Question: C++ To the right is what failed for testing. The ones with the red X's have failed to build. My code is written below. Main.cpp______________________________
C++
To the right is what failed for testing. The ones with the red X's have failed to build. 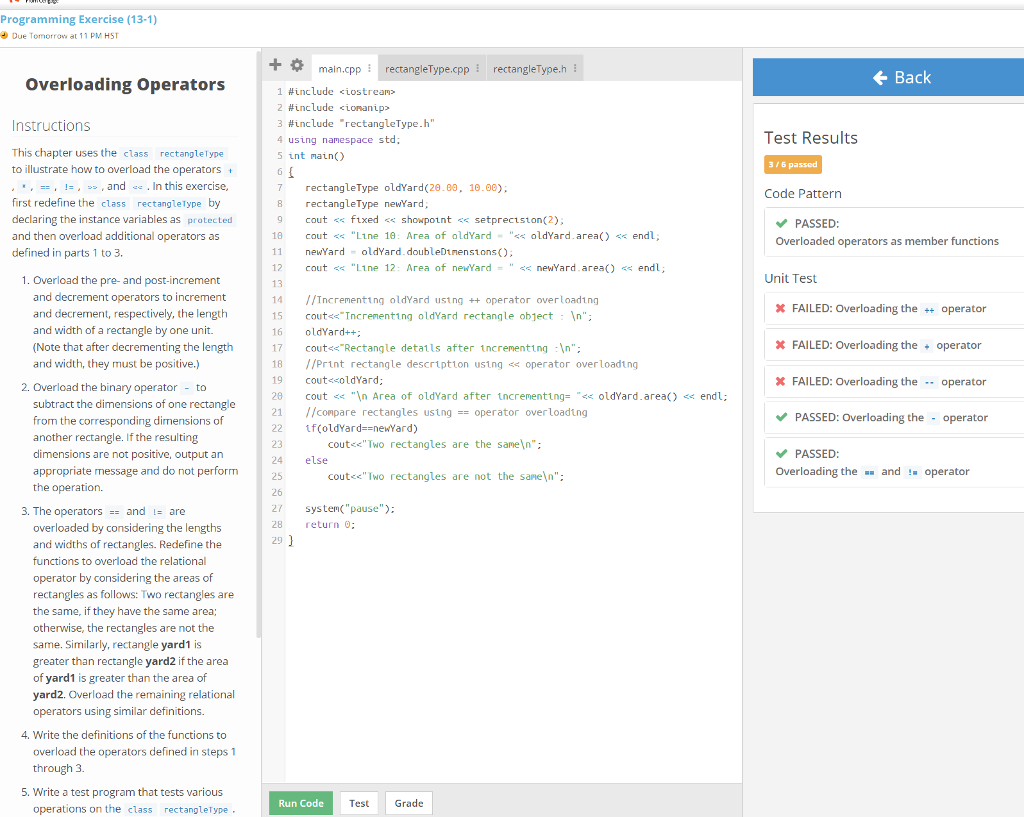 My code is written below.
My code is written below.
Main.cpp______________________________
#include rectangleType.cpp_________________________ #include "rectangleType.h" //Default constructor rectangleType::rectangleType() { } //Parameerized consgtructor rectangleType::rectangleType(double _length,double _width) { length = _length; width = _width; } //Set Dimention function void rectangleType::setDimension(double _length,double _width) { length = _length; width = _width; } //get length function double rectangleType::getLength() { return length; } //get width function double rectangleType::getWidth() { return width; } // area function double rectangleType::area() { double area; area = length*width; return area; } // perimeter function double rectangleType::perimeter() { double perimeter; perimeter = 2*(length+width); return perimeter; } // doubleDimensions function rectangleType rectangleType::doubleDimensions() { length = 2 * length; width = 2 * width; return *this; } //print function void rectangleType::print() { cout } //++ operator overloading rectangleType rectangleType::operator++() { length++; width++; return *this; } //-- operator overloading rectangleType rectangleType::operator--() { length--; width--; return *this; } //- operator overloading rectangleType rectangleType::operator-(rectangleType& other) { if(length //Input and Output operator overloading ostream & operator istream &operator>>( istream &input, rectangleType &r ) { input >> r.length >>r.width; return input; } rectangleType.h_____________________ #ifndef RECTANGLETYPE_H #define RECTANGLETYPE_H #include friend ostream& operator>( istream &input, rectangleType &r ); private: double length; double width; }; #endif // RECTANGLETYPE_H
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


