Question: B 2 ( a ) For a metallic alloy specimen with a uniform cross - sectional area of ( 3 2 5 mathrm
Ba For a metallic alloy specimen with a uniform crosssectional area of mathrm~mm a gauge length of mm and a modulus of elasticity of GPa if the maximum tensile load at which plastic deformation begins is mathrm~N estimate the maximum elastic extension of the specimen.
marks
b A cylindrical specimen with a diameter of mm is stressed elastically in tension under a force of mathrm~N Determine the reduction in diameter of the specimen. Given: Poisson's ratio and modulus of elasticity for this material are and GPa respectively.
marks
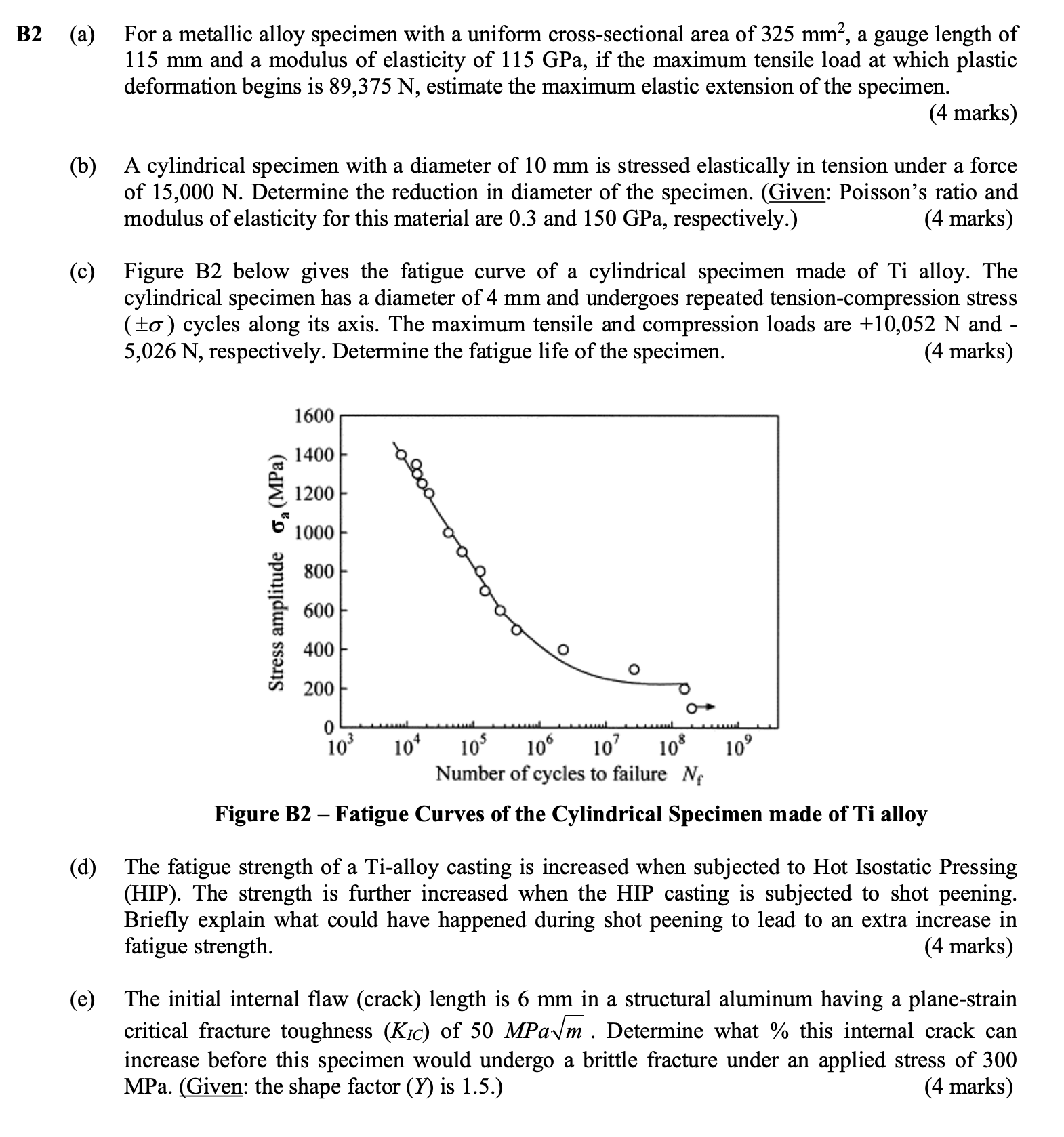
c Figure B below gives the fatigue curve of a cylindrical specimen made of Ti alloy. The cylindrical specimen has a diameter of mm and undergoes repeated tensioncompression stress pm sigma cycles along its axis. The maximum tensile and compression loads are mathrm~N and mathrm~N respectively. Determine the fatigue life of the specimen.
Figure B Fatigue Curves of the Cylindrical Specimen made of Ti alloy
d The fatigue strength of a Tialloy casting is increased when subjected to Hot Isostatic Pressing HIP The strength is further increased when the HIP casting is subjected to shot peening. Briefly explain what could have happened during shot peening to lead to an extra increase in fatigue strength.
e The initial internal flaw crack length is mm in a structural aluminum having a planestrain critical fracture toughness KI C of mathrmMPasqrtm Determine what this internal crack can increase before this specimen would undergo a brittle fracture under an applied stress of MPa Given: the shape factor Y is
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


