Question: Answer #3 only Purpose To assess your ability to: solve basic linear programming problems by using Excel Solver solve basic linear programming problems by using
Answer #3 only

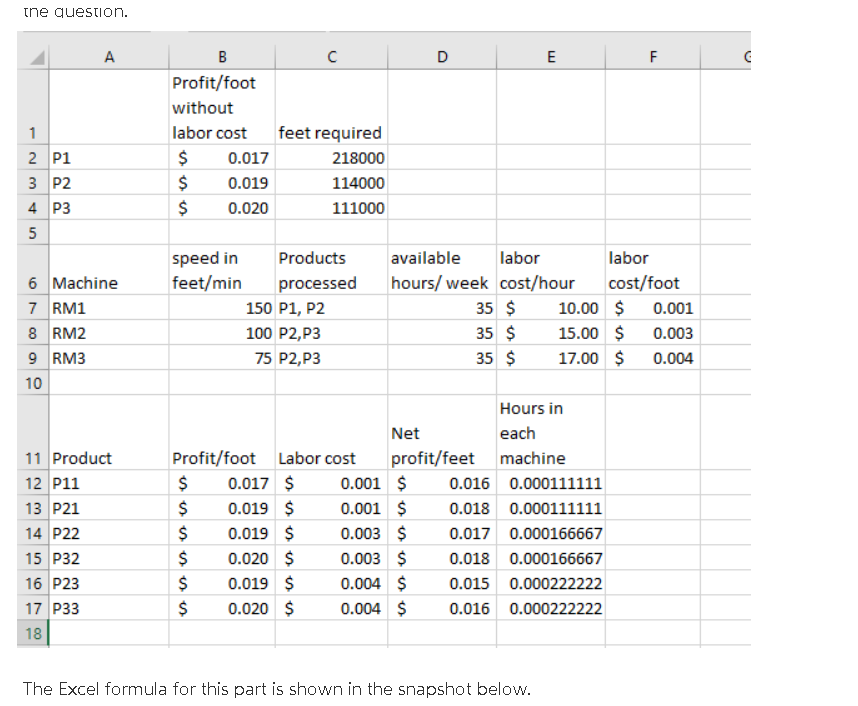
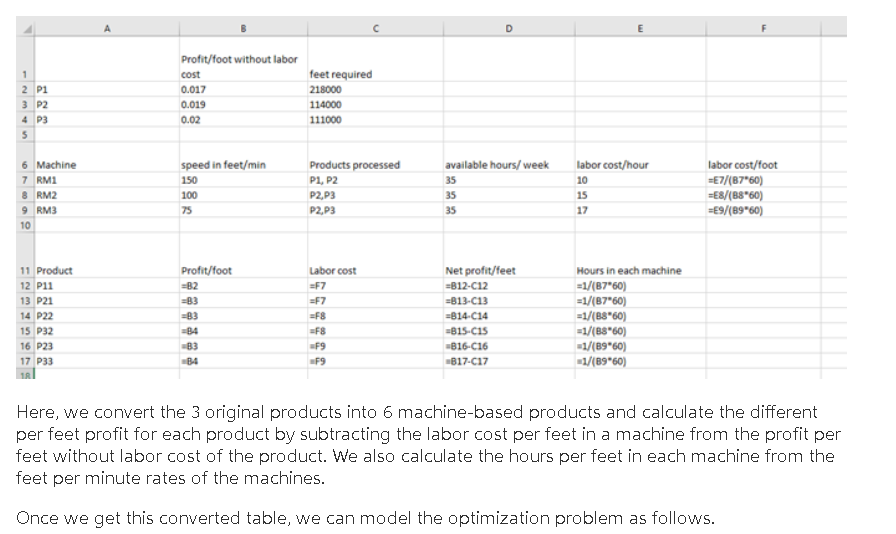
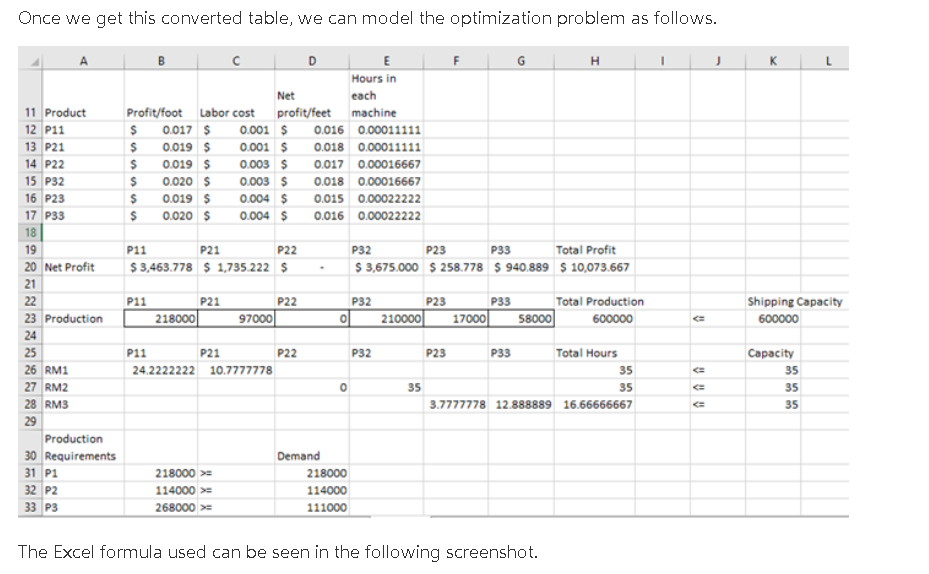
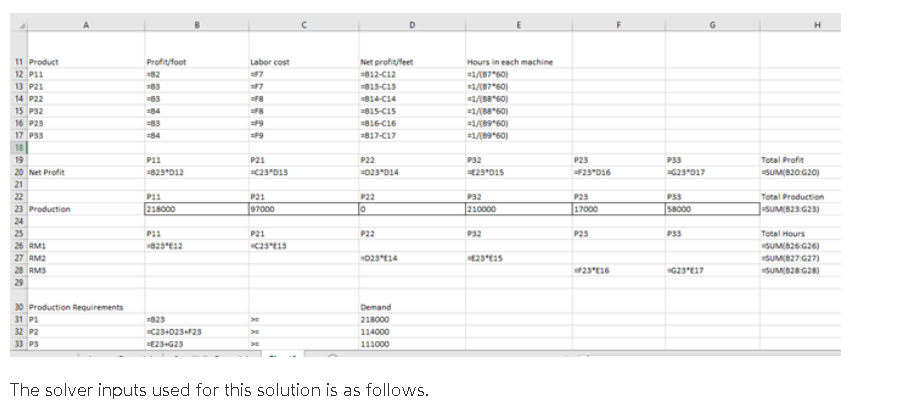
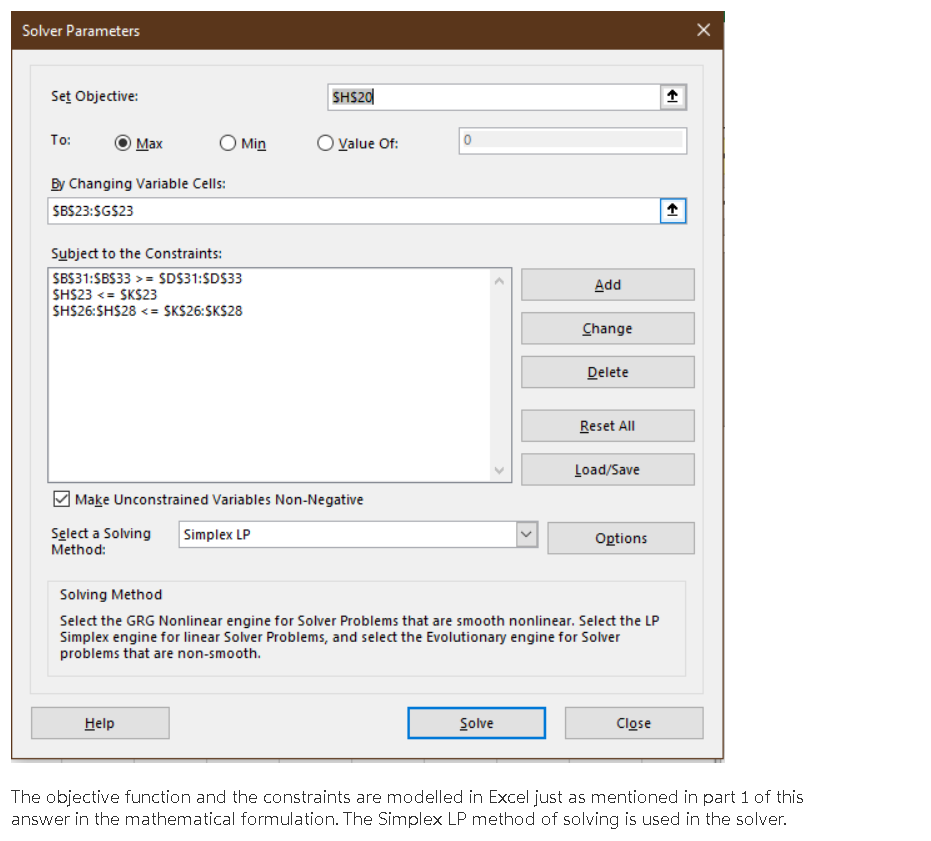

Purpose To assess your ability to: solve basic linear programming problems by using Excel Solver solve basic linear programming problems by using a graphical solution perform sensitivity analysis on linear programming solutions Overview You will use the following information to complete this assignment. The Ohio Metal Works (OMW) produces three main products from steel bars-- P1, P2 and P3. The features of these products are given below. P1 P2 P3 Profit (excluding labor Minimum Weekly Production cost) perfoot of product Requirement (feet) $0.017 218,000 $0.019 114,000 $0.020 111,000 One of the initial steps is a shaping operation performed by rolling machines. There are three machines available for this purpose-- RM1, RM2 and RM3. Their features are given by the following table. Machine RM1 RM2 RM3 Speed in Feet/Min 150 100 75 Products Processed in the Machine P1, P2 P2, P3 | P2, P3 Available Hours Per Week 35 35 35 Labor Cost Operating Hour $10 $15 $17 Also, the shipping department has a limit of 600,000 feet per week, regardless of thickness. Action Items 1. Determine the objective functions and constraints of this case if the objective of the OMW is to maximize the profits. 