Question: (4) Consider a Zn/Hg amalgam, forming a non-ideal solution where Zn is a non-volatile solute, and Hg is a solvent with very low vapour pressure.
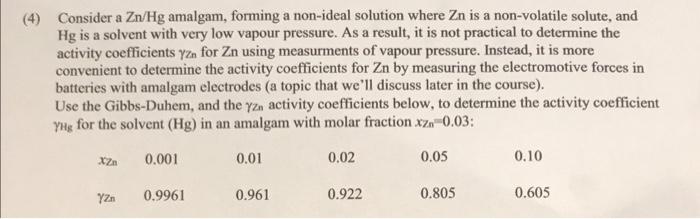
(4) Consider a Zn/Hg amalgam, forming a non-ideal solution where Zn is a non-volatile solute, and Hg is a solvent with very low vapour pressure. As a result, it is not practical to determine the activity coefficients yzn for Zn using measurments of vapour pressure. Instead, it is more convenient to determine the activity coefficients for Zn by measuring the electromotive forces in batteries with amalgam electrodes (a topic that we'll discuss later in the course). Use the Gibbs-Duhem, and the yzn activity coefficients below, to determine the activity coefficient Yng for the solvent (Hg) in an amalgam with molar fraction xz0.03: 0.001 0.01 0.02 0.05 0.10 Y n 0.9961 0.961 0.922 0.805 0.605
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


