Question: ABC has two main product lines, each with their own models. There are five SKUs altogether: Product A- Standard, Product A- Premium, Product B,
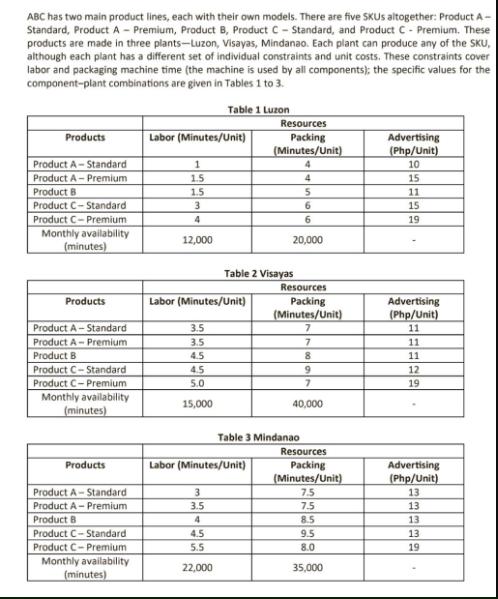
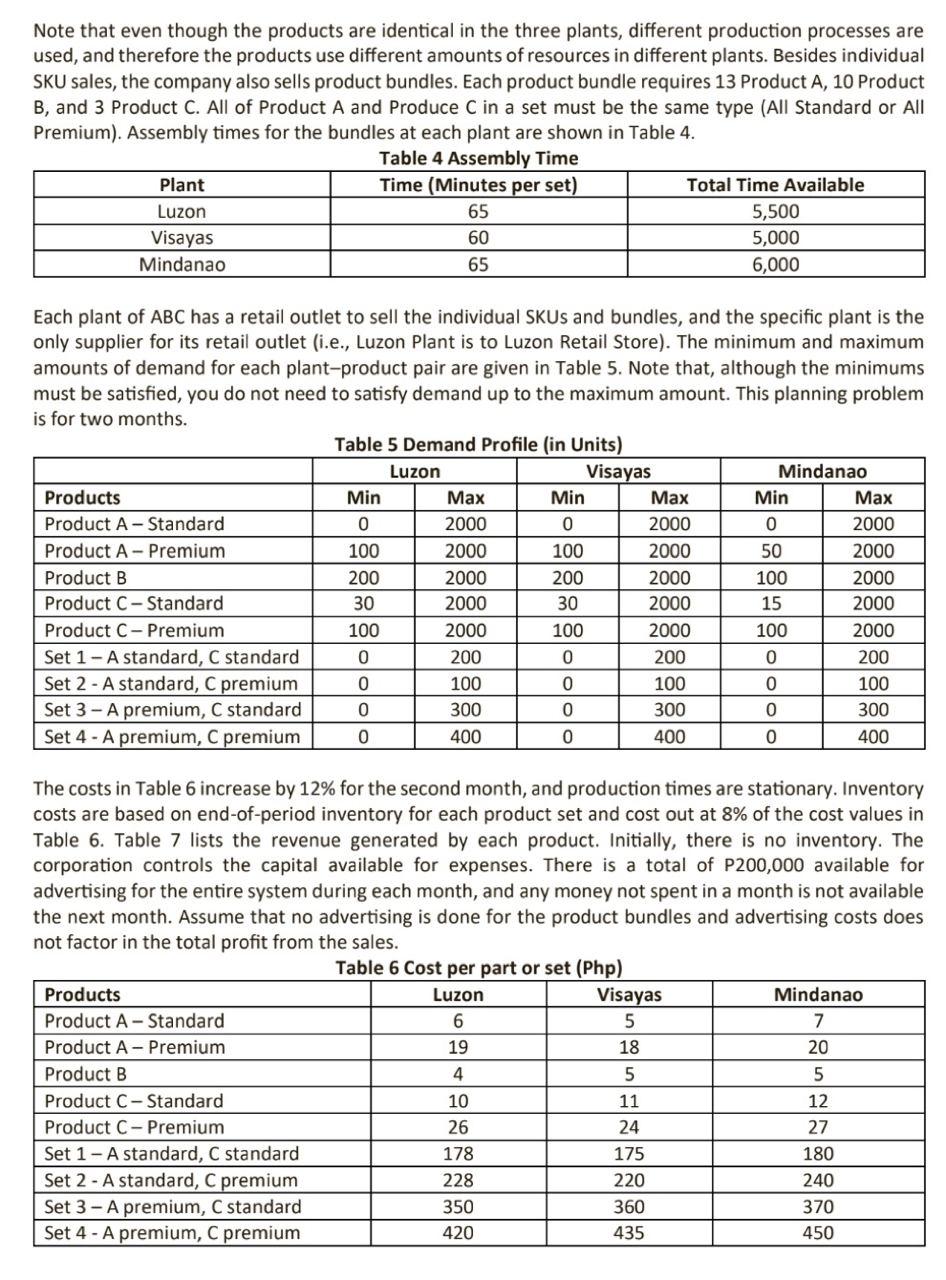
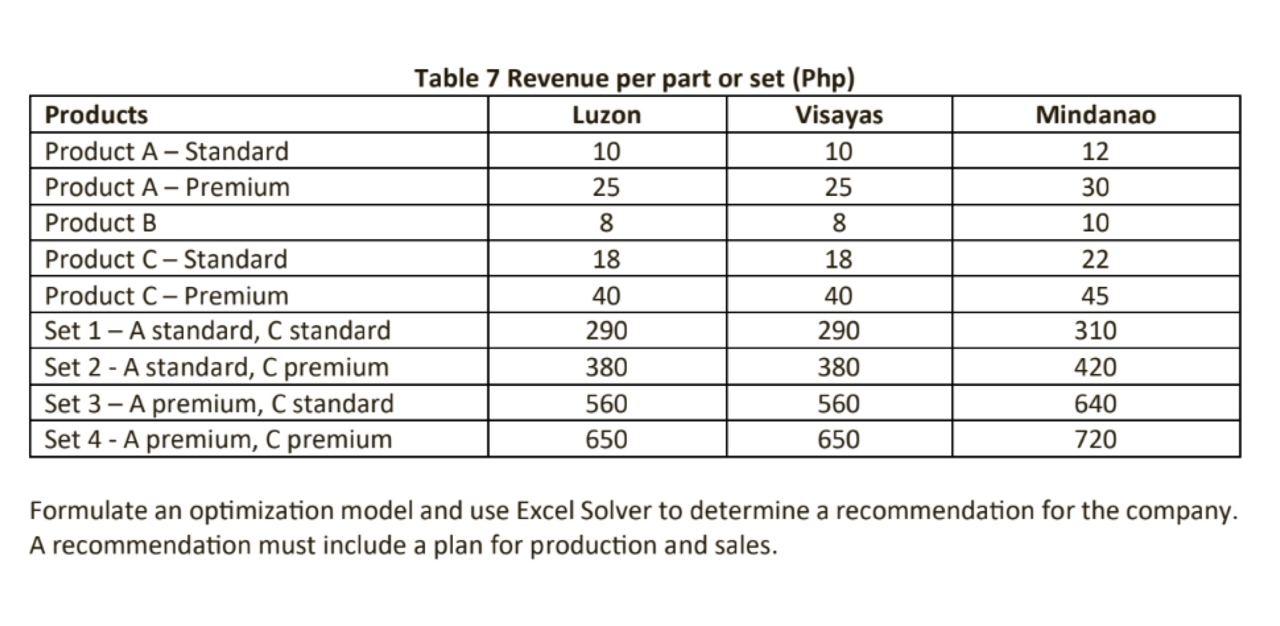
ABC has two main product lines, each with their own models. There are five SKUs altogether: Product A- Standard, Product A- Premium, Product B, Product C- Standard, and Product C- Premium. These products are made in three plants-Luzon, Visayas, Mindanao. Each plant can produce any of the SKU, although each plant has a different set of individual constraints and unit costs. These constraints cover labor and packaging machine time (the machine is used by all components); the specific values for the component-plant combinations are given in Tables 1 to 3. Table 1 Luzon Products Product A-Standard Product A- Premium Product B Product C-Standard Product C-Premium Monthly availability (minutes) Products Product A- Standard Product A- Premium Product B Product C-Standard Product C-Premium Monthly availability (minutes) Products Product A-Standard Product A-Premium Product B Product C- Standard Product C-Premium Monthly availability (minutes) Labor (Minutes/Unit) 1 1.5 1.5 3 4 12,000 Labor (Minutes/Unit) 3.5 3.5 4.5 4.5 5.0 15,000 3 3.5 Table 2 Visayas Labor (Minutes/Unit) 4 4.5 5.5 22,000 Resources Packing (Minutes/Unit) 4 4 5 6 6 20,000 Resources Packing (Minutes/Unit) 7 Table 3 Mindanao 7 8 9 7 40,000 Resources Packing (Minutes/Unit) 7.5 7.5 8.5 9.5 8.0 35,000 Advertising (Php/Unit) 10 15 11 15 19 Advertising (Php/Unit) 11 11 11 12 19 Advertising (Php/Unit) 13 13 13 13 19 Note that even though the products