Question: 31.4 Java Chapter 31 LISTING 31.4 MultiThreadServer.java 1 import java.io.*; 2 import java.net.*; 3 import java.util.Date; 4 import javafx.application.Application; 5 import javafx.application.Platform; 6 import javafx.scene.Scene;
31.4 Java Chapter 31
LISTING 31.4 MultiThreadServer.java 1 import java.io.*; 2 import java.net.*; 3 import java.util.Date; 4 import javafx.application.Application; 5 import javafx.application.Platform; 6 import javafx.scene.Scene; 7 import javafx.scene.control.ScrollPane; 8 import javafx.scene.control.TextArea; 9 import javafx.stage.Stage; 10 11 public class MultiThreadServer extends Application { 12 // Text area for displaying contents 13 private TextArea ta = new TextArea(); 14 15 // Number a client 16 private int clientNo = 0; 17 18 @Override // Override the start method in the Application class 19 public void start(Stage primaryStage) { 20 // Create a scene and place it in the stage 21 Scene scene = new Scene(new ScrollPane(ta), 450, 200); 22 primaryStage.setTitle("MultiThreadServer"); // Set the stage title 23 primaryStage.setScene(scene); // Place the scene in the stage 24 primaryStage.show(); // Display the stage 25 26 new Thread( () -> { 27 try { 28 // Create a server socket 29 ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8000); 30 ta.appendText("MultiThreadServer started at " 31 + new Date() + ' '); 32 33 while (true) { 34 // Listen for a new connection request 35 Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); 36 37 // Increment clientNo 38 clientNo++; 39 40 Platform.runLater( () -> { 41 // Display the client number 42 ta.appendText("Starting thread for client " + clientNo + 43 " at " + new Date() + ' '); 44 45 // Find the client's host name, and IP address 46 InetAddress inetAddress = socket.getInetAddress(); 47 ta.appendText("Client " + clientNo + "'s host name is " 48 + inetAddress.getHostName() + " "); 49 ta.appendText("Client " + clientNo + "'s IP Address is " 50 + inetAddress.getHostAddress() + " "); 51 }); 52 53 // Create and start a new thread for the connection 54 new Thread(new HandleAClient(socket)).start(); 55 } 56 } 57 catch(IOException ex) { 58 System.err.println(ex); 59 } 60 }).start(); 61 } 62 63 // Define the thread class for handling new connection 64 class HandleAClient implements Runnable { 65 private Socket socket; // A connected socket 66 67 /** Construct a thread */ 68 public HandleAClient(Socket socket) { 69 this.socket = socket; 70 } 71 72 /** Run a thread */ 73 public void run() { 74 try { 75 // Create data input and output streams 76 DataInputStream inputFromClient = new DataInputStream( 77 socket.getInputStream()); 78 DataOutputStream outputToClient = new DataOutputStream( 79 socket.getOutputStream()); 80 81 // Continuously serve the client 82 while (true) { 83 // Receive radius from the client 84 double radius = inputFromClient.readDouble(); 85 86 // Compute area 87 double area = radius * radius * Math.PI; 88 89 // Send area back to the client 90 outputToClient.writeDouble(area); 91 92 Platform.runLater(() -> { 93 ta.appendText("radius received from client: " + 94 radius + ' '); 95 ta.appendText("Area found: " + area + ' '); 96 }); 97 } 98 } 99 catch(IOException e) { 100 ex.printStackTrace(); 101 } 102 } 103 } 104 }
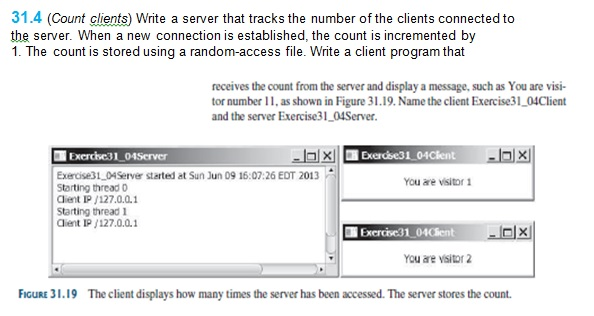
Write a server that tracks the number of the clients connected to server. When a new connection is established, the count is incremented by 1. The count is stored using a random-access file. Write a client program that receives the count from the server and display a message, such as You are visitor number 11, as shown in Figure 31.19. Name the client Exercise31_04Client and the server Exercise31_04Server
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


