Question: 5. Consider the two-period binomial model with So = $100, u = 2, d = 1/2, and r = 1/2. As usual, 12 = {dd,
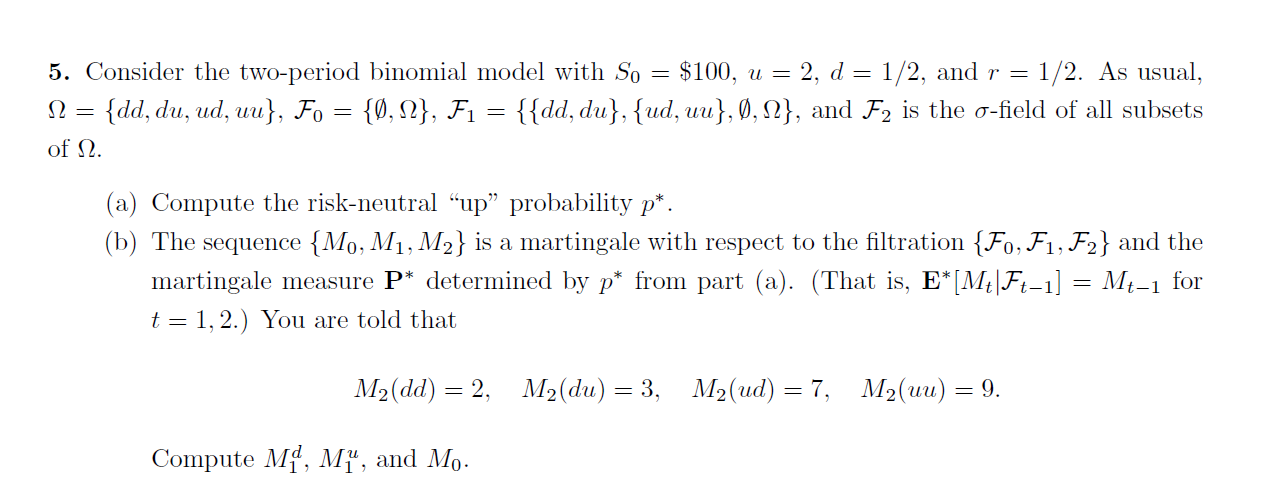
5. Consider the two-period binomial model with So = $100, u = 2, d = 1/2, and r = 1/2. As usual, 12 = {dd, du, ud, uu}, Fo = {0,12}, F1 = {{dd, du}, {ud, uu}, 0,12}, and F2 is the o-field of all subsets of 12. (a) Compute the risk-neutral up probability p*. (b) The sequence {Mo, M1, M2} is a martingale with respect to the filtration {F0,F1,F2} and the martingale measure P* determined by p* from part (a). (That is, E*[Mt|Ft-1] = Mt-1 for t=1, 2.) You are told that M2(dd) = 2, M2(du) = 3, M2(ud) = 7, M2(uu) = 9. Compute Md, M, and Mo. 5. Consider the two-period binomial model with So = $100, u = 2, d = 1/2, and r = 1/2. As usual, 12 = {dd, du, ud, uu}, Fo = {0,12}, F1 = {{dd, du}, {ud, uu}, 0,12}, and F2 is the o-field of all subsets of 12. (a) Compute the risk-neutral up probability p*. (b) The sequence {Mo, M1, M2} is a martingale with respect to the filtration {F0,F1,F2} and the martingale measure P* determined by p* from part (a). (That is, E*[Mt|Ft-1] = Mt-1 for t=1, 2.) You are told that M2(dd) = 2, M2(du) = 3, M2(ud) = 7, M2(uu) = 9. Compute Md, M, and Mo
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


