Question: Calculus 3 : > Section 11.7: Problem 1 {1 point] The function f has continuous second derivatives. and a critical point at [6, 2}. Suppose
![Calculus 3 :> Section 11.7: Problem 1 {1 point] The function](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6667d29308cac_1466667d292dbf64.jpg)


![as a commaseparated lisL {e.g., {111,1), {2, e, 1}, {2,111. 3}}. C]](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6667d2955f264_1496667d29547dd3.jpg)


Calculus 3 :
>


![of these (d) Point S is ?Section 11.7: Problem 13 {1 point]](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6667d29891a35_1526667d2987f5d8.jpg)
![A contour diagram for a function fix, 1:] is shown below. Estimate](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6667d298e102b_1526667d298c222c.jpg)
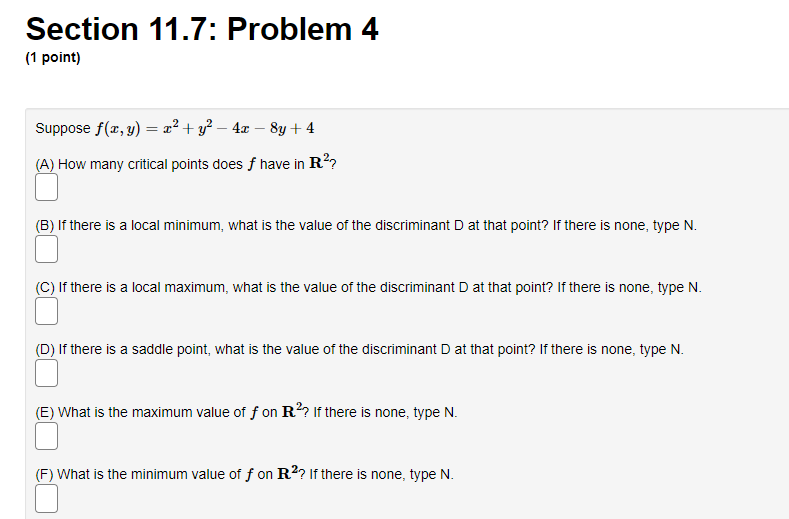
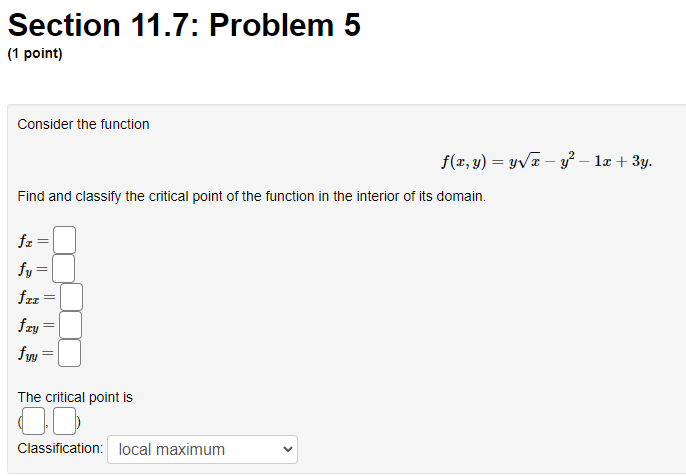
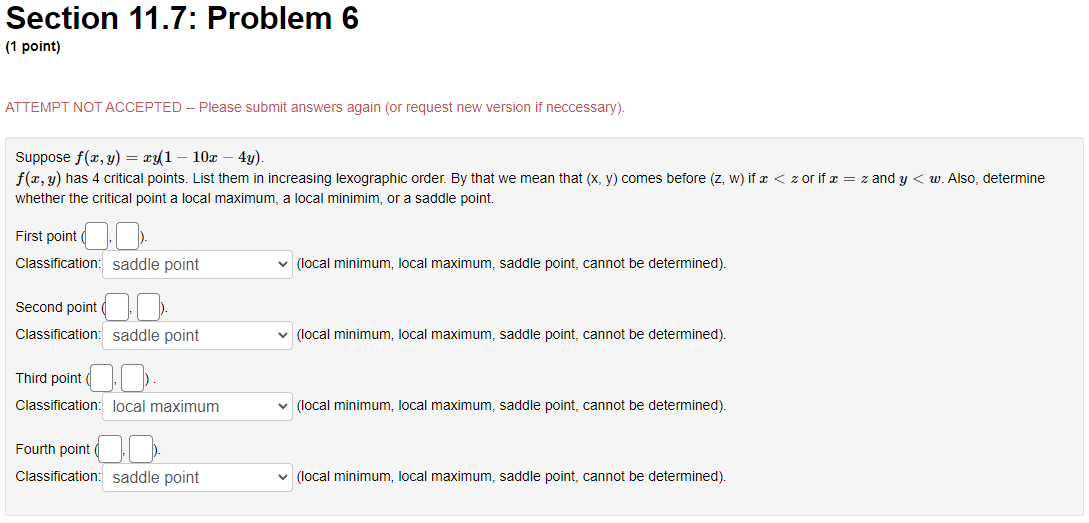
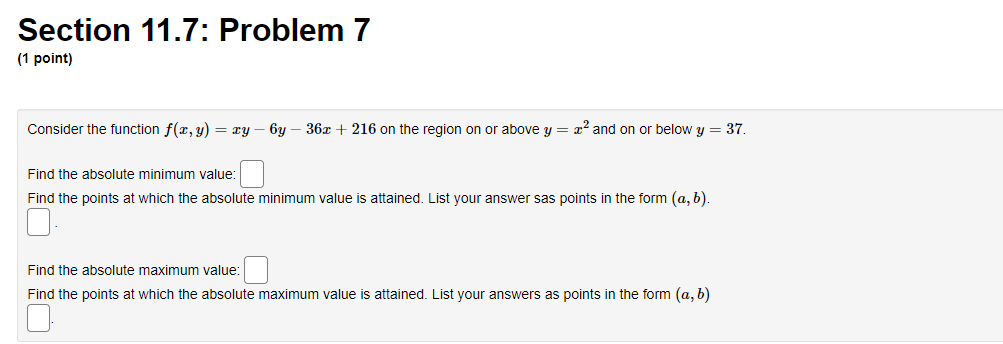


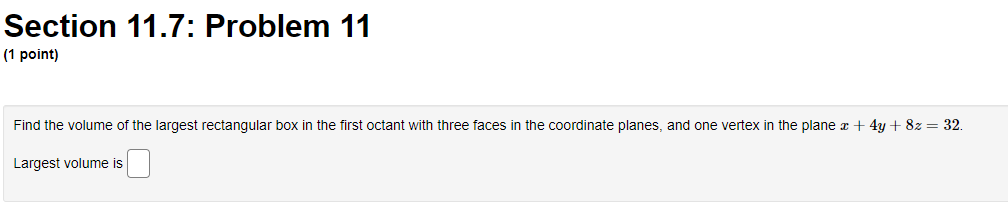
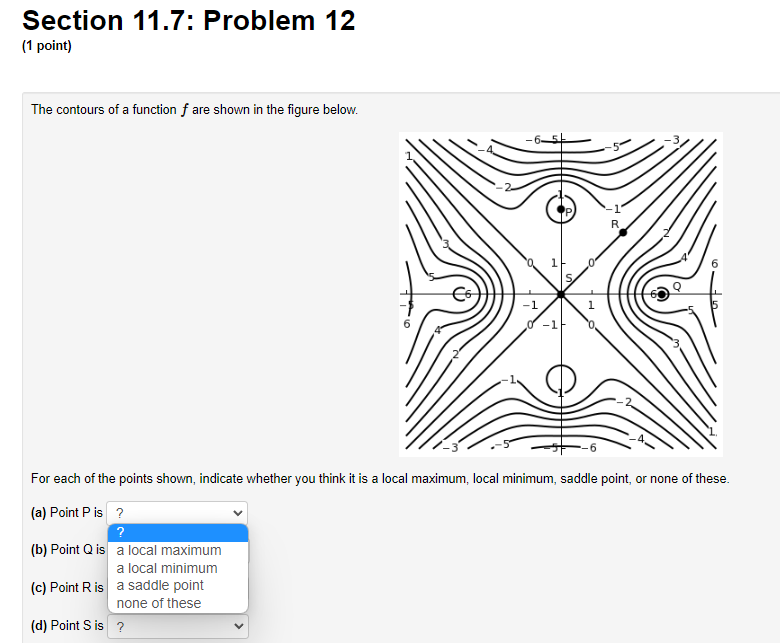
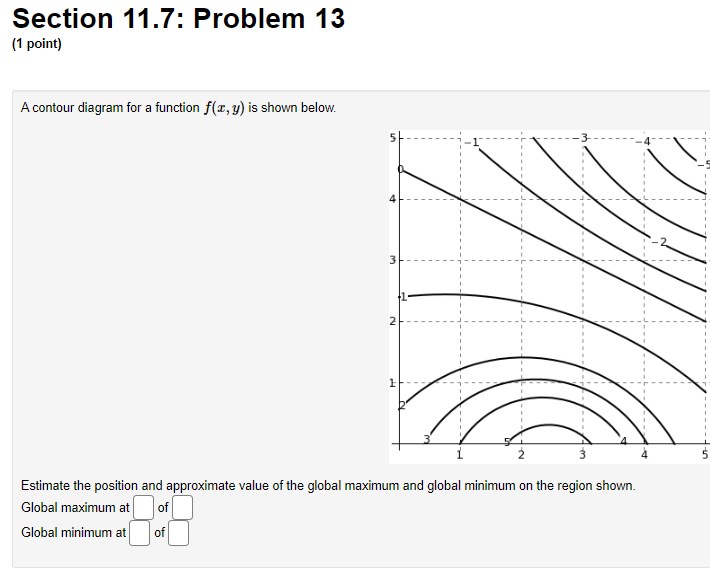
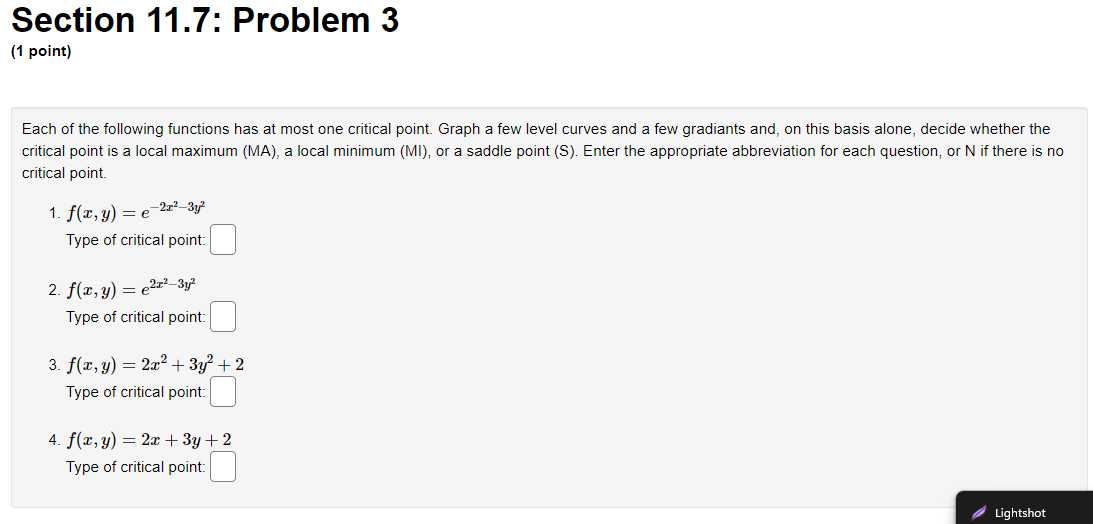
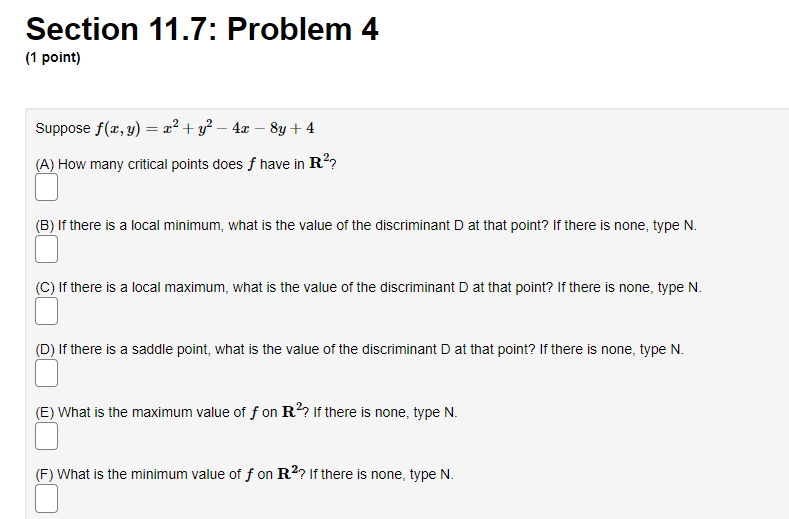
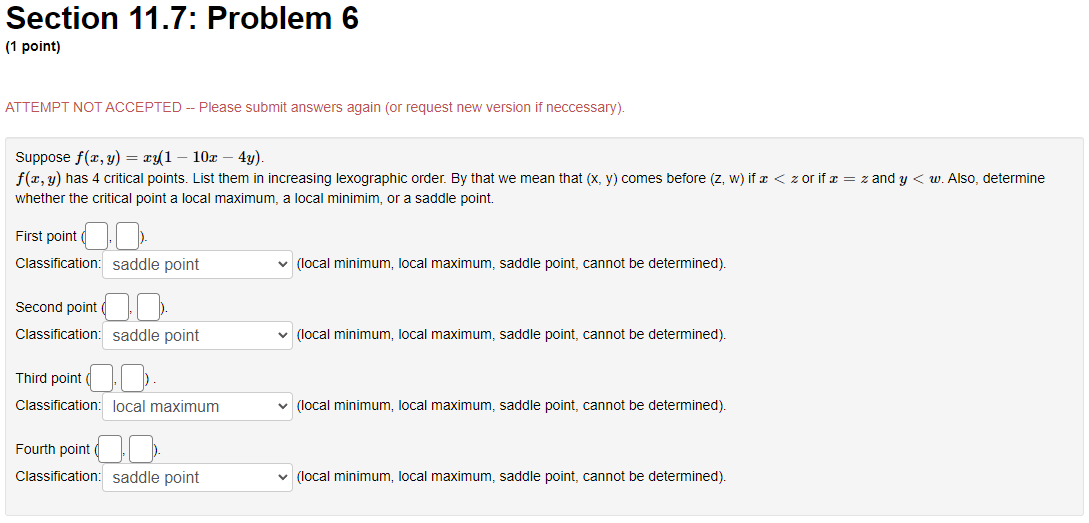
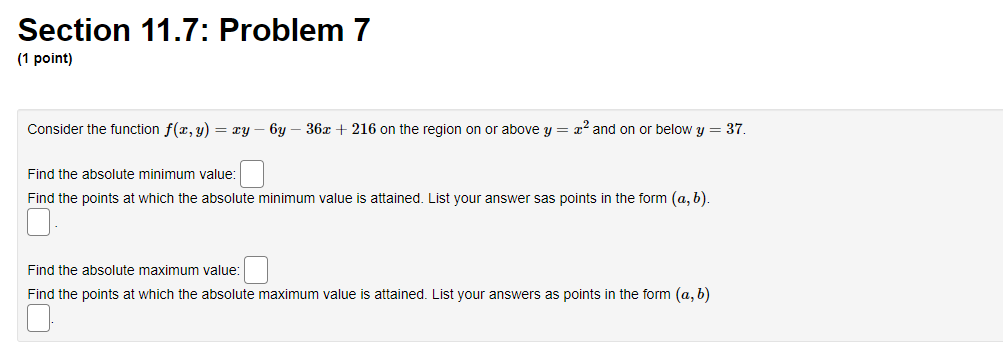
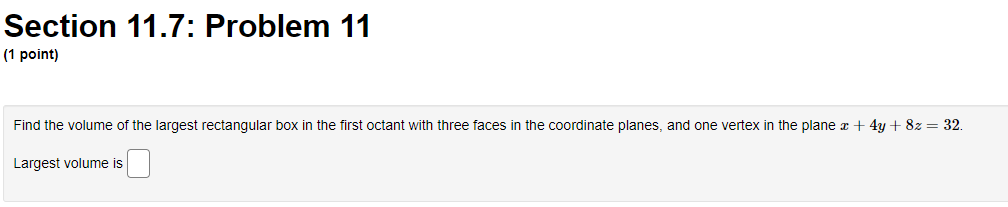
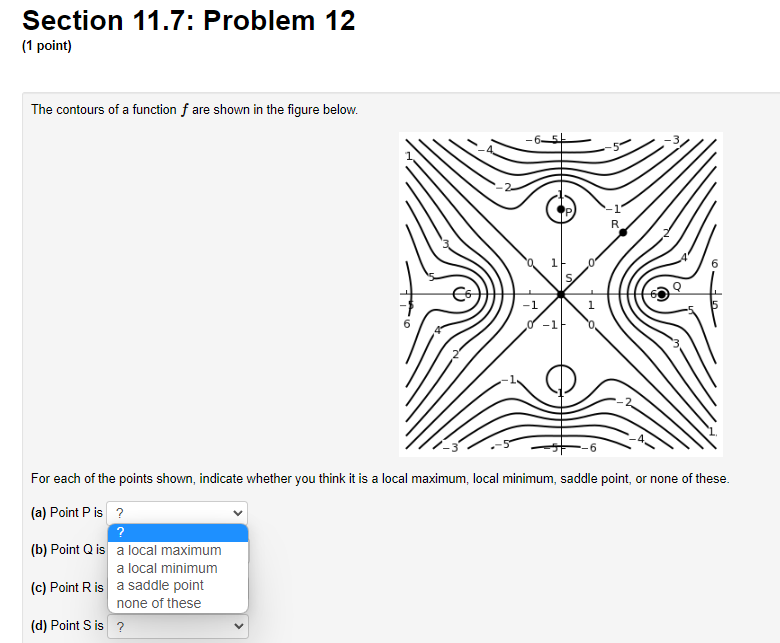
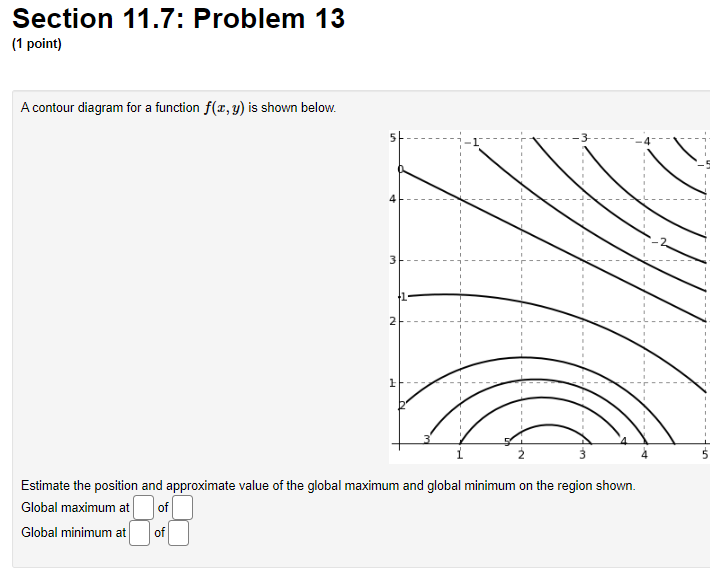
Section 11.7: Problem 1 {1 point] The function f has continuous second derivatives. and a critical point at [6, 2}. Suppose fut6: 2) = : fad: 2} = 9, rat6. 