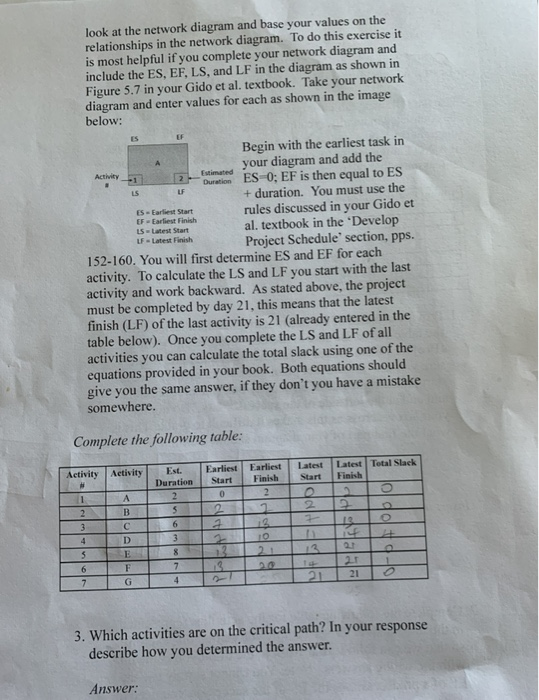
Question: below: Begin with the earliest task in your diagram and add the Duwe ES-0; EF is then equal to ES duration. You must use the
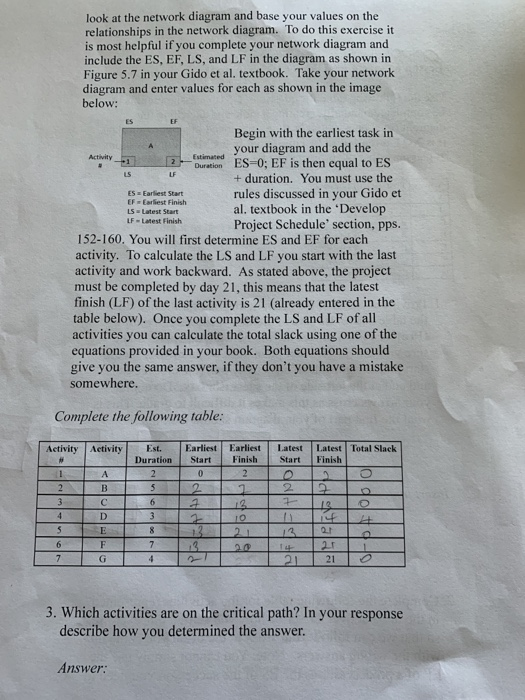
below: Begin with the earliest task in your diagram and add the Duwe ES-0; EF is then equal to ES duration. You must use the rules discussed in your Gido et al. textbook in the Develop Project Schedule' section, pps. 152-160. You will first determine ES and EF for each activity. To calculate the Land LF you start with the last activity and work backward. As stated above, the project must be completed by day 21, this means that the latest finish (LF) of the last activity is 21 (already entered in the table below). Once you complete the LS and LF of all activities you can calculate the total slack using one of the equations provided in your book. Both equations should give you the same answer, if they don't you have a mistake somewhere Complete the following able rtant Eart I A 2 10 + 3 G 7 95 3. Which activities are on the critical path? In your response describe how you determined the answer Answer: . a) Activities on critical path: b) Description of how it was determined: 4. What is the duration of the critical path? In your response describe how you determined the answer. Answer: a) Critical path duration: b) Description of how it was determined: 5. Why is it important to determine the critical path of a project? What happens if activities on this path are delayed? What happens if activities on this path are accelerated? Answer: a) It is important because: b) If activities are delayed: c) If activities are accelerated: 2. Complete the following table for the activities represented in the table above. Describe how you started this exercise so that we can follow your work in the event you come up with the wrong answers. Note: You cannot simply use the EF of a predecessor as the ES of the successor, you need to look at the network diagram and base your values on the relationships in the network diagram. To do this exercise it is most helpful if you complete your network diagram and include the ES, EF, LS, and LF in the diagram as shown in Figure 5.7 in your Gido et al. textbook. Take your network diagram and enter values for each as shown in the image below: 15 Estimated Activity -1 2 LS UF ES - Earliest Start EF - Earliest Finish LS Latest Start LF - Latest Finish Begin with the earliest task in your diagram and add the Duration ESO; EF is then equal to ES + duration. You must use the rules discussed in your Gido et al. textbook in the Develop Project Schedule' section, pps. 152-160. You will first determine ES and EF for each activity. To calculate the LS and LF you start with the last activity and work backward. As stated above, the project must be completed by day 21, this means that the latest finish (LF) of the last activity is 21 (already entered in the table below). Once you complete the LS and LF of all activities you can calculate the total slack using one of the equations provided in your book. Both equations should give you the same answer, if they don't you have a mistake somewhere. Complete the following table: Activity Activity Latest Start Latest Total Slack Finish Est. Duration 2 S Earliest Start 0 2 Earliest Finish 2 2 18 1 2 3 4 2 6 B D E F G FITY - PF PIO 2 $ 3 8 7 4 6 20 21 21 7 3. Which activities are on the critical path? In your response describe how you determined the answer. Answer: 2. Complete the following table for the activities represented in the table above. Describe how you started this exercise so that we can follow your work in the event you come up with the wrong answers. Note: You cannot simply use the EF of a predecessor as the ES of the successor, you need to inet.fe wiadne inselnurinata natia19 AARAZA Alia look at the