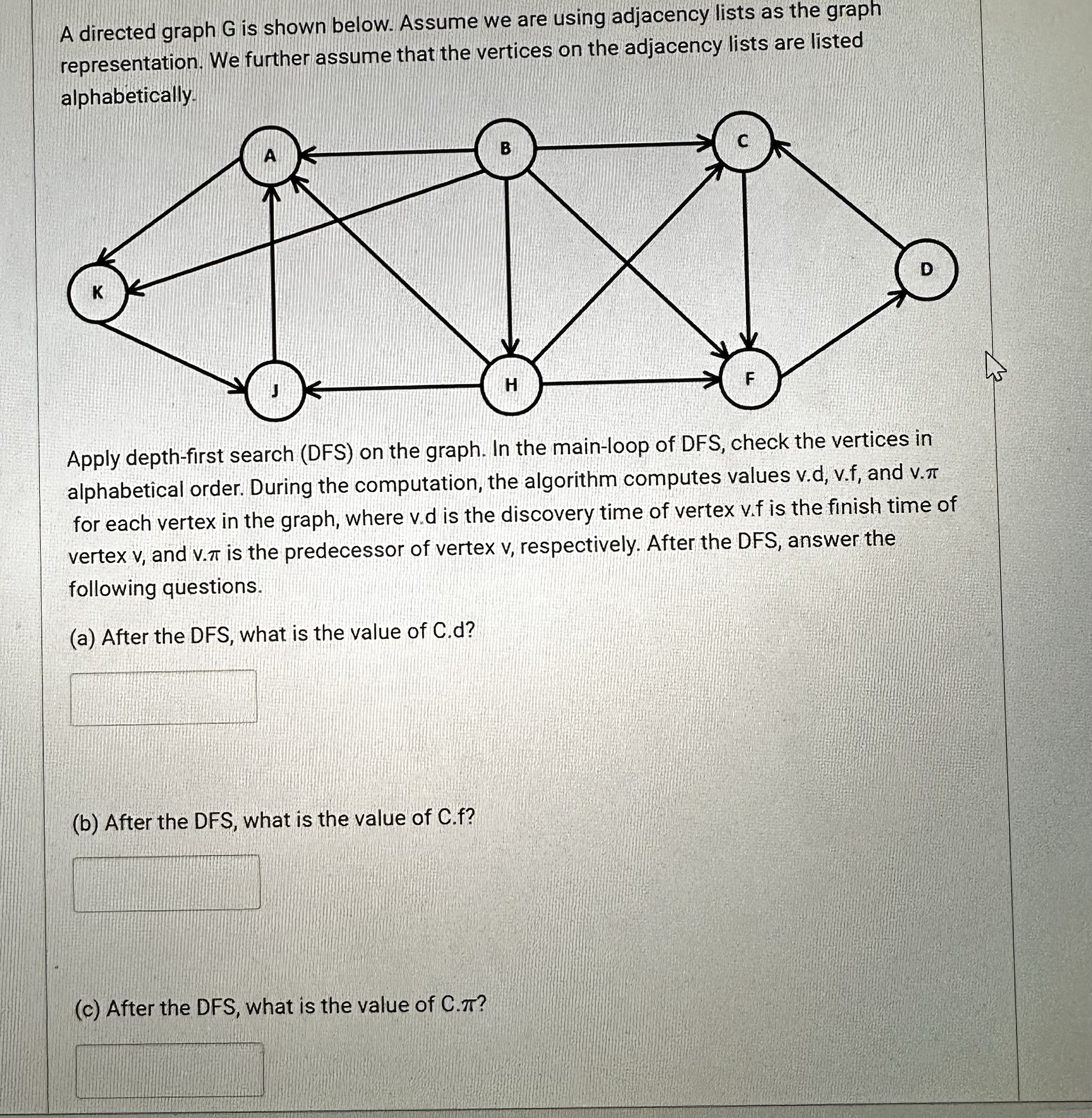
Question: A directed graph G is shown below. Assume we are using adjacency lists as the graph representation. We further assume that the vertices on the
A directed graph is shown below. Assume we are using adjacency lists as the graph representation. We further assume that the vertices on the adjacency lists are listed
Apply depthfirst search DFS on the graph. In the mainloop of DFS check the vertices in alphabetical order. During the computation, the algorithm computes values vd vf and for each vertex in the graph, where is the discovery time of vertex is the finish time of vertex and is the predecessor of vertex respectively. After the DFS answer the following questions.
a After the DFS what is the value of Cd
b After the DFS what is the value of Cf
c After the DFS what is the value of C
d After the DFS what is the value of Dd
e After the DFS what is the value of Df
f After the DFS what is the value of D
A directed graph is shown below. Assume we are using adjacency lists as the graph representation. We further assume that the vertices on the adjacency lists are listed
Apply depthfirst search DFS on the graph. In the mainloop of DFS check the vertices in alphabetical order. During the computation, the algorithm computes values vd vf and v for each vertex in the graph, where is the discovery time of vertex is the finish time of vertex and is the predecessor of vertex respectively. After the DFS answer the following questions. PART af
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