2} = 4. Then the point {5, 2}: 0A. is a local maximum 0 E. is a saddle point C) C. is a local minimum {:1 D. cannot be determined 0 E. None ofthe above Section 11.7: Problem 10 [1 point: Find the peintte} en the surface :42 = my + 1 which are closest to the point [4, 5,110. List points as a commaseparated lisL {e.g., {111,1), {2, e, 1}, {2,111. 3}}. C] Section 11.7: Problem 11 (1 point) Find the volume of the largest rectangular box in the first octant with three faces in the coordinate planes, and one vertex in the plane a + 4y + 8z = 32. Largest volume isSection 11.7: Problem 12 (1 point) The contours of a function f are shown in the figure below. -1 1 -1 For each of the points shown, indicate whether you think it is a local maximum, local minimum, saddle point, or none of these. (a) Point P is ? ? (b) Point Q is a local maximum a local minimum (c) Point R is a saddle point none of these (d) Point S is ?Section 11.7: Problem 13 {1 point] A contour diagram for a function fix, 1:] is shown below. Estimate the position and approximate value of the global maximum and global minimum on the region shown. Global maximum at of Global minimum at of Section 11.7: Problem 2 (1 point) The function f has continuous second derivatives, and a critical point at (4, 5). Suppose fra (4, 5) = 14, fry(4, 5) = -1, fyy(4, 5) = 4. Then the point (4, 5): O A. is a local minimum O B. cannot be determined O C. is a saddle point O D. is a local maximum O E. None of the aboveSection 11.7: Problem 3 (1 point) Each of the following functions has at most one critical point. Graph a few level curves and a few gradiants and, on this basis alone, decide whether the critical point is a local maximum (MA), a local minimum (MI), or a saddle point (S). Enter the appropriate abbreviation for each question, or N if there is no critical point. 1. f(x, y) = e 2x2 3y Type of critical point: 2. f(x, y) = e212-3yz Type of critical point: 3. f(x, y) = 2x2 + 3y- + 2 Type of critical point 4. f(x, y) = 2x + 3y + 2 Type of critical point: LightshotSection 11.7: Problem 4 (1 point) Suppose f(x, y) = x2 + y' - 4x - 8y + 4 (A) How many critical points does f have in R?? (B) If there is a local minimum, what is the value of the discriminant D at that point? If there is none, type N. C) If there is a local maximum, what is the value of the discriminant D at that point? If there is none, type N. (D) If there is a saddle point, what is the value of the discriminant D at that point? If there is none, type N. (E) What is the maximum value of f on R. ? If there is none, type N. (F) What is the minimum value of f on R? If there is none, type N.Section 11.7: Problem 5 (1 point) Consider the function f(x, y) = yvr - y' - 1x + 3y. Find and classify the critical point of the function in the interior of its domain. fy fTI = fry = fuy = The critical point is Classification: local maximumSection 11.7: Problem 6 (1 point) ATTEMPT NOT ACCEPTED Please submit answers again (or request new version if neccessary). Suppose f(z,y) = 2:311 10m 4y). z, 9') has 4 critical points. List them in increasing lexographic order. By that we mean that (x, y} comes before (2, w) if a: a: z or if z = z and y ) on the plane > = 2x + 4y + 2 which is closest to the origin. T. 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