network diagram and base your values on the relationships in the network diagram. To do this exercise it is most helpful if you complete your network diagram and include the ES, EF, LS, and LF in the diagram as shown in Figure 5.7 in your Gido et al. textbook. Take your network diagram and enter values for each as shown in the image below: ES EF Activity Estimated 2 LF LS ES Earliest Start EF Earliest Finish Ls Latest Start LF Latest Finish Begin with the earliest task in your diagram and add the Duration ESO; EF is then equal to ES + duration. You must use the rules discussed in your Gido et al. textbook in the Develop Project Schedule' section, pps. 152-160. You will first determine ES and EF for each activity. To calculate the LS and LF you start with the last activity and work backward. As stated above, the project must be completed by day 21, this means that the latest finish (LF) of the last activity is 21 (already entered in the table below). Once you complete the LS and LF of all activities you can calculate the total slack using one of the equations provided in your book. Both equations should give you the same answer, if they don't you have a mistake somewhere. Complete the following table: Activity Activity # Latest Start Latest Total Slack Finish Est. Duration 2 5 Earliest Earliest Start Finish 0 2 2 2 1 2 3 4 2 6 A B D E F G 112 3 8 $ 13 BOT 13 6 7 7 4 21 21 3. Which activities are on the critical path? In your response describe how you determined the answer. Answer: a) Activities on critical path: b) Description of how it was determined: 4. What is the duration of the critical path? In your response describe how you determined the answer. Answer: a) Critical path duration: b) Description of how it was determined: 5. Why is it important to determine the critical path of a project? What happens if activities on this path are delayed? What happens if activities on this path are accelerated? Answer: a) It is important because: b) If activities are delayed: c) If activities are accelerated: below: Begin with the earliest task in your diagram and add the Duwe ES-0; EF is then equal to ES duration. You must use the rules discussed in your Gido et al. textbook in the Develop Project Schedule' section, pps. 152-160. You will first determine ES and EF for each activity. To calculate the Land LF you start with the last activity and work backward. As stated above, the project must be completed by day 21, this means that the latest finish (LF) of the last activity is 21 (already entered in the table below). Once you complete the LS and LF of all activities you can calculate the total slack using one of the equations provided in your book. Both equations should give you the same answer, if they don't you have a mistake somewhere Complete the following able rtant Eart I A 2 10 + 3 G 7 95 3. Which activities are on the critical path? In your response describe how you determined the answer Answer: . a) Activities on critical path: b) Description of how it was determined: 4. What is the duration of the critical path? In your response describe how you determined the answer. Answer: a) Critical path duration: b) Description of how it was determined: 5. Why is it important to determine the critical path of a project? What happens if activities on this path are delayed? What happens if activities on this path are accelerated? Answer: a) It is important because: b) If activities are delayed: c) If activities are accelerated: 2. Complete the following table for the activities represented in the table above. Describe how you started this exercise so that we can follow your work in the event you come up with the wrong answers. Note: You cannot simply use the EF of a predecessor as the ES of the successor, you need to look at the network diagram and base your values on the relationships in