Question: A manager faces the following two probability distributions for sales: a. For Distribution 1, the expected sales are ______________. For Distribution 2, the expected sales
A manager faces the following two probability distributions for sales:
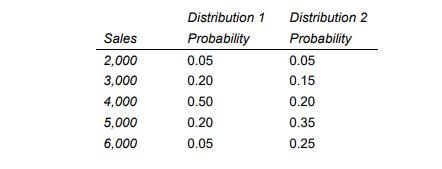
a. For Distribution 1, the expected sales are ______________. For Distribution 2, the expected sales are ______________.
b. For Distribution 1, the variance is ______________. For Distribution 2, the variance is ______________.
c. For Distribution 1, the standard deviation is ______________. For Distribution 2, the standard deviation is ______________.
d. Distribution ____ is the riskier of the two distributions of sales
e. For Distribution 1, the coefficient of variation is ______________. For Distribution 2, the coefficient of variation is ______________. Distribution _____ has the greater level of risk relative to its mean.
f. Assume the utility function of the manager is the following:

Is the marginal utility of the manager increasing or decreasing with the value of the sales? Is the manager, then, risk-averse or risk-prone (risk-lover)?
g. What are the expected utilities of the two different distributions of sales? Which one would the manager choose?
Distribution 1 Distribution 2 Sales 2,000 3,000 4,000 5,000 Probability 0.05 Probability 0.05 0.15 0.20 0.50 0.20 0.05 0.20 0.35 0.25 6,000 Sales Utility of Sales U(S) 2,000 0.05(2,000) 3,000 0.12(3,000) 4,000 0.25(4,000) 5,000 0.28(5,000) 6,000 0.30(6,000)
Step by Step Solution
3.50 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To answer the questions lets analyze each part systematically a Expected Sales The expected sales ES for a distribution is calculated as ES sum Xi tim... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


