Question: a class in numerical methods; please help complete the code. thanks! (a) [7] Write a function that computes a't bn-1 until the difference between subsequent
 a class in numerical methods; please help complete the code. thanks!
a class in numerical methods; please help complete the code. thanks!
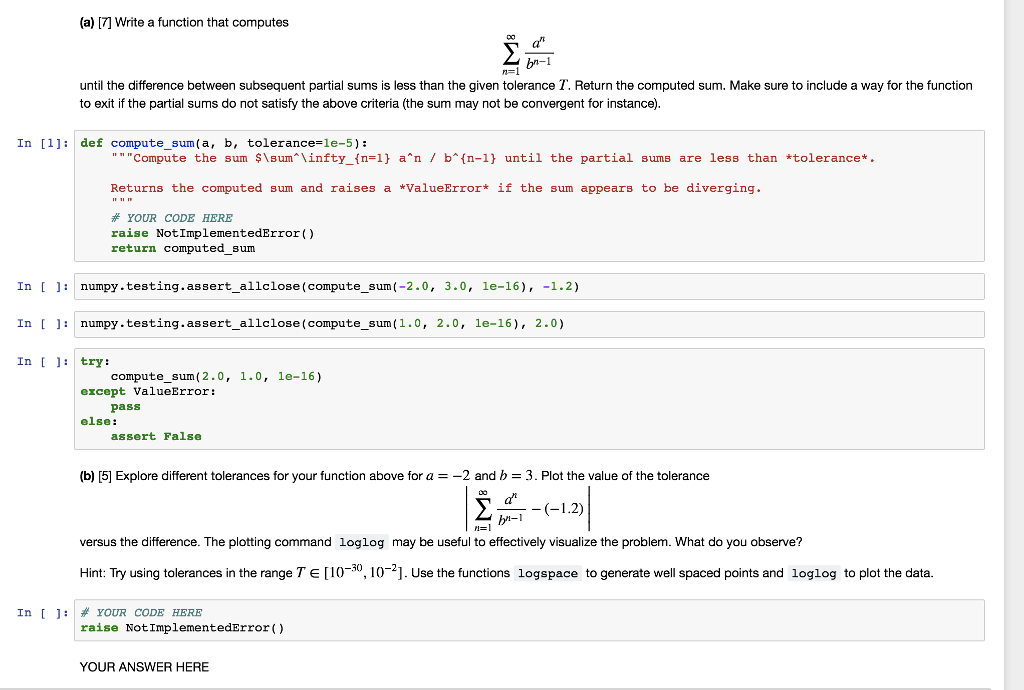
(a) [7] Write a function that computes a't bn-1 until the difference between subsequent partial sums is less than the given tolerance T. Return the computed sum. Make sure to include a way for the function to exit if the partial sums do not satisfy the above criteria (the sum may not be convergent for instance) In [1]: def compute-sum ( a, "" "Compute b, tolerance=1e-5): the sum $\sum^ \ infty-{n=1} a"n / b"(n-1} until the partial sums are less than *tolerance* . Returns the computed sum and raises a *ValueError* if the sum appears to be diverging. # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError () return computed sum In 1 numpy.testing.assert_allclose (compute_sum (-2.0, 3.0, le-16),1.2) In numpy.testing.assert_allclose (compute_sum(1.0, 2.0, le-16), 2.0) In : try: computesum (2.0, 1.0, le-16) except ValueError: pass else: assert False (b) [5] Explore different tolerances for your function above for a2 and b3. Plot the value of the tolerance d" bn-1 versus the difference. The plotting command loglog may be useful to effectively visualize the problem. What do you observe? Hint: Try using tolerances in the range Te[10-30, 102]. Use the functions logspace to generate well spaced points and loglog to plot the data. In [ ]: # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError() YOUR ANSWER HERE (a) [7] Write a function that computes a't bn-1 until the difference between subsequent partial sums is less than the given tolerance T. Return the computed sum. Make sure to include a way for the function to exit if the partial sums do not satisfy the above criteria (the sum may not be convergent for instance) In [1]: def compute-sum ( a, "" "Compute b, tolerance=1e-5): the sum $\sum^ \ infty-{n=1} a"n / b"(n-1} until the partial sums are less than *tolerance* . Returns the computed sum and raises a *ValueError* if the sum appears to be diverging. # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError () return computed sum In 1 numpy.testing.assert_allclose (compute_sum (-2.0, 3.0, le-16),1.2) In numpy.testing.assert_allclose (compute_sum(1.0, 2.0, le-16), 2.0) In : try: computesum (2.0, 1.0, le-16) except ValueError: pass else: assert False (b) [5] Explore different tolerances for your function above for a2 and b3. Plot the value of the tolerance d" bn-1 versus the difference. The plotting command loglog may be useful to effectively visualize the problem. What do you observe? Hint: Try using tolerances in the range Te[10-30, 102]. Use the functions logspace to generate well spaced points and loglog to plot the data. In [ ]: # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError() YOUR ANSWER HERE
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


