Question: 26. The first step in the decision-making process of chapter 7, is to identify and define the problem. 27. Creativity is one of our greatest
26. The first step in the decision-making process of chapter 7, is to identify and define the problem.
27. Creativity is one of our greatest personal assets, even though it may not be recognized.
28. Step 3 of the decision-making process, making a decision, is the easiest of the four steps in this process.
29. The Mount Everest case in chapter 7, illustrates the do ethical reasoning for all of the steps of the decision-making process.
30. Self-confidence means you do not need others as team members to succeed at work.
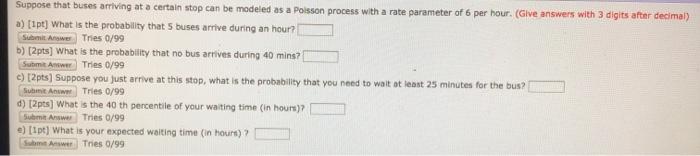
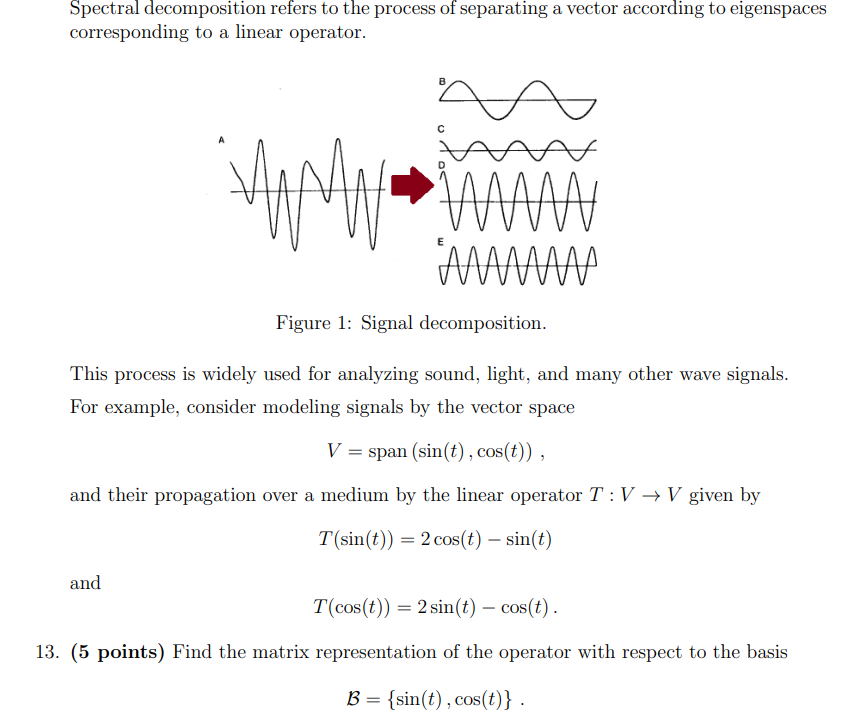

Suppose that buses arriving at a certain stop can be modeled as a Poisson process with a rate parameter of 6 per hour. (Give answers with 3 digits after decimal) a) [1pt] What is the probability that 5 buses arrive during an hour? Submit Answer. Tries 0/99 b) [2pts] What is the probability that no bus arrives during 40 mins? Submit Amver Tries 0/99 c) [2pts] Suppose you just arrive at this stop, what is the probability that you need to wait at least 25 minutes for the bus? Submit Apoem Tries 0/99 d) [2pts] What is the 40'th percentile of your waiting time (In hours]? Subma Arwer Tries 0/99 e) [1pt] What is your expected waiting time (in hours) ? Submit Answer Tries 0/99Spectral decomposition refers to the process of separating a vector according to eigenspaces corresponding to a linear operator. 0 A M Do U i U U 6 Figure 1: Signal decomposition. This process is widely used for analyzing soundJ light? and many other wave signals. For example1 consider modeling signals by the vector space V = span [sin(t) ,cos[t)) , and their propagation over a medium by the linear operator T : V > V given by T(sin{t)) = 2cos{t) sin(t) and T(cos(t)) = 2 sin(t) cos(t) . 13. (5 points} Find the matrix representation of the operator with respect to the basis 3 = {sin(t) ,cos(t)} . 1. Determine the mean-square value of the random process with spectral density defined by: Sx (w) = 1 - 2. Consider a random process with spectral density Sx (@)). The process has mean-square value of 4. Determine the mean-square values of random processes having the following spectral densities: a) 25x(w) b) Sx (2() c) Sx(w/2) 3. Consider a stationary random process with spectral density defined as: Sx(w) = 3216(w) + 876(w - 3) + 876(w + 3) + 32no(w -6) + 32no(w +6) a) What is the mean value of this process? b) What is the variance of this process? c) What are the discrete frequencies of this process
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