2. Create an Excel Solver model to solve the problem and answer the questions in Action Item 3. A help document and template for setting up the problem/case study have been provided here: o Help Document o Solution Template 3. Write a one-to two-page paper answering the following questions. a. What are the objective functions and constraints of this case if the objective of the OMW is to maximize the profits? b. What is the value of an additional hour of capacity on the rolling machine RM2? c. What is the value of an additional two hours of capacity on the rolling machine RM1? d. If the speed of rolling machine RM3 could be doubled without changing the labor cost, what would it be worth per week? Hint: i. Convert labor costs from "$/hour" to "feet/hour" when determining objective function. ii. There are three main products, but since these products are processed in three different machines, there are actually six different products with different net profit values. iii. Convert speed from "feet/min" to "hours/feet" when dealing with time constraints (available hours per week). the question. D E LL G 1 2 P1 3 P2 4 P3 5 B Profit/foot without labor cost feet required $ 0.017 218000 $ 0.019 114000 $ 0.020 111000 6 Machine 7 RM1 8 RM2 9 RM3 10 speed in Products feet/min processed 150 P1, P2 100 P2,P3 75 P2,P3 available labor labor hours/ week cost/hour cost/foot 35 $ 10.00 $ 0.001 35 $ 15.00 $ 0.003 35 $ 17.00 $ 0.004 11 Product 12 P11 13 P21 14 P22 15 P32 16 P23 17 P33 18 Hours in Net each Profit/foot Labor cost profit/feet machine $ 0.017 $ 0.001 $ 