Question: 12. Consider N = 2.0 X 1023 oxygen molecules, contained in a cubical vessel 0.10 m on a side. The gas temperature is 300 K.
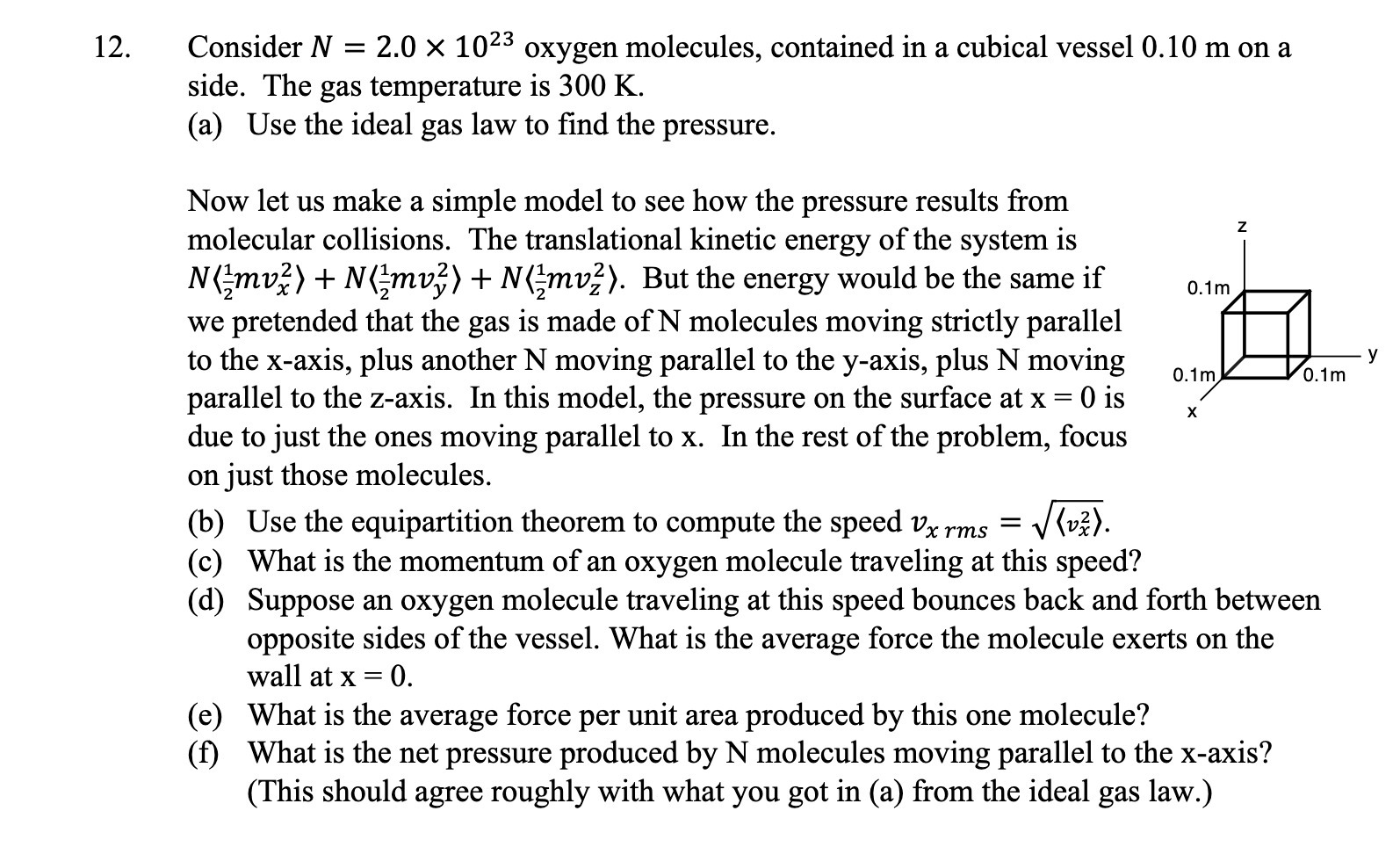
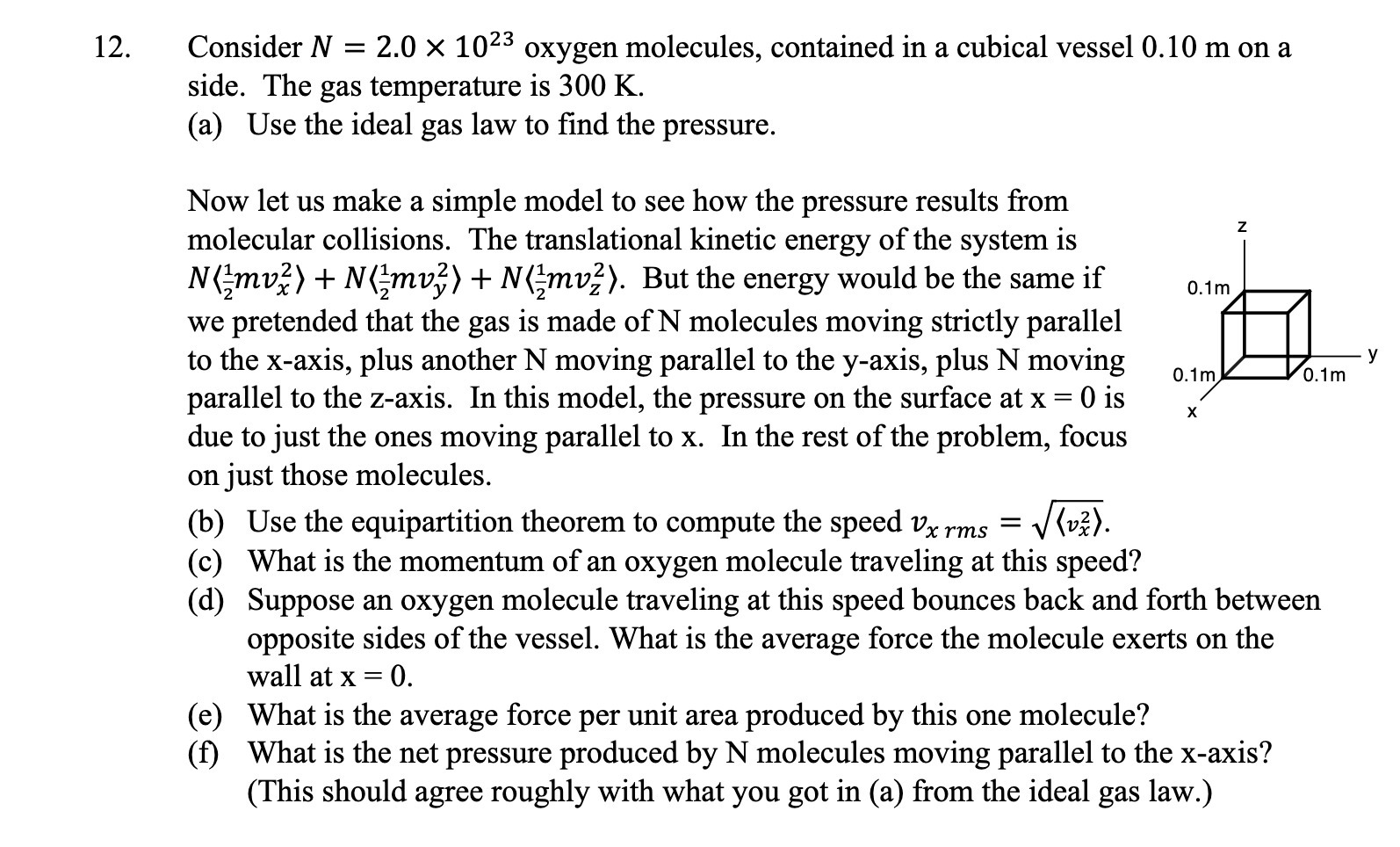
12. Consider N = 2.0 X 1023 oxygen molecules, contained in a cubical vessel 0.10 m on a side. The gas temperature is 300 K. (a) Use the ideal gas law to nd the pressure. Now let us make a simple model to see how the pressure results from molecular collisions. The translational kinetic energy of the system is N (gmvf) + N (gmvf) + N (gmvzz). But the energy would be the same if 0.1m we pretended that the gas is made of N molecules moving strictly parallel to the x-axis, plus another N moving parallel to the yaxis, plus N moving 0.1m 0.1m V parallel to the z-axis. In this model, the pressure on the surface at x = O is due to just the ones moving parallel to x. In the rest of the problem, focus on just those molecules. (b) Use the equipartition theorem to compute the speed 12,; ms = \\Rv). (c) What is the momentum of an oxygen molecule traveling at this speed? ((1) Suppose an oxygen molecule traveling at this speed bounces back and forth between opposite sides of the vessel. What is the average force the molecule exerts on the wall at X = 0. (e) What is the average force per unit area produced by this one molecule? (i) What is the net pressure produced by N molecules moving parallel to the x-axis? (This should agree roughly with what you got in (a) from the ideal gas law.) X
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


