Question: Calculating Depreciation Schedules - Using Straight-Line, Units-of-Production, and Double-Declining-Balance Methods in Excel: *Please Include the Excel Formulas in Your Answer* A B C D begin{tabular}{l|l}
Calculating Depreciation Schedules - Using Straight-Line, Units-of-Production, and Double-Declining-Balance Methods in Excel:
*Please Include the Excel Formulas in Your Answer*
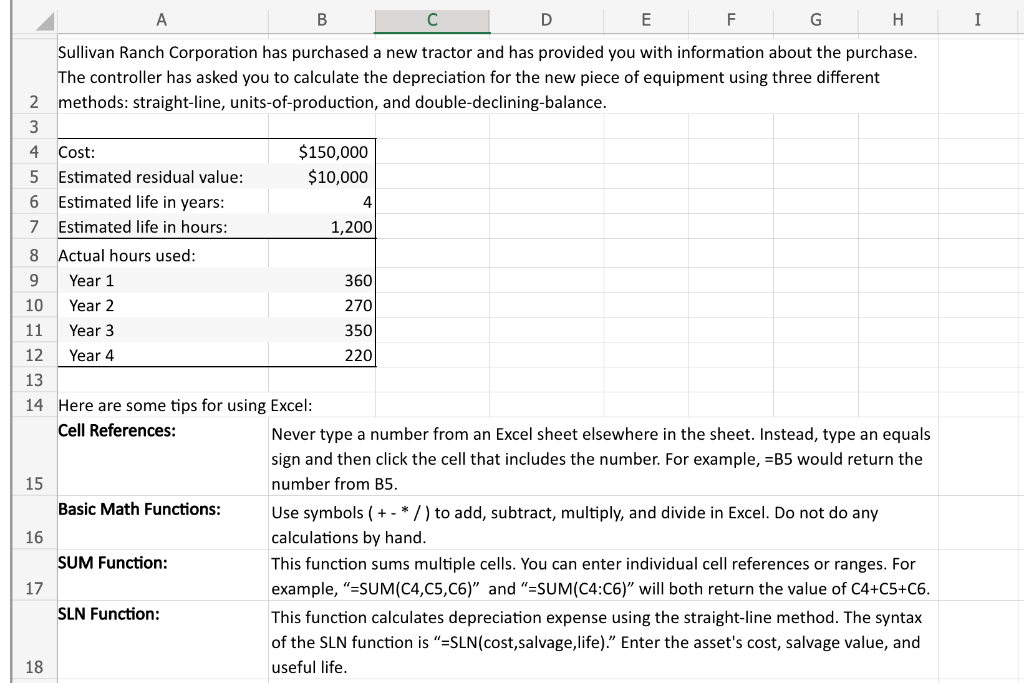
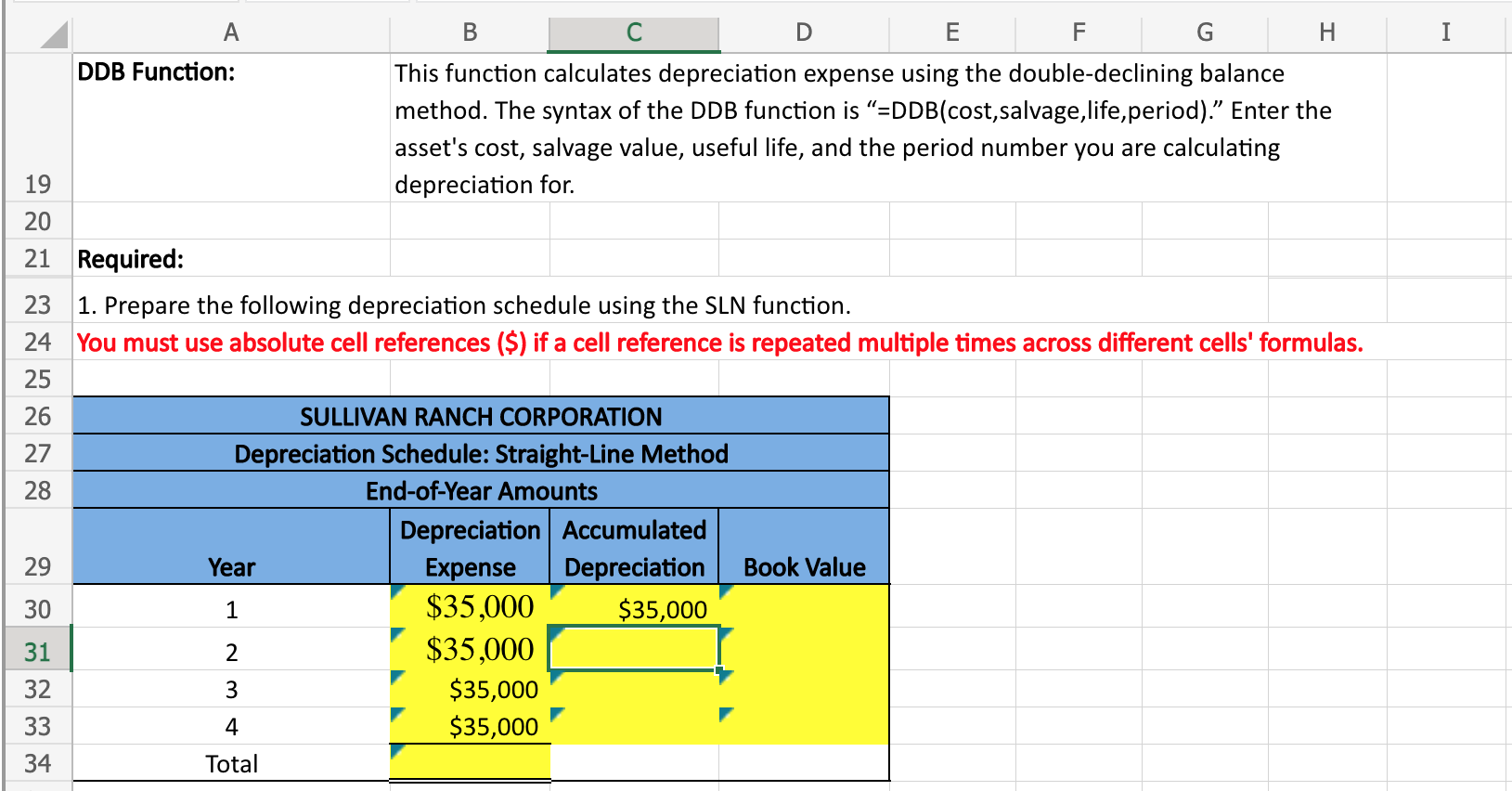
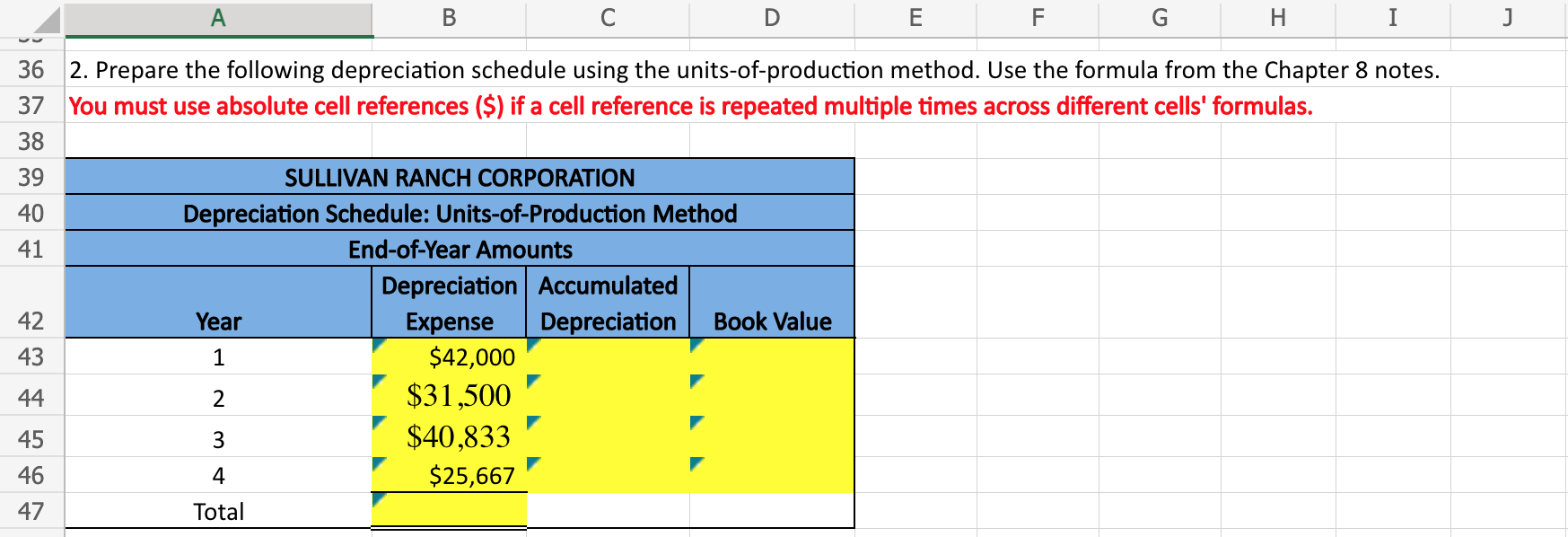
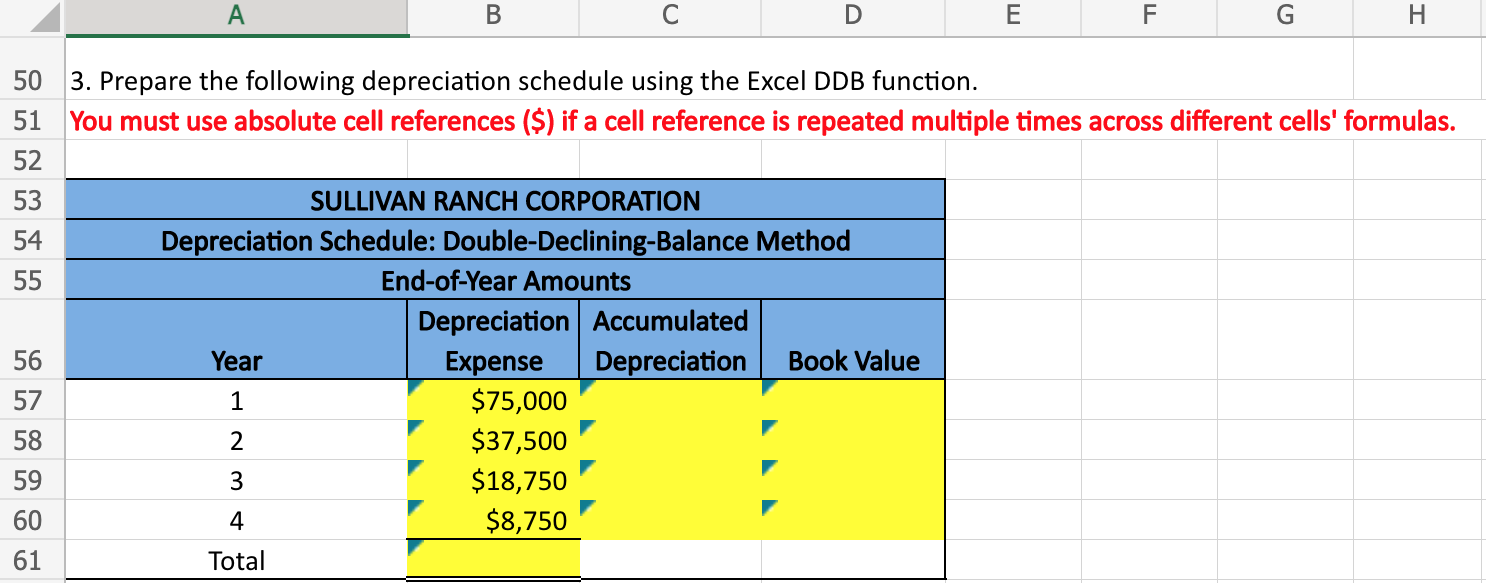
A B C D \begin{tabular}{l|l} E & F \end{tabular} G I Sullivan Ranch Corporation has purchased a new tractor and has provided you with information about the purchase. The controller has asked you to calculate the depreciation for the new piece of equipment using three different 2 methods: straight-line, units-of-production, and double-declining-balance. 13 14 Here are some tips for using Excel: Cell References: Never type a number from an Excel sheet elsewhere in the sheet. Instead, type an equals sign and then click the cell that includes the number. For example, =B5 would return the 15 number from B5. Basic Math Functions: Use symbols ( + * / ) to add, subtract, multiply, and divide in Excel. Do not do any 16 calculations by hand. SUM Function: This function sums multiple cells. You can enter individual cell references or ranges. For 17 example, "=SUM(C4,C5,C6)" and "=SUM(C4:C6)" will both return the value of C4+C5+C6. SLN Function: This function calculates depreciation expense using the straight-line method. The syntax of the SLN function is "=SLN(cost,salvage,life)." Enter the asset's cost, salvage value, and 18 useful life. 1. Prepare the following depreciation schedule using the SLN function. You must use absolute cell references ($) if a cell reference is repeated multiple times across different cells' formulas. 2. Prepare the following depreciation schedule using the units-of-production method. Use the formula from the Chapter 8 notes. You must use absolute cell references (\$) if a cell reference is repeated multiple times across different cells' formulas. 3. Prepare the following depreciation schedule using the Excel DDB function. You must use absolute cell references ($) if a cell reference is repeated multiple times across different cells' formulas
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


