speeds, you estimate that the error in any individual Ua value is 0.3 m/s. a. Given the error in a, b, and Ua, calculate the total error in wind speed measurements made with the anemometer. [6 points] b. Show which of the three contributing errors has the largest impact on the total error in Us. Hint: The answer may depend on the wind speed. [5 points] 3. Data were collected from three anemometers in the 3x3 wind tunnel behind Guggenheim Hall. The three anemometers are a Davis anemometer, a sonic anemometer, and a NIST-calibrated anemometer (Young anemometer). The Young anemometer gives a voltage Vyoung proportional to wind speed, and the NIST-certified calibration equation is UNIST = C V Young + d, where c = 12.12 0.08 m s V, d = 0.08 0.05 m s, and UNIST is the NIST wind speed in m s. The table below shows the mean "wind speed" (in this case, voltage in V or rotation rates in # rotations per 200 seconds) for each anemometer for four different wind speeds that were measured, including the standard deviation of the mean for each: Wind speed VYoung (V) VYoung (V) RDavis (r/200 s) RDavis (r/200 s) Vsonic (V) OV Sonic (V) 1 0.758 0.0168 3.115 0.846 0.452 0.003840 2 1.273 0.0250 2.713 0.954 0.749 0.006252 3 1.719 0.0329 3.66 0.475 1.002 0.009226 4 2.093 0.0417 4.45 0.499 1.222 0.008688 1 2 3 4 a. You have an equation relating UNIST and VYoung above. There are also linear relationships among the other anemometers: VYoung = eRDavis + f and VYoung = gVsonic + h that you do not know all the details of but now have the tools to calculate. Perform linear regressions to calculate the values of the slopes (e, g) and intercepts (f, h) as well as their errors. (Hint: recall the code used in question 4 of Homework 1!) [20 points] b. Using the equations derived in the previous part, come up with two equations: one relating UNIST and RDavis and one relating UNIST and Vsonic. These equations will convert the units of V and r/200 s into wind speeds that can be directly compared! [15 points] C. Populate the missing values in the table below using your equations relating UNIST to each of the three anemometers. All of your values should be in m s. [20 points] Wind Speed Young U [m s] Davis Sonic
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


