Question: (c) Atomic radius, crystal structure, electronegativity and the most common valence state for several different hypothetical elements (represented as A to K) are tabulated
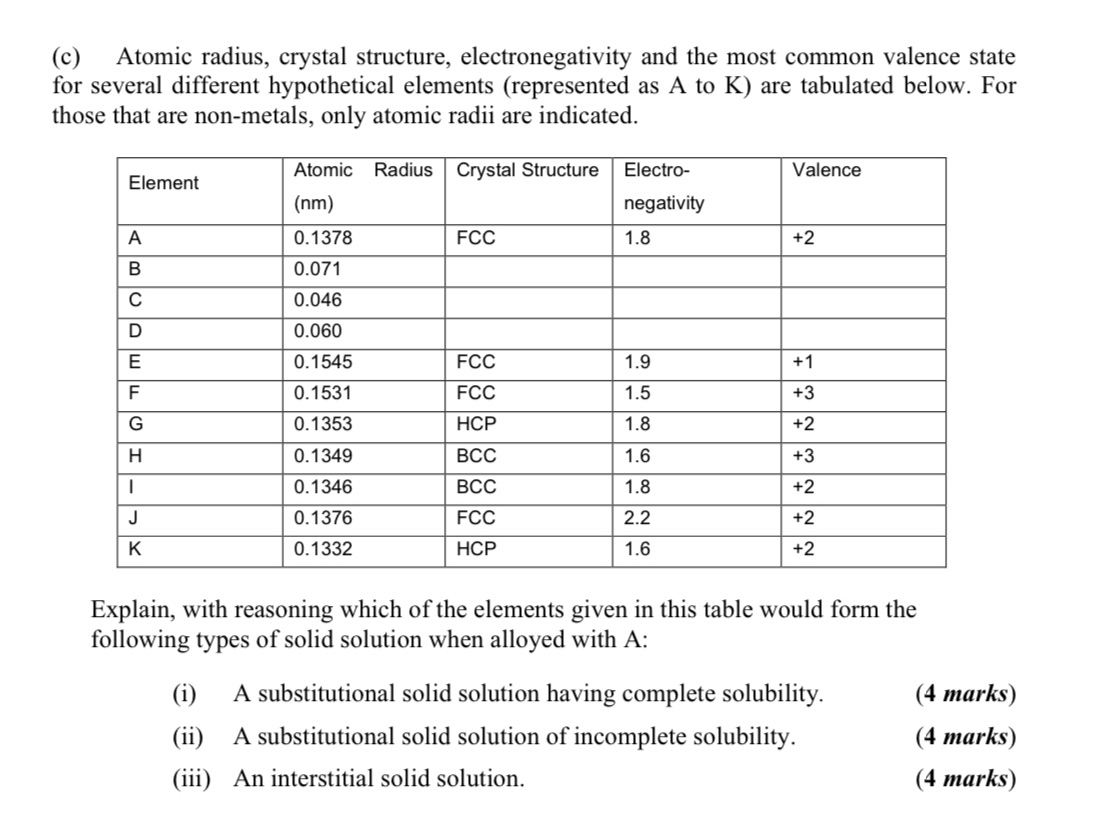
(c) Atomic radius, crystal structure, electronegativity and the most common valence state for several different hypothetical elements (represented as A to K) are tabulated below. For those that are non-metals, only atomic radii are indicated. Atomic Radius Crystal Structure Electro- Valence Element (nm) negativity A 0.1378 FCC 1.8 +2 BCDEF 0.071 0.046 0.060 0.1545 FCC 1.9 +1 0.1531 FCC 1.5 +3 G 0.1353 HCP 1.8 +2 H 0.1349 BCC 1.6 +3 | 0.1346 BCC 1.8 +2 J 0.1376 FCC 2.2 +2 K 0.1332 HCP 1.6 +2 Explain, with reasoning which of the elements given in this table would form the following types of solid solution when alloyed with A: (i) A substitutional solid solution having complete solubility. (4 marks) (ii) A substitutional solid solution of incomplete solubility. (iii) An interstitial solid solution. (4 marks) (4 marks)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


