Question: 4. Consider a one-dimensional, steady-state heat conduction problem where heat diffuses across a solid wall between the boundaries x = 0 and x =
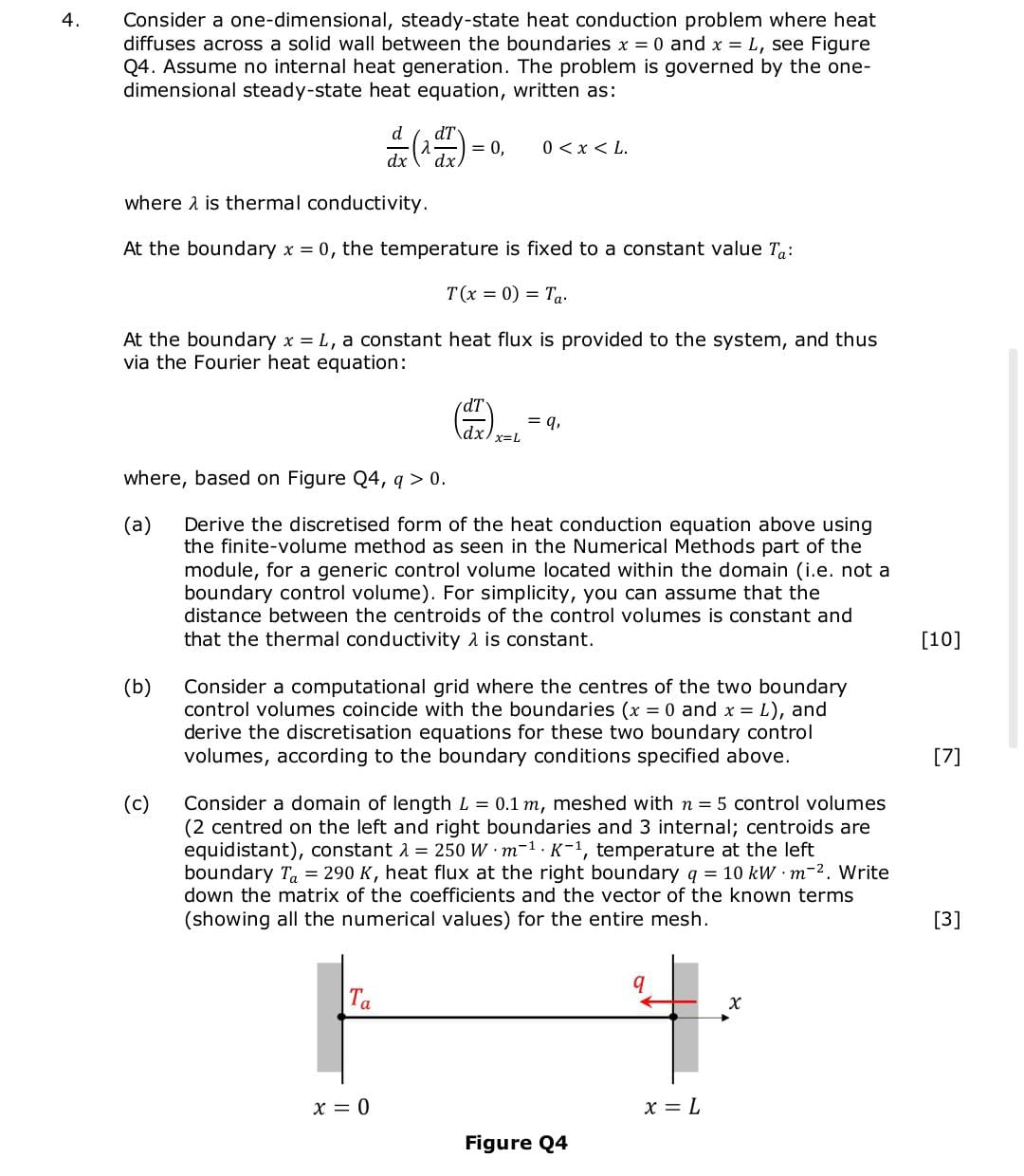
4. Consider a one-dimensional, steady-state heat conduction problem where heat diffuses across a solid wall between the boundaries x = 0 and x = L, see Figure Q4. Assume no internal heat generation. The problem is governed by the one- dimensional steady-state heat equation, written as: d dx *-* dT = 0, dx. 0 < x 0. (dT dx = 9, x=L (a) Derive the discretised form of the heat conduction equation above using the finite-volume method as seen in the Numerical Methods part of the module, for a generic control volume located within the domain (i.e. not a boundary control volume). For simplicity, you can assume that the distance between the centroids of the control volumes is constant and that the thermal conductivity is constant. [10] (b) Consider a computational grid where the centres of the two boundary control volumes coincide with the boundaries (x = 0 and x L), and derive the discretisation equations for these two boundary control volumes, according to the boundary conditions specified above. [7] (c) Consider a domain of length L = 0.1 m, meshed with n = 5 control volumes (2 centred on the left and right boundaries and 3 internal; centroids are equidistant), constant = 250 W m K-1, temperature at the left boundary T = 290 K, heat flux at the right boundary q = 10 kW m2. Write down the matrix of the coefficients and the vector of the known terms (showing all the numerical values) for the entire mesh. Ta 9 x x 0 x = L Figure Q4 [3]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


