Question: 40.5C Initial, 23.3C Final Temp 0.50g Mg 100.3g HCL Data Analysis - Record Values in the Data Table 1. Use the graph or raw data
40.5C Initial, 23.3C Final Temp 0.50g Mg 100.3g HCL 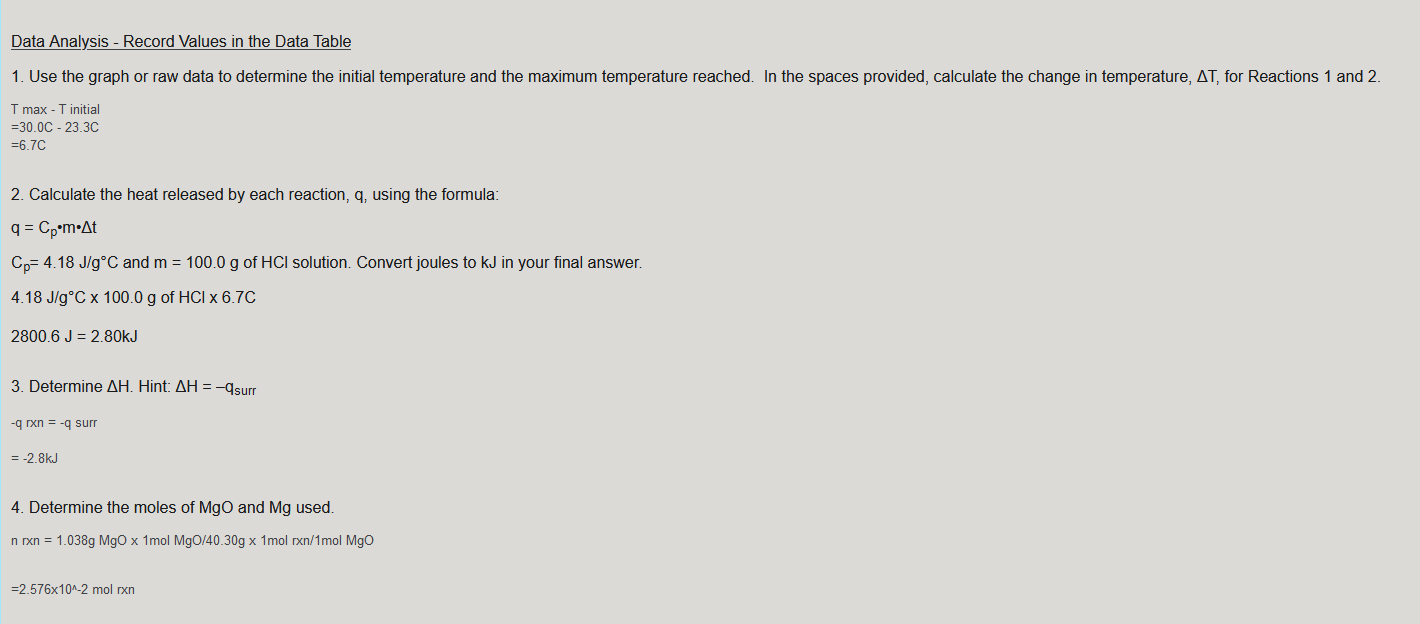
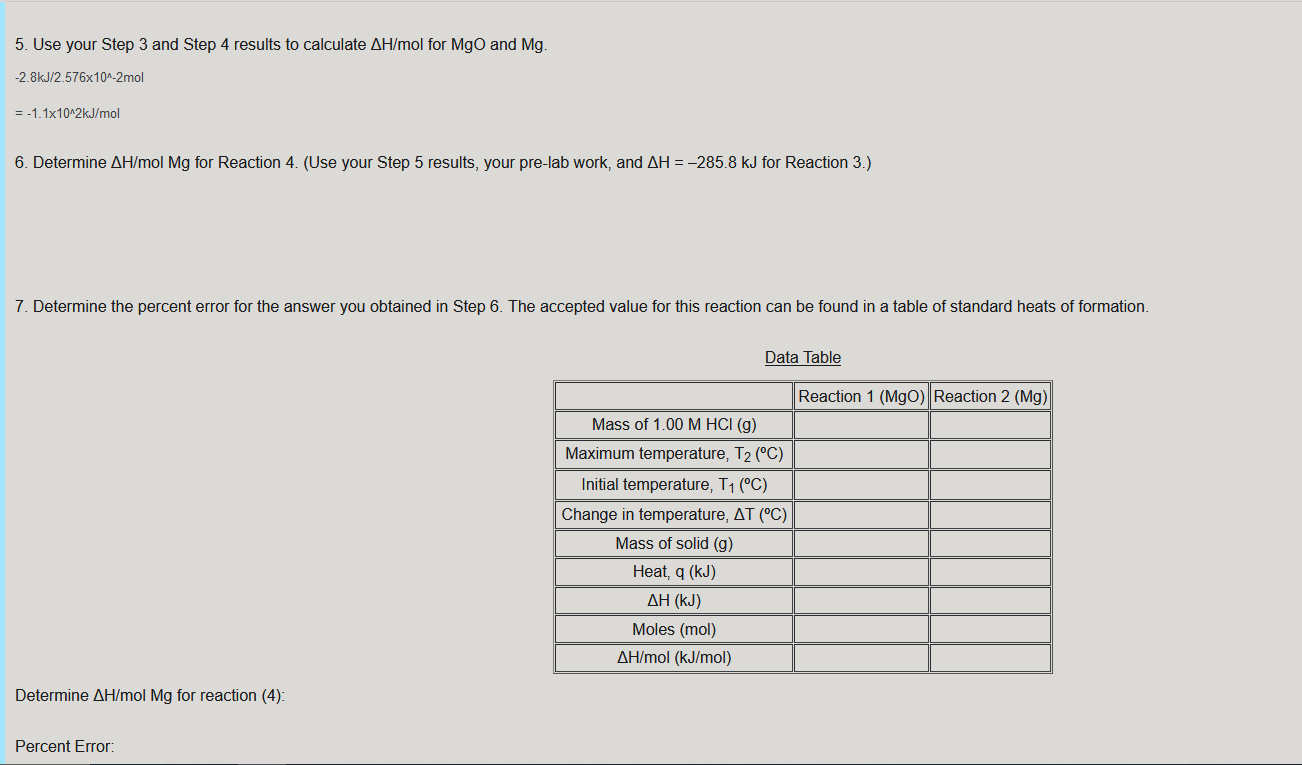
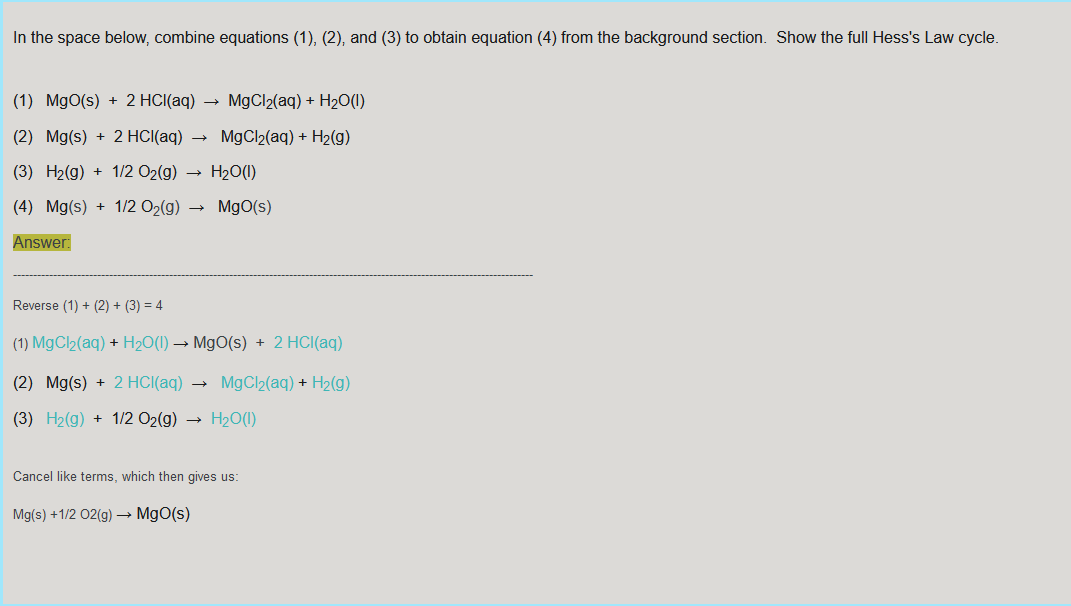
Data Analysis - Record Values in the Data Table 1. Use the graph or raw data to determine the initial temperature and the maximum temperature reached. In the spaces provided, calculate the change in temperature, AT, for Reactions 1 and 2 T max - T initial 30.0c - 23 3C =6.7C 2. Calculate the heat released by each reaction, q, using the formula: q = Cpm.At Cp= 4.18 J/gC and m = 100.0 g of HCl solution. Convert joules to kJ in your final answer. 4.18 J/gC x 100.0 g of HCI x 6.7C 2800.6 J = 2.80kJ 3. Determine AH. Hint: AH = -Asurr - rxn = -9 surr = -2.8kJ 4. Determine the moles of MgO and Mg used. n rxn = 1.038g MgO x 1mol Mg0/40.30g x 1mol rxn/1mol Mgo =2.576x10^-2 mol rxn 5. Use your Step 3 and Step 4 results to calculate AH/mol for MgO and Mg. -2.8kJ/2.576x10^-2mol = -1.1x10^2kJ/mol 6. Determine AH/mol Mg for Reaction 4. (Use your Step 5 results, your pre-lab work, and AH = -285.8 kJ for Reaction 3.) 7. Determine the percent error for the answer you obtained in Step 6. The accepted value for this reaction can be found in a table of standard heats of formation. Data Table Reaction 1 (MgO) Reaction 2 (Mg) Mass of 1.00 M HCl (g) Maximum temperature, T2 (C) Initial temperature, T1 (C) Change in temperature, AT (C) Mass of solid (g) Heat, q (kJ) (kJ) Moles (mol) AH/mol (kJ/mol) Determine AH/mol Mg for reaction (4): Percent Error: In the space below, combine equations (1), (2), and (3) to obtain equation (4) from the background section. Show the full Hess's Law cycle. (1) MgO(s) + 2 HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq) + H20(1) (2) Mg(s) + 2 HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq) + H2(9) (3) H2(g) + 1/2O2(g) H2O(1) (4) Mg(s) + 1/2O2(9) Mgo(s) Answer: Reverse (1) + (2) + (3) = 4 (1) MgCl2(aq) + H2O(l) MgO(s) + 2 HCl(aq) (2) Mg(s) + 2 HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq) + H2(9) (3) H2(g) + 1/2 O2(g) H2O(1) Cancel like terms, which then gives us: Mg(s) + 1/2O2(g) MgO(s)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


