Question: answer questions 1. Why should the Erlenmeyer flask used for the first step of this reaction be dry? 2. What possible side products could be

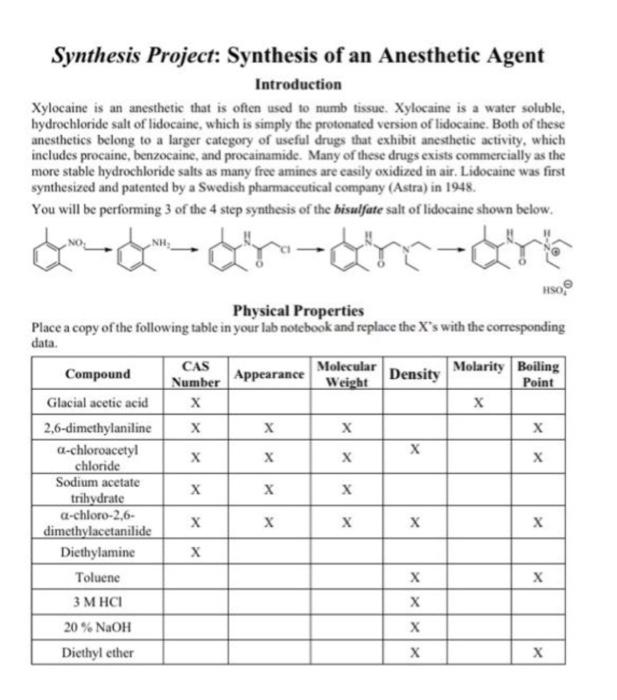
1. Why should the Erlenmeyer flask used for the first step of this reaction be dry? 2. What possible side products could be formed during the reaction (excluding salts) that might lower the yield of your product? 3. What is the role of the sodium acetate solution in the reaction? Hint: HCl is produced during the acyl substitution reaction. 4. Why is it important that the crude product be washed until there is no residual acetic acid? (Hint: Consider the next reaction.) 5. Why does the acid chloride functional group react preferentially over the alkyl chloride functional group of a-chloroacetyl chloride? 6. Why is diethyl amine used in excess in the preparation of lidocaine reaction? 7. Why is ethanol be a poor choice of a solvent for the reaction between 2,6-dimethylaniline and a-chloroacetyl chloride? Synthesis Project: Synthesis of an Anesthetic Agent Introduction Xylocaine is an anesthetic that is often used to numb tissue. Xylocaine is a water soluble, hydrochloride salt of lidocaine, which is simply the protonated version of lidocaine. Both of these anesthetics belong to a larger category of useful drugs that exhibit anesthetic activity, which includes procaine, benzocaine, and procainamide. Many of these drugs exists commercially as the more stable hydrochloride salts as many free amines are easily oxidized in air. Lidocaine was first synthesized and patented by a Swedish pharmaceutical company (Astra) in 1948. You will be performing 3 of the 4 step synthesis of the bisulfate salt of lidocaine shown below. ---ay-ay-ay's Physical Properties Place a copy of the following table in your lab notebook and replace the X's with the corresponding data. Compound CAS Molecular Number Appearance Molarity Boiling Weight Density Point Glacial acetic acid X 2,6-dimethylaniline X X X a-chloroacetyl X X chloride Sodium acetate X trihydrate X a-chloro-2,6- X dimethylacetanilide Diethylamine Toluene 3 M HCI X 20% NaOH Diethyl ether x
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


