Question: -3000 4 15- 10-1 Hraise CO/CO, ratio 600 800 Origin 10- 10-1 10-6 10-1 10-6 10-5 10-1 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 10-2 2200 2400
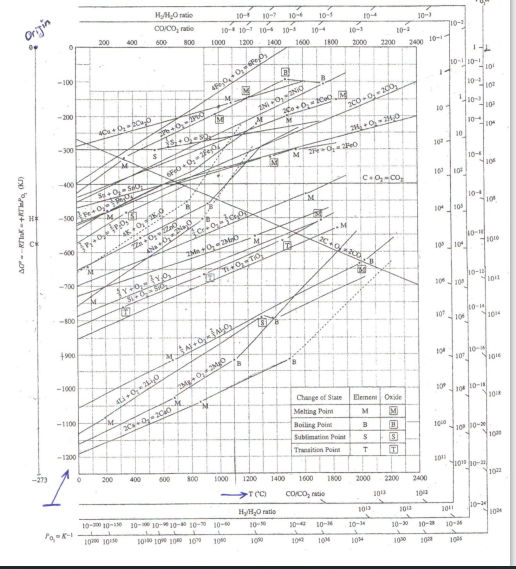

-3000 4 15- 10-1 Hraise CO/CO, ratio 600 800 Origin 10- 10-1 10-6 10-1 10-6 10-5 10-1 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 10-2 2200 2400 200 400 2000 1 - 10-10-1 LO! -100 101 48,00 ZNO, NO 2000-200 10 2009 -200 110- 10 10- 0 30 bowo M 20 -100 MO, PO 10- 0.00, C.CO -400 SSO M 10+ 101 100 H+ AG-Ink, K) 46 2 No Oy ac 200 MA 100 CH . ZM-2Mb 100 104 TOTO bo- 30 100 Yoyo OS 101 10-14 101 20 -500 14 101 HO +900 107 4340 MO -1000 wo- 104 00 Change of State Melting Point Boiling Point blimation Point Transition Point Element Oxide M M B 3 -1100 II 1010 2010- 2200 S T T -1200 1011 2010- You -273 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1500 2000 2200 2400 $_1 -TCC CO/CO, 30 10 300 30 IM H/H, nato 10-10 101 10- 10- 10- 10-30 10-20 10-18 10-10-010-10-10 10-10 1000 1010 10100 100 100 10 1010 ION 104 101 1014 ON 1046 Use the Ellingham Diagram to answer the following questions. 1-)4G800 =? For 4Li + 02 2Li20 reaction at 8000 2-) Sort the stability of Mgo, Y203, Cao, Cr203, A1203 oxides from higher to lower at 900 degree celcius 3-)What is the equilibrium partial oxygen pressure (PO2, 500) of the 4Cu + 02 + 2Cu20 reaction at 500C? 4-)Which metal (s) do you use to reduce Si02 at 800C? Explain. 5-)What should be the pressure of the environment in order to convert y metal to oxide at 1000C. Explain. 6-) Can A1203 be reduced by chromium (Cr) at 8000. Explain
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


