Question: (3) You and a classmate are assigned a project on which you will receive one combined grade. You each want to receive a good grade,


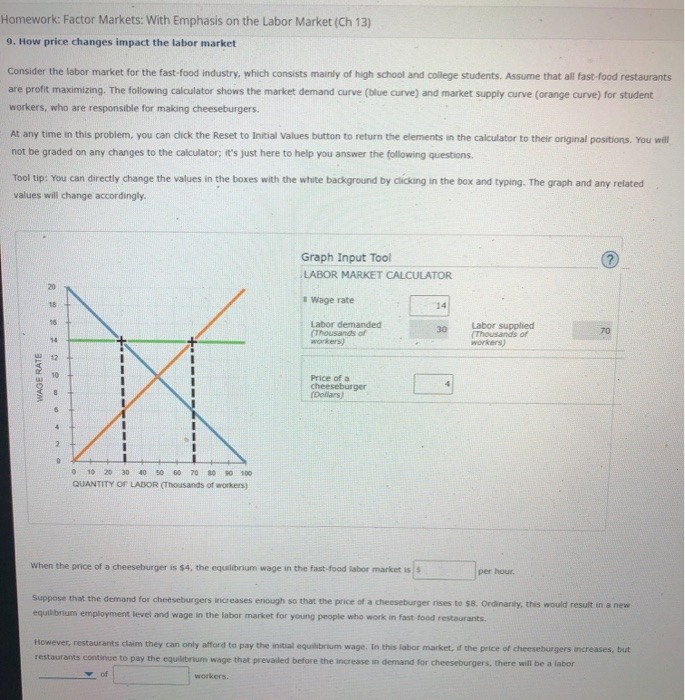
(3) You and a classmate are assigned a project on which you will receive one combined grade. You each want to receive a good grade, but you also want to avoid hard work. In particular, here is the situation: If you both work hard, you get an A, which gives you each 40 units of happiness .If only one of you works hard, you both get a B, which gives you each 30 units of happiness. .If neither of you works hard, you both get a D, which gives each of you 10 units of happiness. . Working hard costs 25 units of happiness. (a) Fill in the following payoff matrix: Your decision Work Shirk Classmate's Work decision Shirk (b) What is the likely outcome? Explain your answer. T (c) If you get this classmate as your partner on a series of projects throughout the year, rather than only once, how might that change the outcome you predicted in part (b)?28. A mandatory arbitration clause in a contract may be rescinded if: if (Circle all that apply) a. One of the parties files bankruptcy b. The parties have unequal bargaining power c. The dispute is between two businesses d. It was entered into as a result of the fraud of one of the parties 29. The Constitution has enumerated the following powers as exclusive to the federal government (Circle all that apply) a. Taxation of income b. Bankruptcy c. Environmental regulation of businesses d. Civil rights protection 30. Which of the following are concurrent powers of the state and federal governments? (Circle all that apply) a. Establishment of post offices b. War powers C. Regulation of commerce d. Consumer protection 31. The Full Faith and Credit clause is intended to ensure that parties will not be required to 32. All states are required to treat the citizens of other states the same as they treat their own citizens under the Constitution's clause. 33. Under federalism, the federal government regulates e-commerce that substantially affects 34. Civil rights protected by the Bill of Rights include the following (Circle all that apply) a. Right to the equal protection of laws b. Right to vote C. Right to engage in political speech d. Right to travel 35. The word "persons" as used in the Bill of Rights includes the following (Circle all that apply) a. Citizens b. Non-citizens c. Corporations d. Partnerships 36. Laws that limit a fundamental right, such as the right to vote, must (Circle all that apply)HW 1 (1) - Word (Product Activation Failed) SERT DESIGN PAGE LAYOUT REFERENCES MAILINGS REVIEW VIEW 1. Towards the end of the 20th century, the U.S. government wanted to save money by closing a small portion of its domestic military installations. While many people agreed that saving money was a desirable goal, people in areas potentially affected by a closing soon reacted negatively. Congress finally selected a panel whose task was to develop a list of installations to close, with the legislation specifying that Congress could not alter the list. Since the goal was to save money, why was this problem so hard to solve? 2. Your car gets 29 miles per gallon (mpg) at 60 miles per hour (mph) and 25 mpg a 70 mph. At what speed should you make a 525-mile trip: a. If gas costs $3 per gallon and your time is worth $18 per hour b. If gas costs $4 per gallon and your time is worth $12 per hour c. If gas costs $5 per gallon and your time is worth $9 per hour 3. A firm is planning to manufacture a new product. As the selling price is increased, the quantity that can be sold decreases. Numerically the sales department estimates: P =$475-0.250 Where P = selling price per unit and Q = quantity sold On the other hand, management estimates that the average unit cost of manufacturing and selling the product will decrease as the quantity sold increases, They estimate C = $480 + $22,500 Where C = cost to produce and sell Q per year The firm's management wishes to maximize profit. What quantity should be sold? How much profit will be made? ENGLISH (CANADA)Homework: Factor Markets: With Emphasis on the Labor Market (Ch 13) 9. How price changes impact the labor market Consider the labor market for the fast-food industry, which consists mainly of high school and college students. Assume that all fast-food restaurants are profit maximizing. The following calculator shows the market demand curve (blue curve) and market supply curve (orange curve) for student workers, who are responsible for making cheeseburgers. At any time in this problem, you can click the Reset to Initial Values button to return the elements in the calculator to their original positions. You will not be graded on any changes to the calculator; it's just here to help you answer the following questions. Tool tip: You can directly change the values in the boxes with the white background by clicking in the box and typing. The graph and any related values will change accordingly. Graph Input Tool (?) LABOR MARKET CALCULATOR Wage rate 14 Labor demanded Labor supplied Thousands of Thousand's of 70 workers) workers WAGE RATE Price of a cheeseburger 0 10 2 040 50 60 70 10 90 QUANTITY OF LABOR (Thousands of workers) When the price of a cheeseburger is $4, the equilibrium wage in the fast-food labor market is $ per hour. Suppose that the demand for cheeseburgers increases enough so that the price of a cheeseburger rises to $8. Ordinarily, this would result in a new equilibrium employment level and wage in the labor market for young people who work in fast food restaurants. However, restaurants claim they can only afford to pay the initial equilibrium wage. In this labor market, If the price of cheeseburgers increases, but restaurants continue to pay the equilibrium wage that prevailed before the increase in demand for cheeseburgers, there will be a labor Z of workers
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


