Question: ( adapted from Prob. 2 , p . 3 9 9 , Brown's Introductory Physics II ) Consider the diagram below. A long straight wire
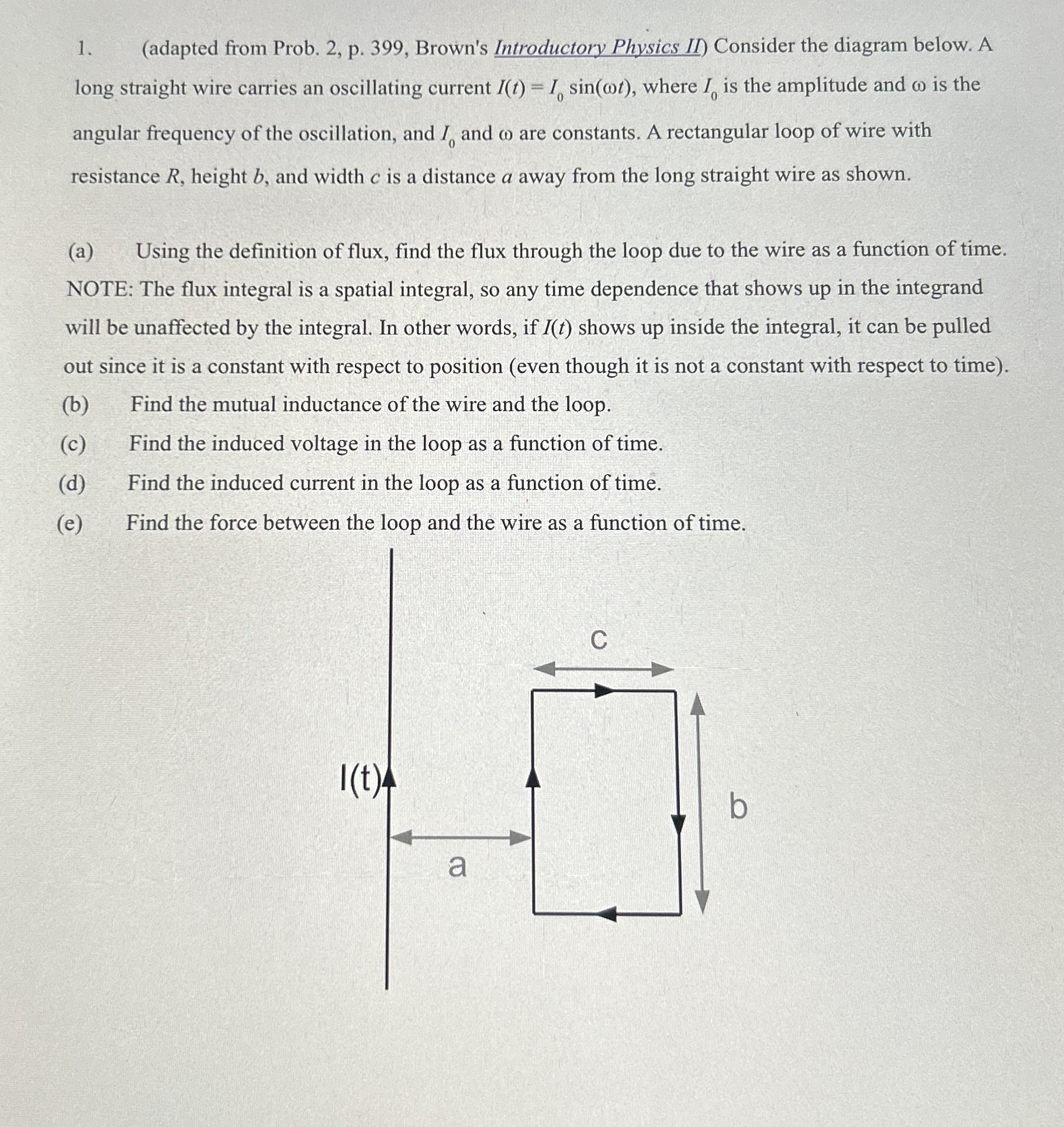
adapted from Prob. p Brown's Introductory Physics II Consider the diagram below. A long straight wire carries an oscillating current where is the amplitude and is the angular frequency of the oscillation, and and are constants. A rectangular loop of wire with resistance height and width is a distance a away from the long straight wire as shown.
a Using the definition of flux, find the flux through the loop due to the wire as a function of time. NOTE: The flux integral is a spatial integral, so any time dependence that shows up in the integrand will be unaffected by the integral. In other words, if shows up inside the integral, it can be pulled out since it is a constant with respect to position even though it is not a constant with respect to time
b Find the mutual inductance of the wire and the loop.
c Find the induced voltage in the loop as a function of time.
d Find the induced current in the loop as a function of time.
e Find the force between the loop and the wire as a function of time.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


