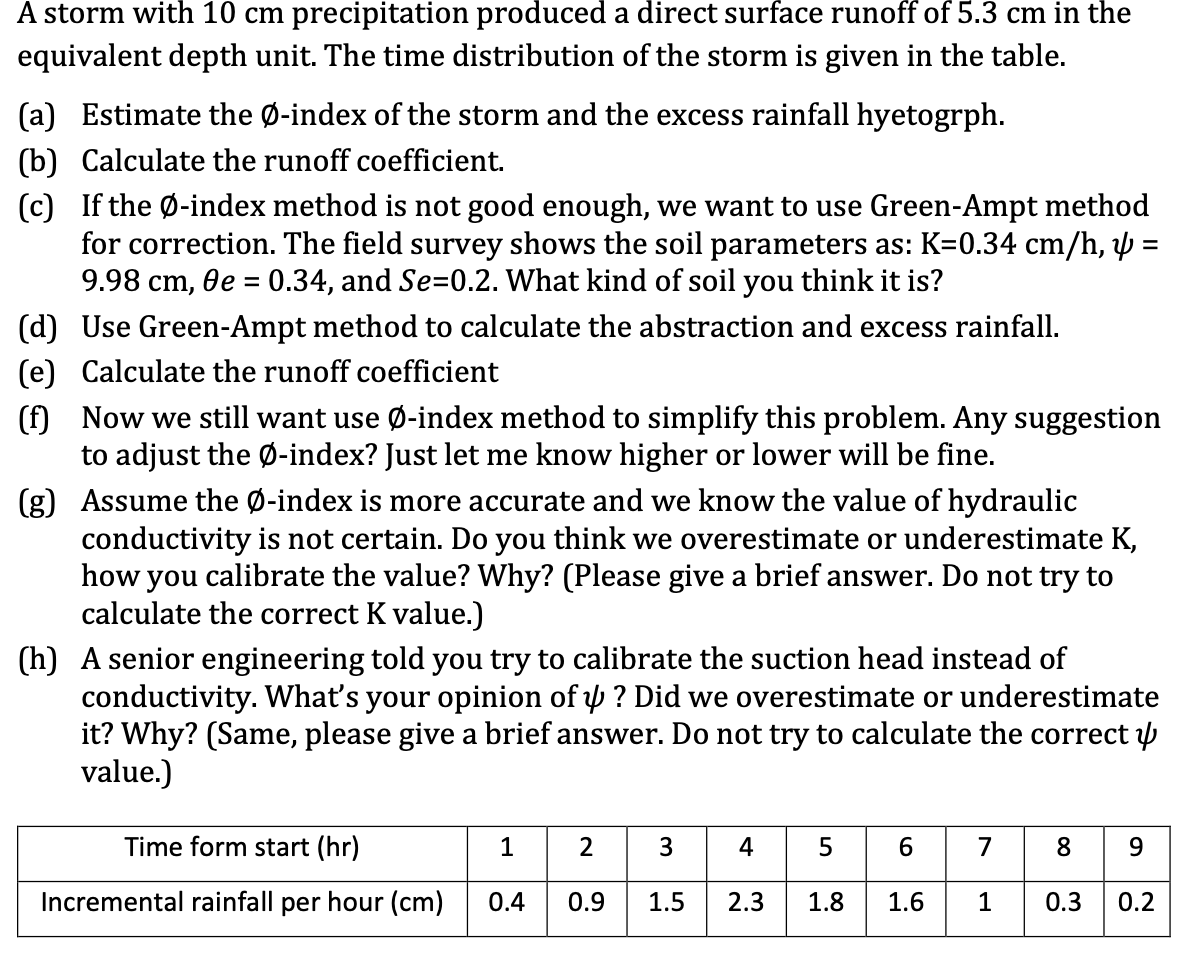
Question: A storm with 1 0 cm precipitation produced a direct surface runoff of 5 . 3 cm in the equivalent depth unit. The time distribution
A storm with cm precipitation produced a direct surface runoff of cm in the equivalent depth unit. The time distribution of the storm is given in the table.
a Estimate the emptyset index of the storm and the excess rainfall hyetogrph.
b Calculate the runoff coefficient.
c If the emptyset index method is not good enough, we want to use GreenAmpt method for correction. The field survey shows the soil parameters as: mathrmKmathrm~cmmathrmhpsimathrm~cmtheta e and S e What kind of soil you think it is
d Use GreenAmpt method to calculate the abstraction and excess rainfall.
e Calculate the runoff coefficient
f Now we still want use emptyset index method to simplify this problem. Any suggestion to adjust the varnothing index? Just let me know higher or lower will be fine.
g Assume the emptyset index is more accurate and we know the value of hydraulic conductivity is not certain. Do you think we overestimate or underestimate K how you calibrate the value? Why? Please give a brief answer. Do not try to calculate the correct K value.
h A senior engineering told you try to calibrate the suction head instead of conductivity. What's your opinion of psi Did we overestimate or underestimate it Why? Same please give a brief answer. Do not try to calculate the correct psi value.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