0.016 0.000111111 $ 0.019 $ 0.001 $ 0.018 0.000111111 $ 0.019 $ 0.003 $ 0.017 0.000166667 $ 0.020 $ 0.003 $ 0.018 0.000166667 $ 0.019 $ 0.004 $ 0.015 0.000222222 $ 0.020 $ 0.004 $ 0.016 0.000222222 The Excel formula for this part is shown in the snapshot below. 1 2 P1 3 P2 4 P3 5 Profit/foot without labor cost 0.017 0.019 0.02 feet required 218000 114000 111000 available hours/week 35 6 Machine 7 RMI 8 RM2 9 RM3 10 speed in feet/min 150 100 75 Products processed P1, P2 P2,P3 P2.P3 labor cost/hour 10 15 17 labor cost/foot =E7/(87*60) =E8/(B8*60) =E9/(89-60) 35 35 11 Product 12 P11 13 P21 14 P22 15 P32 16 P23 17 P33 1R Profit/foot -B2 =B3 =B3 -34 -B3 -B4 Labor cost -F7 =F7 =F8 Net profit/feet =B12-C12 =B13-C13 =B14-C14 =B15-cis -B16-C16 B17-C17 Hours in each machine =1/(B7*60) =1/(B7*60) =1/(B8"60) =1/(88*60) -1/(89*60) -1/(89*60) -F8 -F9 F9 Here, we convert the 3 original products into 6 machine-based products and calculate the different per feet profit for each product by subtracting the labor cost per feet in a machine from the profit per feet without labor cost of the product. We also calculate the hours per feet in each machine from the feet per minute rates of the machines. Once we get this converted table, we can model the optimization problem as follows. Once we get this converted table, we can model the optimization problem as follows. F G D E Hours in Net each Profit/foot Labor cost profit/feet machine $ 0.017 $ 0.001 $ 0.016 0.00011111 $ 0.019 S 0.001 $ 0.018 0.00011111 $ 0.019 S 0.003s 0.017 0.00016667 $ 0.020 $ 0.003 $ 0.018 0.00016667 $ 0.019 $ 