Question: Based on the article, answer the following questions: Do you need additional information areas to evaluate the article findings/conclusions? Summarize the findings/conclusions. Were the findings
Based on the article, answer the following questions:
- Do you need additional information areas to evaluate the article findings/conclusions?
- Summarize the findings/conclusions. Were the findings substantively important?
- What additional questions are suggested by the articles conclusions?
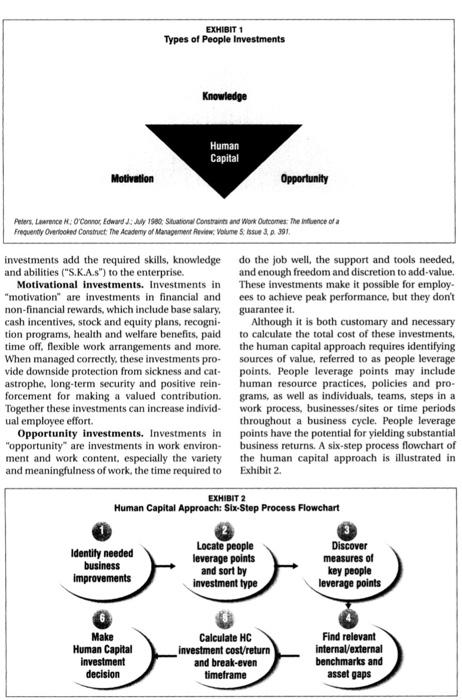
hen a product or service is adver- formance. Labor productivity has been used to tised at a price 25% lower than quantify direct labor output. They may have been what you just paid for the same relevant for the industrial revolution, but in this, thing, you know you left money the first year of the new millennium, these meaon the table. It's not as clear, but sures of human value seem both outdated and sellers often feel even more incomplete. uneasy when their house sells at In the information revolution, where thinking list price on the first day it's has become at least as valuable as doing, the offered. Could they have gotten knowledge worker has emerged as a dominant more? As consumers, we con- source of value creation. The impact of knowl- stantly attempt to maximize edge work on business performance and the value in the marketplace. Buy rapidly expanding information and service econlow, sell high is the adage in omy highlight the importance of this much larger investment circles. But what group of employees. In this era, the knowledge about the labor market? people possess is viewed by some as the new facCompanies don't literally buy and sell people, tor of production. Yet there aren't enough reveal- course, like stock transactions. However, they ing, readily available metrics of knowledge workof course, like stock transactions. However, they ing, readily available metrics of knowledge workdo hire people with some expectation that they er value. The same is true for the general work will receive a payback on the deal. For years, force overall. organizations have attempted to correlate quan- At a macro level, it appears some organizations tifiable improvements in business performance are gaining a substantially better return on their to those who had direct impact. Stock apprecia- people. Microsoft's market value per employee is tion and earnings growth have been associated about $18M; Cisco's is $15M. For most industrial with top executives. Orders and revenue genera- companies, it is less than $500K. If you work at a tion have been measures of sales personnel per- public company, what is yours? How does it com- Frequenty Cveriocied Consmet The Acaderiy of Masagement firvitw. Yolume 5 issua 3 a 391 . Note: Human capital factors are highlighted in bold. A Briet history of allempls To improve the Return on Human Capilal A fair day's wage for a fair day's (National Cach Register Company) enable them to support their famiwork? During the peak of the and William Filene \& Sons, the lies and build a better life. These industrial revolution, human cap- department store, introduced so-called "welfare plans" ended up ital was quantified using stop- what was called a "welfare plan." being little more than expensive watches and clipboards on the Welfare plans were intended to debt for the companies that implefactory floor to determine "stan- make life more secure and com- mented them. The result was a low and every task. The faster people such needs as housing, education, Growing unrest and workplace worked, the greater the return. and factory conditions. The devel- discord between managers and Workers werent expected to ques- opment of company cities and workers forced a change in strate- tion, think, or solve problems. towns, modern ventilated facto- gy for improving return on human They were cogs in the production ries, libraries, savings and loans, capital in the pre-Worid War If era. process, and a paycheck every and social clubs were investments The power of shop foremen had week was considered reward made to reduce the incredibly high reached its peaks authority to hire, enough. Back then, calculating the worker turnover rates (which often fire, and set basic terms of return on human capital was a exceeded 100 percent). But they employment often rested solely simple efficiency equation. didn'. Workers were pootly paid. with them. In many instances, The origins of the earliest form They didn' want low-interest their decisions were capricious. of human capital management go loans and Saturday-night dances Workers who curried favor back to the late 1800 s when NCR they wanted a wage that would received preferential treatment. In will be improved. In the case of Qualex, the busi- servatively estimated at $11,400 per departing ness performance to be improved included pro- employee. Absences were estimated to cost at ductivity and quality. least $235 per no-show day. These costs were response, companies curtailed the "People management" evolved stock market, low inflation and authority of shop foremen. beyond simple caretaking and low unemployment as outcomes Investments were made in labor protection of employees. Work in the 1990s. relationships and worker safety. processes were reengineered, Now, in this first year of the new The payback was a workplace in hierarchies flattened, and organi- millennium, the forces affecting which people focused on their zations and jobs were redesigned. the return on human capital are jobs, not the inequities or Workers, in turn, took on a differ- changing once again. From a time unpleasantness of their environ- ent role. They needed to become when business and industry was ment. Eventually, this stability far more flexible and responsive dominated by the need for natural evolved into an expectation of to the needs of customers, work resources, through a period when continued employment: long in teams, be responsible for availability of financial capital tenure with a company was con- quality and service, solve prob- often limited market access, busi- sidered entitlement. Considering lems, and reduce cycle time. To ness has arrived at a point where the booming markets of the time help them accomplish this, com- knowledge and its application are and the fact that there weren't panies invested in training and the most vital resources. Rather enough people to do the work, redesigned jobs and pay plans- than simply fulfilling employees' trading security for loyalty seemed and literally eradicated the basic needs or defending them like a reasonable return on human cradle-to-grave employment poli- against domineering supervisors capital. But the 1970 s brought unstable become so complacent. The for more and different knowledge marketsandfluctuatingeconomreturns