the network diagram. To do this exercise it is most helpful if you complete your network diagram and include the ES, EF, LS, and LF in the diagram as shown in Figure 5.7 in your Gido et al. textbook. Take your network diagram and enter values for each as shown in the image below: 15 Estimated Activity -1 2 LS UF ES - Earliest Start EF - Earliest Finish LS Latest Start LF - Latest Finish Begin with the earliest task in your diagram and add the Duration ESO; EF is then equal to ES + duration. You must use the rules discussed in your Gido et al. textbook in the Develop Project Schedule' section, pps. 152-160. You will first determine ES and EF for each activity. To calculate the LS and LF you start with the last activity and work backward. As stated above, the project must be completed by day 21, this means that the latest finish (LF) of the last activity is 21 (already entered in the table below). Once you complete the LS and LF of all activities you can calculate the total slack using one of the equations provided in your book. Both equations should give you the same answer, if they don't you have a mistake somewhere. Complete the following table: Activity Activity Latest Start Latest Total Slack Finish Est. Duration 2 S Earliest Start 0 2 Earliest Finish 2 2 18 1 2 3 4 2 6 B D E F G FITY - PF PIO 2 $ 3 8 7 4 6 20 21 21 7 3. Which activities are on the critical path? In your response describe how you determined the answer. Answer: 2. Complete the following table for the activities represented in the table above. Describe how you started this exercise so that we can follow your work in the event you come up with the wrong answers. Note: You cannot simply use the EF of a predecessor as the ES of the successor, you need to inet.fe wiadne inselnurinata natia19 AARAZA Alia look at the network diagram and base your values on the relationships in the network diagram. To do this exercise it is most helpful if you complete your network diagram and include the ES, EF, LS, and LF in the diagram as shown in Figure 5.7 in your Gido et al. textbook. Take your network diagram and enter values for each as shown in the image below: ES EF Activity Estimated 2 LF LS ES Earliest Start EF Earliest Finish Ls Latest Start LF Latest Finish Begin with the earliest task in your diagram and add the Duration ESO; EF is then equal to ES + duration. You must use the rules discussed in your Gido et al. textbook in the Develop Project Schedule' section, pps. 152-160. You will first determine ES and EF for each activity. To calculate the LS and LF you start with the last activity and work backward. As stated above, the project must be completed by day 21, this means that the latest finish (LF) of the last activity is 21 (already entered in the table below). Once you complete the LS and LF of all activities you can calculate the total slack using one of the equations provided in your book. Both equations should give you the same answer, if they don't you have a mistake somewhere. Complete the following table: Activity Activity # Latest Start Latest Total Slack Finish Est. Duration 2 5 Earliest Earliest Start Finish 0 2 2 2 1 2 3 4 2 6 A B D E F G 112 3 8 $ 13 BOT 13 6 7 7 4 21 21 3. Which activities are on the critical path? In your response describe how you determined the answer. Answer: a) Activities on critical path: b) Description of how it was determined: 4. What is the duration of the critical path? In your response describe how you determined the answer. Answer: a) Critical path duration: b) Description of how it was determined: 5. Why is it important to determine the critical path of a project? What happens if activities on this path are delayed? What happens if activities on this path are accelerated? Answer: a) It is important because: b) If activities are delayed: c) If activities are accelerated