Question: a. Declare three private double instance variables: x, y and radius. The instance variables x and y represent the coordinates of the center of the
a. Declare three private double instance variables: x, y and radius. The instance variables x and y represent the coordinates of the center of the circle. Note that you should not declare any other instance variables other than these three.
b. Fill in the code for method toString, which should return a string containing values for the center of the circle, x and y, and the radius of the circle. The returned string value should be formatted as below:
center: (x,y)
radius: r
c. Fill in the code for the accessor (getter) methods: getX, getY and getRadius properly. Note that accessors are also called getter methods.
d. Fill in the code for the mutator (setter) methods: setX, setY properly. Mutators are also called setter methods. CSCI 1301: Introduction to Computing and Programming Spring 2018 Lab 09 Classes and Methods
e. Fill in the code for the mutator(setter) method: setRadius properly. Note that: i. If the new radius value passed as a parameter to the method is not valid, than the method should leave the original radius unchanged. ii. A radius is valid only when it is greater than or equal to 0.
f. Fill in the code for the method area that returns the area of the circle, computed by PI * radius2
g. Use the value of PI provided by the constant Math.PI.
h. Fill in the code of the method perimeter that returns the perimeter of the circle computed by 2 * PI * radius
i. Fill in the code of the method diameter that returns the diameter of the circle.
j. Fill in the code of the method isUnitCircle that returns true if the radius of the circle is 1 and is centered at the origin, i.e., the coordinates of the circles center are (0, 0). Otherwise, this method returns false.
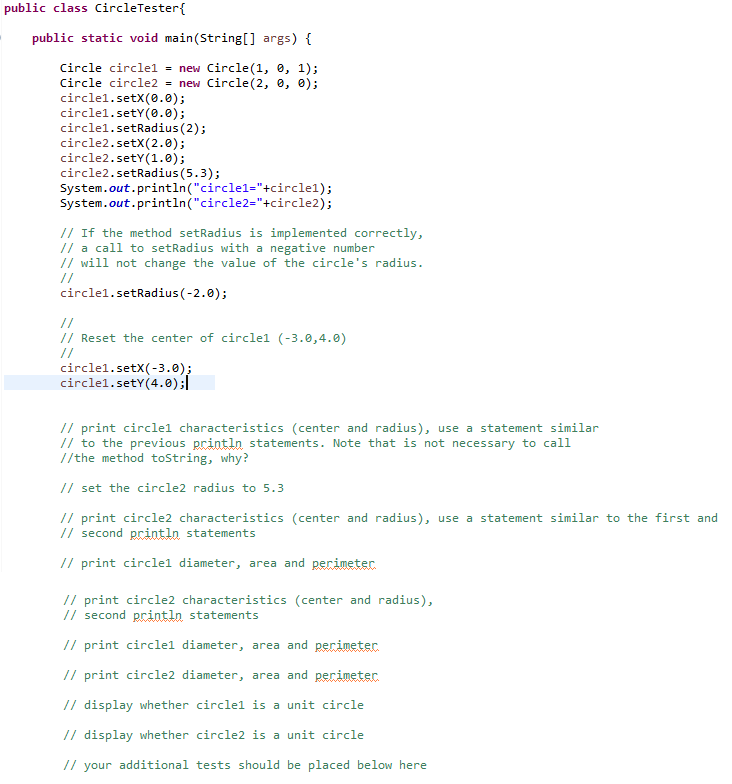
3. The CircleTester.java file contains a driver program to try and test out your Circle class. Using the comments in the CircleTester.java file, finish the file so that it does the following:
a. Display the center and radius of circle1.
b. Set the radius of circle2 to 5.3.
c. Display the center and radius of circle2.
d. Display the diameter, area and perimeter of circle1.
e. Display the diameter, area and perimeter of circle2.
f. Display a message that indicates whether or not circle1 is a unit circle.
g. Display a message that indicates whether or not circle2 is a unit circle.
4. Compile and test your Circle and CircleTester files, and verify your code is working properly. Then, set breakpoints in your methods, and the first line of the CircleTester class, and observe the flow of control within an Object-Oriented program.
5. Add to your Circle class the following methods:
a. public boolean equals(Circle anotherCircle) This method returns true when the radius and centers of both circles are the same; otherwise, it returns false. This method can be implemented in one line.
b. public boolean isConcentric(Circle anotherCircle) The method isConcentric returns true when the circle executing the method has the same center as anotherCircle but two circles are not equal (i.e. their radius is different). CSCI 1301: Introduction to Computing and Programming Spring 2018 Lab 09 Classes and Methods Note: we will use the aforementioned definition of isConcentric for this lab; however, isConcentric may have different definitions outside of this lab exercise.
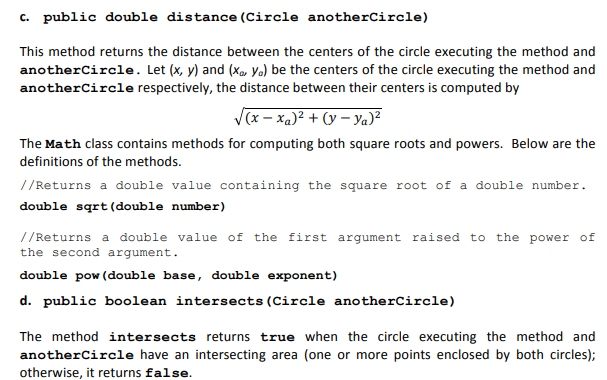
c. public double distance(Circle anotherCircle) This method returns the distance between the centers of the circle executing the method and anotherCircle. Let (x, y) and (xa, ya) be the centers of the circle executing the method and anotherCircle respectively, the distance between their centers is computed by square root (x x(little a))^2 + (y y(little a))^2 The Math class contains methods for computing both square roots and powers.
//Returns a double value containing the square root of a double number. double sqrt(double number) //Returns a double value of the first argument raised to the power of the second argument. double pow(double base, double exponent)
d. public boolean intersects(Circle anotherCircle) The method intersects returns true when the circle executing the method and anotherCircle have an intersecting area (one or more points enclosed by both circles); otherwise, it returns false. Two circles intersect if the distance between the centers of the two circles is less than the sum of their radius. Your method must call the method distance to obtain the distance between the two circles.

c. public double distance (Circle anotherCircle) This method returns the distance between the centers of the circle executing the method and anotherCircle. Let (x, y) and(a Va) be the centers of the circle executing the method and anotherCircle respectively, the distance between their centers is computed by The Hath class contains methods for computing both square roots and powers. Below are the definitions of the methods. //Returns a double value containing the square root of a double number. double sqrt (double number) /Returns a double value of the first argument raised to the power of the second argument double pow (double base, double exponent) d. public boolean intersects (Circle anotherCircle) The method intersects returns true when the circle executing the method and anotherCircle have an intersecting area (one or more points enclosed by both circles); otherwise, it returns false
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


