Question: 3. Suppose that $g: mathbb{R}^{n} ightarrow mathbb{R}^{n}$ is a differentiable map that is invertible. For a jointly continuously distributed random vector $X=left(X_{1}, ldots, X_{n} ight)$,
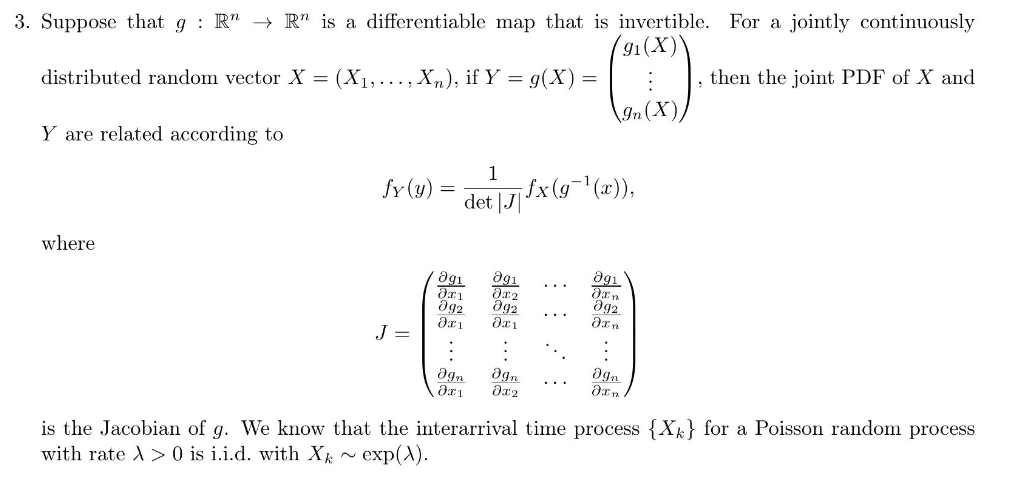
3. Suppose that $g: \mathbb{R}^{n} ightarrow \mathbb{R}^{n}$ is a differentiable map that is invertible. For a jointly continuously distributed random vector $X=\left(X_{1}, \ldots, X_{n} ight)$, if $Y=g(X)=\left(\begin{array}{c}g_{1}(X) \\ \vdots \\ g_{n}(X)\end{array} ight)$, then the joint PDF of $X$ and $Y$ are related according to
$$ f_{Y}(y)=\frac{1}{\operatorname{det}|J|} f_{X}\left(g^{-1}(x) ight) $$
where
$$ J=\left(\begin{array}{cccc} \frac{\partial g_{1}}{\partial x_{1}} & \frac{\partial g_{1}}{\partial x_{2}} & \cdots & \frac{\partial g_{1}}{\partial x_{n}} \\ \frac{\partial g_{2}}{\partial x_{1}} & \frac{\partial g_{2}}{\partial x_{1}} & \cdots & \frac{\partial g_{2}}{\partial x_{n}} \\ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ \frac{\partial g_{n}}{\partial x_{1}} & \frac{\partial g_{n}}{\partial x_{2}} & \cdots & \frac{\partial g_{n}}{\partial x_{n}} \end{array} ight) $$
is the Jacobian of $g$. We know that the interarrival time process $\left\{X_{k} ight\}$ for a Poisson random process with rate $\lambda>0$ is i.i.d. with $X_{k} \sim \exp (\lambda)$. (a) Find an invertible transformation $S^{(n)}=T\left(X^{(n)} ight)$ that relates the $n$ epoch times $S^{(n)}=\left(S_{1}, \ldots, S_{n} ight)$ to the inter-arrival times $X^{(n)}=\left(X_{1}, \ldots, X_{n} ight)$.
(b) What is the joint $\operatorname{PDF} f_{X^{(n)}}\left(x^{(n)} ight)$ ?
(c) Using the above remark find another proof for
$$ f_{S^{(n)}}\left(s^{(n)} ight)=\lambda^{n} e^{-\lambda s_{n}} $$
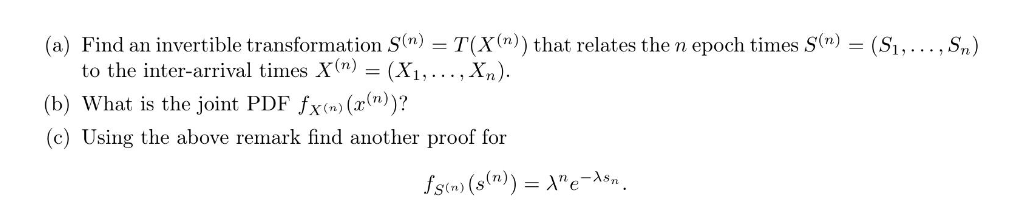
(a) Find an invertible transformation S() = T(X() ) that relates the n epoch times S(") = (S1, . .., Sn) to the inter-arrival times X(") = (X1, ..., Xn). (b) What is the joint PDF fx() (x("))? (c) Using the above remark find another proof for fs(n) (s() ) = 1me-Asn3. Suppose that g : R" - R" is a differentiable map that is invertible. For a jointly continuously 91 ( X ) , then the joint PDF of X and distributed random vector X = (X1, .... Xn), if Y = 9(X) = In Y are related according to 1 fr(y) = fx(g (x)), det |JI where agi ag1 arn 092 ag2 Orn J = agn agn Ogn arn is the Jacobian of g. We know that the interarrival time process {Xx} for a Poisson random process with rate > > 0 is i.i.d. with Xx ~ exp(1)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


