Question: Buffer Overflow Lab Stack Frames Buffer overflows are most commonly implemented by an attack known as stack smashing. To understand this, you need to understand
Buffer Overflow Lab
Stack Frames
Buffer overflows are most commonly implemented by an attack known as stack smashing. To understand this, you need to understand why and how a stack is used. When a procedure is called, it is necessary to save the address to return to, along with other information. On most machines, this is accomplished by pushing the information onto a stack or a last-in-first-out data structure. The set of information saved on the stack for a single call is known as a stack frame. When the procedure returns, the information is removed, or popped, from the stack, and the return address is set as the current instruction pointer. For this simple machine, the stack frame consists of the return address, followed by any parameters for the procedure, followed by the local variables used in the procedure. The stack grows toward low memory.
Step through the program and see the effect of multiple procedure calls and how the stack changes.You will have to scroll the memory window to see the growing stack.
Answer the following questions:
1. List the starting and stopping locations of the main method 2. List the starting and stopping locations of the ProcA method 3. List the starting and stopping locations of each local variable for ProcA 4. List the starting and stopping locations of each parameter passed to ProcA 5. List the location on the stack of the return address, its value, and the actual statement the return address refers to.
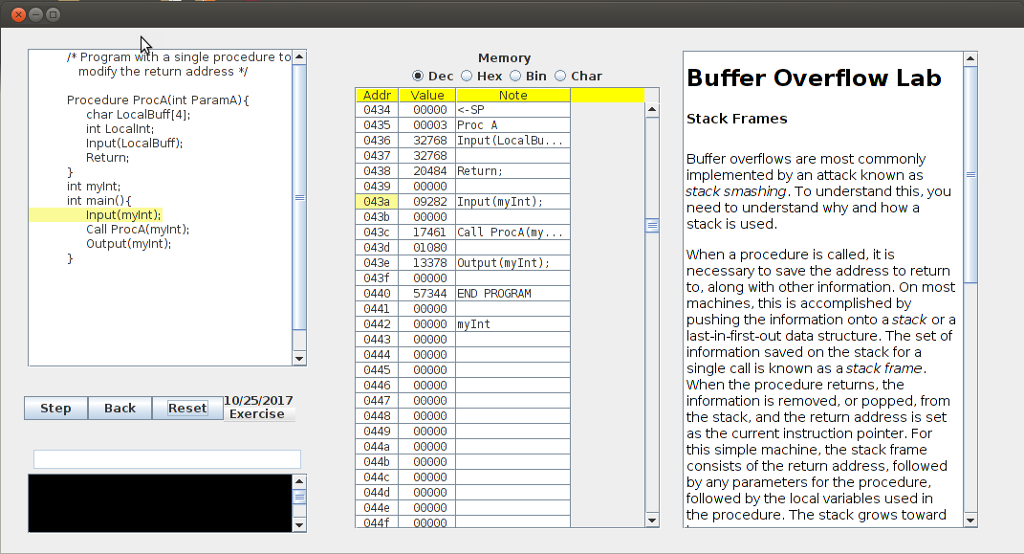
/* Program with a single procedure to Memory Hex O Bin O Char modify the return address O Dec Buffer Overflow Lab Addr Value 043400000
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


