Question: 2. Fused deposition modelling (FDM) is a 3D printing process to build products layer by layer according to a digital model. A research student found
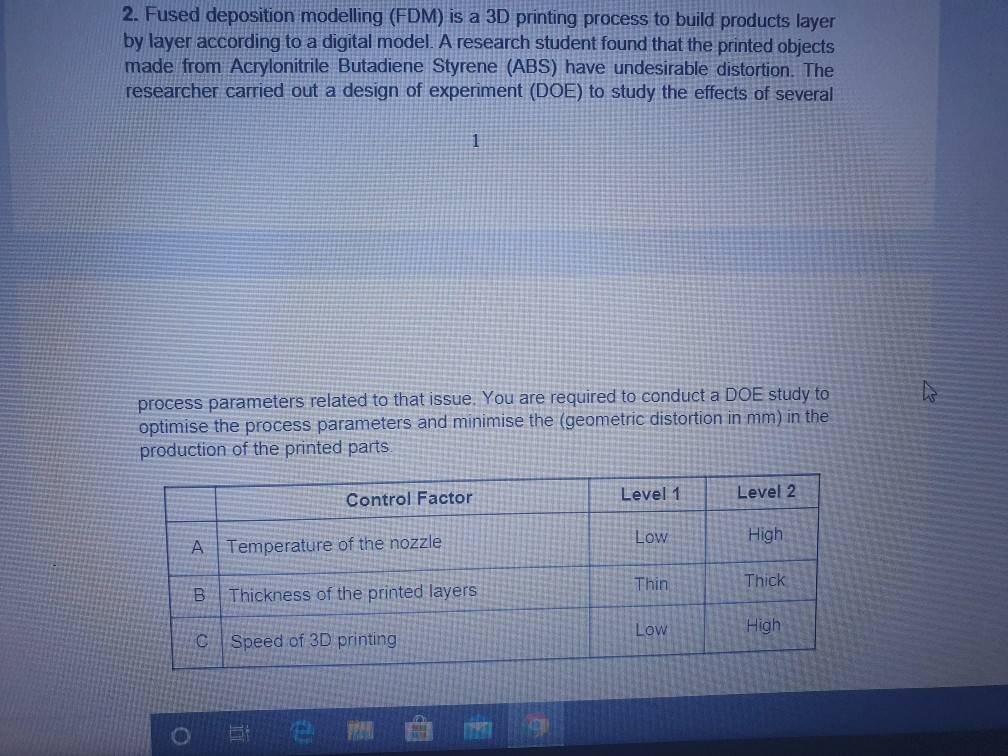
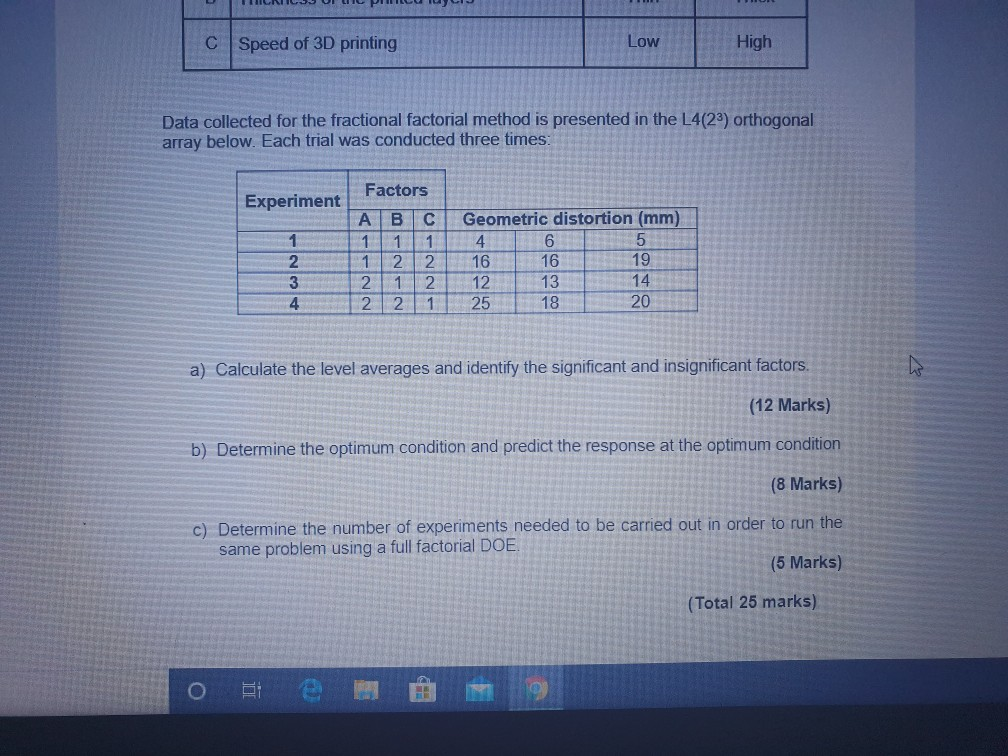
2. Fused deposition modelling (FDM) is a 3D printing process to build products layer by layer according to a digital model. A research student found that the printed obiects made from Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) have undesirable distortion. The researcher carried out a design of experiment (DOE) to study the effects of several process parameters related to that issue. You are required to conduct a DOE study to optimise the process parameters and minimise the (geometric distortion in mm) in the production of the printed parts. Control Factor Level 1 Level 2 Low High A Temperature of the nozzle Thin Thick B Thickness of the printed layers LOW High Speed of 3D printing O PUCCI C Speed of 3D printing Low I High Data collected for the fractional factorial method is presented in the L4(23) orthogonal array below. Each trial was conducted three times: Experiment Geometric distortion (mm) Factors A B C 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 12 2 2 1 AUN 12 25 16 13 18 14 20 a) Calculate the level averages and identify the significant and insignificant factors. (12 Marks) b) Determine the optimum condition and predict the response at the optimum condition (8 Marks) c) Determine the number of experiments needed to be carried out in order to run the same problem using a full factorial DOE (5 Marks) (Total 25 marks) o tem 2. Fused deposition modelling (FDM) is a 3D printing process to build products layer by layer according to a digital model. A research student found that the printed obiects made from Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) have undesirable distortion. The researcher carried out a design of experiment (DOE) to study the effects of several process parameters related to that issue. You are required to conduct a DOE study to optimise the process parameters and minimise the (geometric distortion in mm) in the production of the printed parts. Control Factor Level 1 Level 2 Low High A Temperature of the nozzle Thin Thick B Thickness of the printed layers LOW High Speed of 3D printing O PUCCI C Speed of 3D printing Low I High Data collected for the fractional factorial method is presented in the L4(23) orthogonal array below. Each trial was conducted three times: Experiment Geometric distortion (mm) Factors A B C 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 12 2 2 1 AUN 12 25 16 13 18 14 20 a) Calculate the level averages and identify the significant and insignificant factors. (12 Marks) b) Determine the optimum condition and predict the response at the optimum condition (8 Marks) c) Determine the number of experiments needed to be carried out in order to run the same problem using a full factorial DOE (5 Marks) (Total 25 marks) o tem
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


