Question: a)Linearize your equations using Taylor Series expansion, assuming that X,S,Sf, and D are all variables about which you must expand. (b) Apply a Laplace transformation
a)Linearize your equations using Taylor Series expansion, assuming that X,S,Sf, and D are all variables about which you must expand.
(b) Apply a Laplace transformation to both of your linearized equations, again assuming that all four of X,S,Sf, and D are variables that must be transformed, and getting S(s) isolated on the lefthandside of the equations.
(c) Manipulate (algebraically) your two Laplace-transformed equations to develop the transfer function between the cell concentration X and dilution rate D. (When you do this, you can assume Sf(s) = 0).
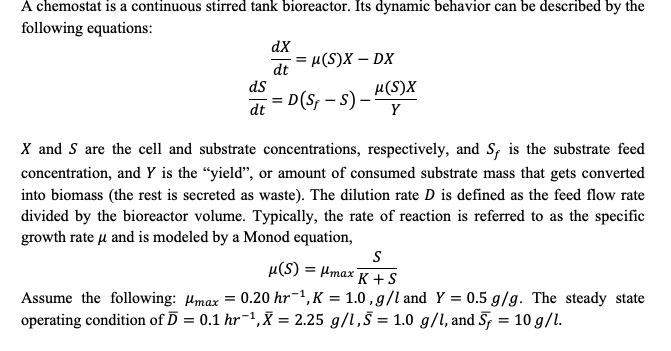
A chemostat is a continuous stirred tank bioreactor. Its dynamic behavior can be described by the following equations: dx (S)X - DX dt ds dt Y D($; - ) H(S)X X and S are the cell and substrate concentrations, respectively, and S, is the substrate feed concentration, and Y is the yield, or amount of consumed substrate mass that gets converted into biomass (the rest is secreted as waste). The dilution rate D is defined as the feed flow rate divided by the bioreactor volume. Typically, the rate of reaction is referred to as the specific growth rate u and is modeled by a Monod equation, S M(S) = Amax K+S Assume the following: Imax = 0.20 hr-1, K = 1.0 g/l and Y = 0.5 g/g. The steady state operating condition of 7 = 0.1 hr-1,X = 2.25 g/1,5 = 1.0 g/l, and 5 = 10 g/l. = = = = = = =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