are identical in the three plants, different production processes are used, and therefore the products use different amounts of resources in different plants. Besides individual SKU sales, the company also sells product bundles. Each product bundle requires 13 Product A, 10 Product B, and 3 Product C. All of Product A and Produce C in a set must be the same type (All Standard or All Premium). Assembly times for the bundles at each plant are shown in Table 4. Table 4 Assembly Time Time (Minutes per set) 65 60 65 Plant Luzon Visayas Mindanao Each plant of ABC has a retail outlet to sell the individual SKUs and bundles, and the specific plant is the only supplier for its retail outlet (i.e., Luzon Plant is to Luzon Retail Store). The minimum and maximum amounts of demand for each plant-product pair are given in Table 5. Note that, although the minimums must be satisfied, you do not need to satisfy demand up to the maximum amount. This planning problem is for two months. Products Product A- Standard Product A Premium Product B Product C-Standard Product C- Premium Set 1-A standard, C standard Set 2- A standard, C premium Set 3-A premium, C standard Set 4-A premium, C premium Products Product A Standard Product A- Premium Product B Product C- Standard Product C- Premium Table 5 Demand Profile (in Units) Luzon Set 1-A standard, C standard Set 2- A standard, C premium Set 3-A premium, C standard Set 4 - A premium, C premium Min 0 100 200 30 100 0 0 0 0 Max 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000 200 100 300 400 Min 0 100 200 30 100 0 0 0 0 Visayas Total Time Available 5,500 5,000 6,000 Max 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000 200 100 300 