0.004 $ 0.015 0.00022222 $ 0.020 $ 0.004 $ 0.016 0.00022222 P11 P21 P22 $ 3,463.778 $ 1,735 222 $ P32 P23 P33 Total Profit $ 3,675.000 $ 258.778 S 940.889 $ 10,073.667 P32 11 Product 12 P11 13 P21 14 P22 15 P32 16 P23 17 P33 18 19 20 Net Profit 21 22 23 Production 24 25 26 RM1 27 RM2 28 RM3 29 Production 30 Requirements 31 P1 32 P2 33 P3 P11 P21 218000 P22 97000 P23 P33 Total Production 210000 17000 58000 600000 Shipping Capacity 600000 o 1 P32 P11 P21 P22 24.2222222 10.7777778 P23 P33 Total Hours 35 35 35 3.7777778 12.888889 16.66666667 VU Capacity 35 35 35 0 218000 > 114000 > 268000 >> Demand 218000 114000 111000 The Excel formula used can be seen in the following screenshot. Profit/foot Labor cost 11 Product 12 PI: 13 221 14 922 15 P32 16 P23 17 P33 13 19 20 Net Profit 21 22 23 Production Net profiteet 312-012 2015-C13 14-C14 2015-CIS =816-C16 =817-C17 Hours in each machine 1/87601 1/8760) 1/589601 1/8601 *1/89'601 =1/(89'60) -83 =84 8 19 *9 P11 *823012 P23 033 P21 -C23013 P22 2023014 23015 23016 -G23*017 Total Profit SUM(B20:620) 211 P22 P21 97000 232 210000 P23 17000 39 58000 Total Production SUM(B23623) 218000 P22 232 P23 233 P11 -823612 P21 239613 25 26 AM 27 RM2 28 RMS 02314 Total Hours SUMB26626) SUMB27.27) SUMB28628 2315 25016 G2317 30 Production Requirements 31 PA 22 P2 33 P3 Demand 218000 114000 111000 C23023123 The solver inputs used for this solution is as follows. Solver Parameters Set Objective: SHS20 1 To: Max Min O Value of: By Changing Variable Cells: $B$23:5GS23 1 Subject to the Constraints: $B$31:5B533 >= $D$31:SD$33 SHS23












