Question: A foundry produces casting. An order for 22 custom-designed castings has been received. The casting process costs $900 per unit. If a casting is not
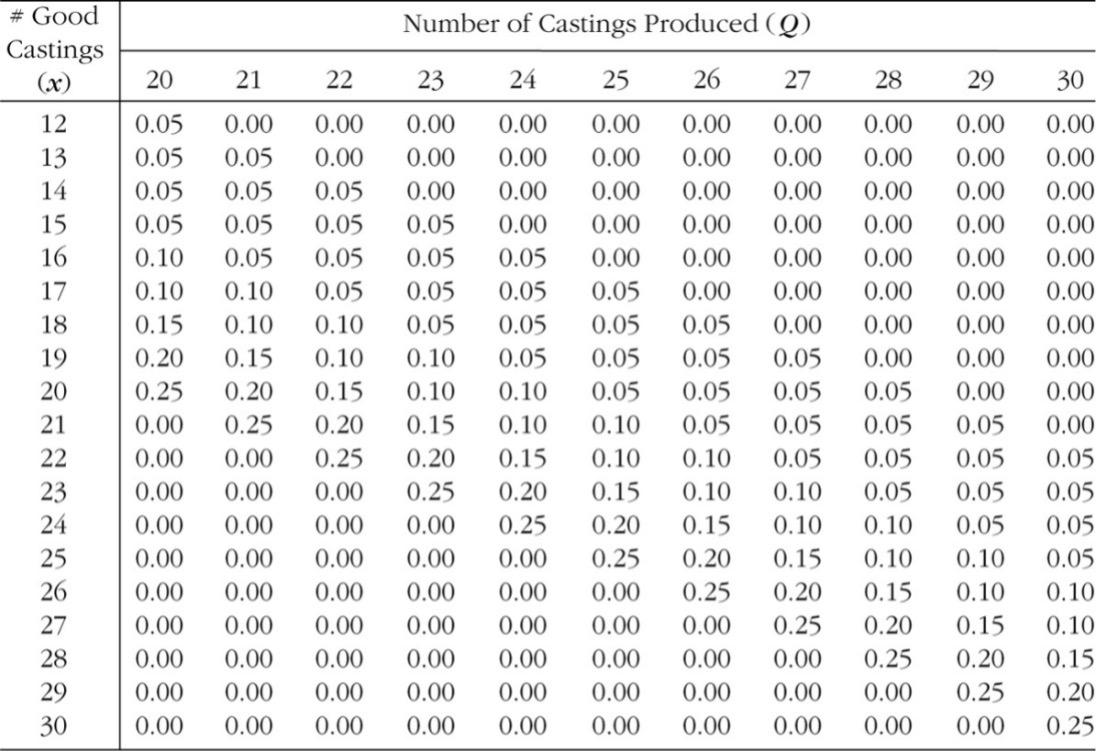
A foundry produces casting. An order for 22 custom-designed castings has been received. The casting process costs $900 per unit. If a casting is not sold, it can be sold as a scrap metal at $100 per unit. The customer has indicated a willingness to pay $2,000 per casting for 22 acceptable casting no more, no less! (If the number of good castings is less than 22, all castings will not be sold and scrapped at $100 per unit; if more than 22, the overage castings will not be sold; all unsold castings will be scrapped.) Based on historical records, the probability distributions given in the following table have been estimated. Q represents the number of casting produced; and x represents the number of good castings out of Q castings.
Conduct following tasks
(1) Construct functions for revenue, cost, and profit
Decision variable
- Q: quantity of units to be produced
Parameters
- x : number of good units produced (random variable)
- p(x): probability of producing x good units
- C(Q, x): cost of producing Q units with x good units
= 900Q
- R(Q, x): revenue from producing Q units with x good units
(Revenue = #products * price)
if x
=100Q
if x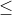 22
22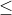 Q : 22 units will be sold. And remained products will be scrapped
Q : 22 units will be sold. And remained products will be scrapped
=2000*22 + 100*(Q-22)
- P(Q, x): profit from producing Q units with x good units
(Profit = Revenue Cost)
if x
if 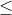 22
22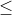 Q : 2000*22 + 100*(Q-22) - 900Q = 41800 -800Q
Q : 2000*22 + 100*(Q-22) - 900Q = 41800 -800Q
Objective function
- Maximize expected profit = E[P(Q)]
- =
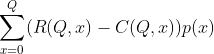
(2) Calculate each expected profit for Q given as follows. Then, decide the best Q value among those three values to maximize the profit. (include excel spreadsheet to calculate results into the report)
| No. | Q |
| 1 | 22, 23, 24 |
using Excel
Number of Castings Produced (Q) # Good Castings (X) 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 0.00 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.10 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 21 0.00 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.10 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.10 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.10 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.10 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.10 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.10 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.10 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.10 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.00 30 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.10 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.10 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.00 0.00 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 (R(Q,x) C(Q,))p(2) RQ, 2)) x T=0Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


