Question: A CSTR is used to run a nitrification process. The simplified reaction is: NH4+0.5N2 We will label the ammonia as A with concentration c. The

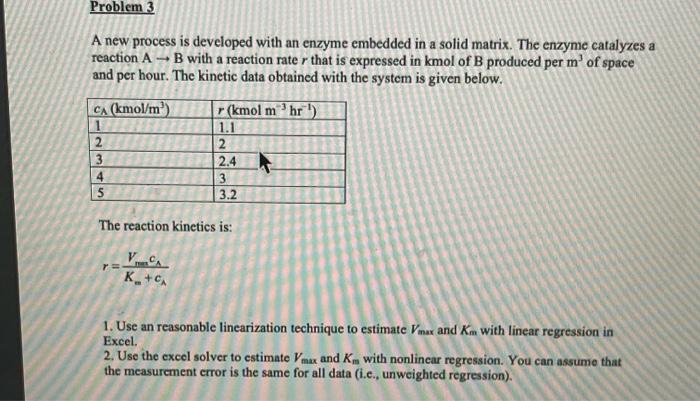

A CSTR is used to run a nitrification process. The simplified reaction is: NH4+0.5N2 We will label the ammonia as A with concentration c. The reactor volume is 5m3, and the volumetric flow rate is 1m3/hr. The initial concentration of A is 0 . The inlet concentration of A is 10mol/m3. The reaction can be treated as homogeneous (noncatalytic). The kinetics is: rA=Km+cA+K1cA2VmincA where Vmax=5molm3hr1,Km=0.5mol/m3,K1=1mol/m3. Note that the units of Vmax are chosen so that we can treat the reaction as a homogeneous noncatalytic reactor and we can ignore the presence of enzymes or biomass. The process is isothermal. 1. Develop the Amulation in excel and plot the concentration of A as a function of time, for 10 hours. 2. Calculate the conversion. 3. Increase the inlet concentration of A to 12mol/m3. Describe what you observe and speculate about the reason for the observation. (Hint: try the simulation at 10mol/m3 inlet concentration again, but now with an initial concentration of 10mol/m3 ) A new process is developed with an enzyme embedded in a solid matrix. The enzyme catalyzes a reaction AB with a reaction rate r that is expressed in kmol of B produced per m3 of space and per hour. The kinetic data obtained with the system is given below. The reaction kinetics is: r=Km+cAVm=cA 1. Use an reasonable linearization technique to estimate Vmax and Km with linear regression in Excel. 2. Use the excel solver to estimate Vmax and Km with nonlinear regression. You can assume that the measurement error is the same for all data (i.c., unweighted regression). Consider a reactor that has flat walls covered with a porous catalytic layer of 2mm thick. The catalytic layer has a density of 2500kg/m3, a porosity of 0.4 and a tortuosity of 4 . The catalytic layer catalyzes the reaction: AB with first-order kinetics with ste constant k=6105m3kg1s1. The diffusivity of A in free Bas,DAB, is 1105m2/s. a. Calculate the Thiele modulus of the reaction in the catalytic layer. b. Calculate the effectiveness factor of the catalytic layer c. Calculate the maximum layer thickness to obtain an effectiveness factor of 0.9 . Note: lt's OK to use a chart in the calculations. It is also OK to use Excel. d. Assume that the process is run in a plug-flow reactor with a gas flow rate of 0.1m3/s and a starting concentration of A of 0.2mol/m3. The effectiveness factor is 0.9 . The process is at constant temperature and pressure, and constant gas density. Calculate the mass of the catalytic layer needed to obtain an exit concentration of A of 0.02mol/m3
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