400 The costs in Table 6 increase by 12% for the second month, and production times are stationary. Inventory costs are based on end-of-period inventory for each product set and cost out at 8% of the cost values in Table 6. Table 7 lists the revenue generated by each product. Initially, there is no inventory. The corporation controls the capital available for expenses. There is a total of P200,000 available for advertising for the entire system during each month, and any money not spent in a month is not available the next month. Assume that no advertising is done for the product bundles and advertising costs does not factor in the total profit from the sales. Table 6 Cost per part or set (Php) Luzon 6 19 4 10 26 178 228 350 420 Visayas 5 18 5 11 24 175 220 360 435 Mindanao Min 0 50 100 15 100 0 0 0 0 Max 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000 200 100 300 400 Mindanao 7 20 5 12 27 180 240 370 450 Products Product A- Standard Product A - Premium Product B Product C - Standard Product C- Premium Set 1 - A standard, C standard Set 2- A standard, C premium Set 3-A premium, C standard Set 4 - A premium, C premium Table 7 Revenue per part or set (Php) Visayas 10 25 8 18 40 290 380 560 650 Luzon 10 25 8 18 40 290 380 560 650 Mindanao 12 30 10 22 45 310 420 640 720 Formulate an optimization model and use Excel Solver to determine a recommendation for the company. A recommendation must include a plan for production and sales.
Step by Step Solution
3.31 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
SOL We can begin by formulating the linear programming model for this problem Lets define the decisi... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


