Question: 4) For the following problem the constraints for a utility maximization problem are given by Ip1x1+p2x2x10,x20 where {I,p1,p2} are the household income and the prices
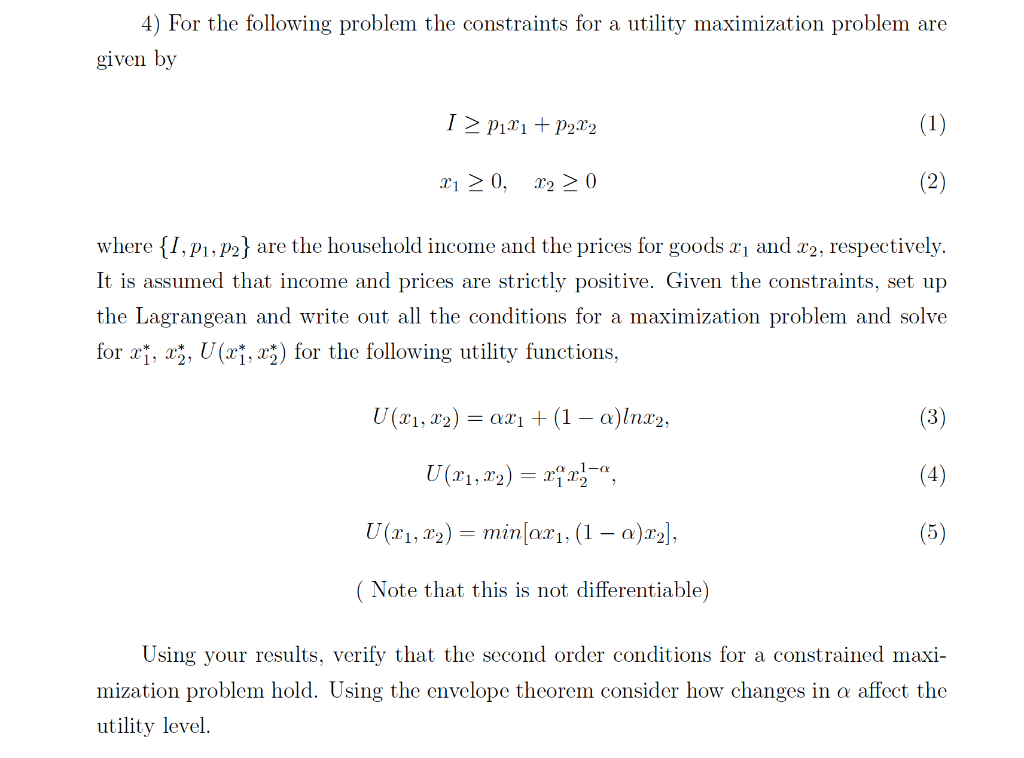
4) For the following problem the constraints for a utility maximization problem are given by Ip1x1+p2x2x10,x20 where {I,p1,p2} are the household income and the prices for goods x1 and x2, respectively. It is assumed that income and prices are strictly positive. Given the constraints, set up the Lagrangean and write out all the conditions for a maximization problem and solve for x1,x2,U(x1,x2) for the following utility functions, U(x1,x2)=x1+(1)lnx2U(x1,x2)=x1x21U(x1,x2)=min[x1,(1)x2] ( Note that this is not differentiable) Using your results, verify that the second order conditions for a constrained maximization problem hold. Using the envelope theorem consider how changes in affect the utility level. 4) For the following problem the constraints for a utility maximization problem are given by Ip1x1+p2x2x10,x20 where {I,p1,p2} are the household income and the prices for goods x1 and x2, respectively. It is assumed that income and prices are strictly positive. Given the constraints, set up the Lagrangean and write out all the conditions for a maximization problem and solve for x1,x2,U(x1,x2) for the following utility functions, U(x1,x2)=x1+(1)lnx2U(x1,x2)=x1x21U(x1,x2)=min[x1,(1)x2] ( Note that this is not differentiable) Using your results, verify that the second order conditions for a constrained maximization problem hold. Using the envelope theorem consider how changes in affect the utility level
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


