Question: (b)How many cycles does it take to execute the above program without any optimizations? (c) Re-schedule the instructions and unroll the loop to schedule it
(b)How many cycles does it take to execute the above program without any optimizations?
(c) Re-schedule the instructions and unroll the loop to schedule it without any delays, collapsing the loop overhead instructions. Assume a one-cycle delayed branch. Show the schedule. How many cycles does it take to execute the code? What is the speedup as compared to part (a)? Note, while unrolling the loop, unroll the loop minimum number of times.
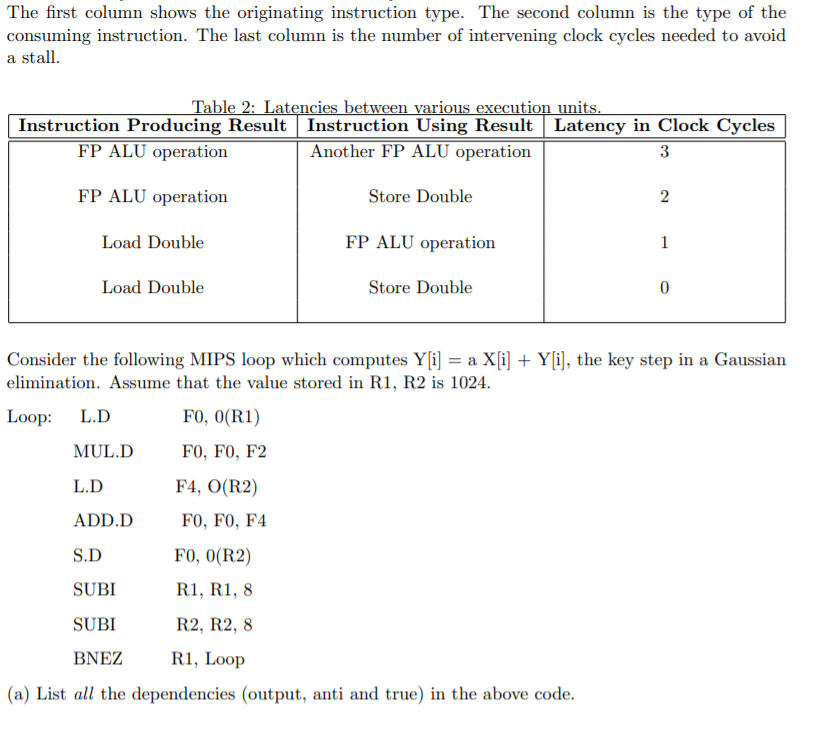
The first column shows the originating instruction type. The second column is the type of the consuming instruction. The last column is the number of intervening clock cycles needed to avoid a stall. Table 2: Latencies between various execution units. Instruction Producing Result Instruction Using Result Latency in Clock Cycles FP ALU operation Another FP ALU operation 3 FP ALU operation Store Double 2 Load Double FP ALU operation 1 Load Double Store Double 0 Consider the following MIPS loop which computes Y[i] = a X[i] + Y[i], the key step in a Gaussian elimination. Assume that the value stored in R1, R2 is 1024. Loop: L.D FO, O(R1) MUL.D FO, FO, F2 L.D F4, O(R2) ADD.D FO, FO, F4 S.D FO, O(R2) SUBI R1, R1, 8 SUBI R2, R2, 8 BNEZ R1, Loop (a) List all the dependencies (output, anti and true) in the above code. The first column shows the originating instruction type. The second column is the type of the consuming instruction. The last column is the number of intervening clock cycles needed to avoid a stall. Table 2: Latencies between various execution units. Instruction Producing Result Instruction Using Result Latency in Clock Cycles FP ALU operation Another FP ALU operation 3 FP ALU operation Store Double 2 Load Double FP ALU operation 1 Load Double Store Double 0 Consider the following MIPS loop which computes Y[i] = a X[i] + Y[i], the key step in a Gaussian elimination. Assume that the value stored in R1, R2 is 1024. Loop: L.D FO, O(R1) MUL.D FO, FO, F2 L.D F4, O(R2) ADD.D FO, FO, F4 S.D FO, O(R2) SUBI R1, R1, 8 SUBI R2, R2, 8 BNEZ R1, Loop (a) List all the dependencies (output, anti and true) in the above code
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


