Question: ANSWER all parts and show ALL work. 18B.9 Diffusion with homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions. Gas A diffuses through a stagnant film to a catalytic surface
ANSWER all parts and show ALL work.
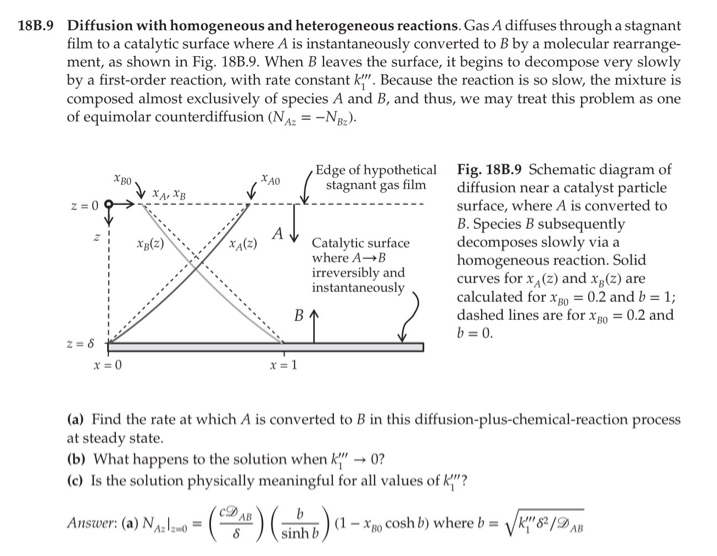
18B.9 Diffusion with homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions. Gas A diffuses through a stagnant film to a catalytic surface where A is instantaneously converted to B by a molecular rearrange- ment, as shown in Fig. 188.9. When B leaves the surface, it begins to decompose very slowly by a first-order reaction, with rate constant k". Because the reaction is so slow, the mixture is composed almost exclusively of species A and B, and thus, we may treat this problem as one of equimolar counterdiffusion (NA2 = -N82). XBO , Z=0O A Xg(2) XA(z) Edge of hypothetical Fig. 18B.9 Schematic diagram of stagnant gas film diffusion near a catalyst particle surface, where A is converted to B. Species B subsequently Catalytic surface decomposes slowly via a where AB homogeneous reaction. Solid irreversibly and curves for xy(z) and xg(2) are instantaneously calculated for Xbo = 0.2 and b = 1; B dashed lines are for X 80 = 0.2 and b=0 B Z=8 X=0 x=1 (a) Find the rate at which A is converted to B in this diffusion-plus-chemical-reaction process at steady state. (b) What happens to the solution when k" 0? (c) Is the solution physically meaningful for all values of k}"? Answer: (a) NA: Izmo " 4)(sinh ) - a cosh ) where = Vk/2u (1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


