Question: ( 5 0 points ) For flow inside tubes at constant volumetric flow rates ( Q ) , the mass transfer rate of a component
points For flow inside tubes at constant volumetric flow rates the mass transfer rate of a
component either from the fluid stream to the tube inside surface or from the tube inside
surface to the fluid stream can be calculated using the following relations:
ubraceubrace
where the final term is the log mean driving force at the inlet and outlet of the tube, :
concentration of at the inside surface of the tube, : concentration of in the inlet fluid stream,
concentration of in the outlet fluid stream, and : the inside surface area of the tube through
which component is transported.
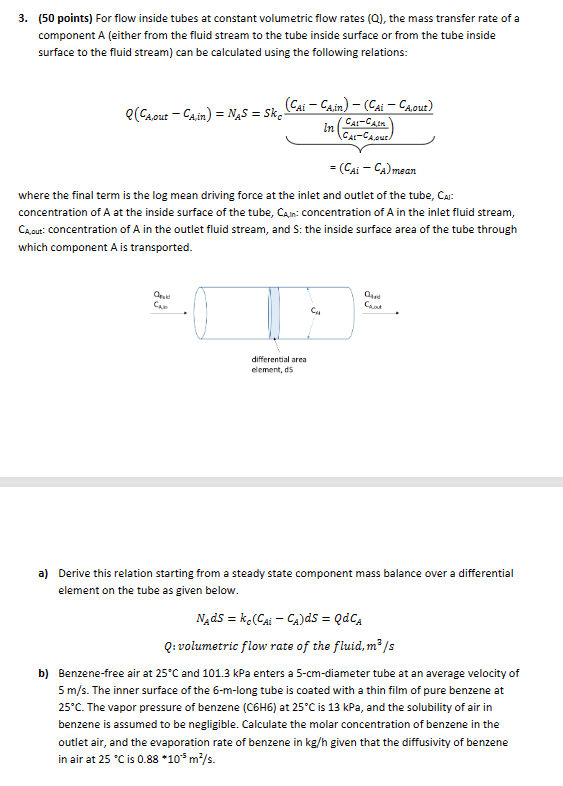
a Derive this relation starting from a steady state component mass balance over a differential
element on the tube as given below.
: volumetric flow rate the fluid,
b Benzenefree air at and kPa enters a cmdiameter tube at an average velocity of
The inner surface of the long tube is coated with a thin film of pure benzene at
The vapor pressure of benzene at is kPa, and the solubility of air in
benzene is assumed to be negligible. Calculate the molar concentration of benzene in the
outlet air, and the evaporation rate of benzene in given that the diffusivity of benzene
in air at is
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


