Question: can you help me solve following question based on the given data. Molarity of HCl= Total: PART 2: DATA ANALYSIS & QUESTIONS Note: If you
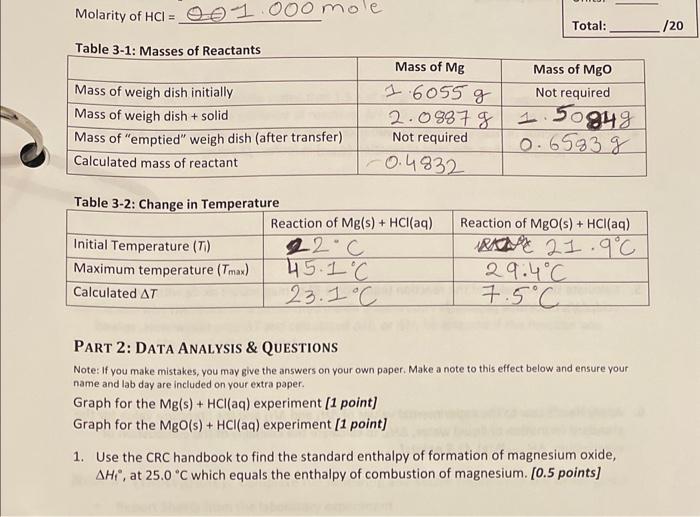


Molarity of HCl= Total: PART 2: DATA ANALYSIS \& QUESTIONS Note: If you make mistakes, you may give the answers on your own paper. Make a note to this effect below and ensure your name and lab day are included on your extra paper. Graph for the Mg(s)+HCl(aq) experiment [1 point] Graph for the MgO(s)+HCl(aq) experiment [1 point] 1. Use the CRC handbook to find the standard enthalpy of formation of magnesium oxide, Hi, at 25.0C which equals the enthalpy of combustion of magnesium. [0.5 points] 2. For the reaction of magnesium with hydrochloric acid, calculate the heat of the solution (qsola) and thus, the heat of reaction (qmn) in Joules. [1 point] 3. Calculate the enthalpy of the reaction (equation 3-5) of magnesium with hydrochloric acid, H4 in kJ/mol. [1 point] 4. For the reaction of magnesium oxide with hydrochloric acid, calculate the heat of the solution (qsoln) and thus, the heat of reaction (qman2) in Joules. [1 point] 5. Calculate the enthalpy of the reaction (equation 3-6) of magnesium oxide with hydrochloric acid, H2, in kJ/mol. [1 point] 6. Apply Hess's Law to the experimental values of H1 and H2 and the literature value for the standard formation of liquid water, H3, to calculate the enthalpy of the combustion of magnesium, Hcomb(Mg). [1.5 points] 7. Calculate your % experimental error. [1 point] Accuracy: (grading use only) / [1 point] 8. Explain why your graphs of temperature versus time exhibit an increase in temperature. Also explain why the temperature reaches a maximum and then steadily decreases. [2 points] 9. The experimental procedure states that 1.5g of magnesium oxide are required. Will the calculated value for the enthalpy of reaction, H2, (Question 5) be affected if you used 1.6g of magnesium oxide instead? Explain why or why not. [ 2 points] 10. Explain why the reaction is performed inside a foam cup rather than in the usual glass beaker. How would your T and calculated H1 or H2 be affected if the reaction was performed in a beaker? [2 points] Molarity of HCl= Total: PART 2: DATA ANALYSIS \& QUESTIONS Note: If you make mistakes, you may give the answers on your own paper. Make a note to this effect below and ensure your name and lab day are included on your extra paper. Graph for the Mg(s)+HCl(aq) experiment [1 point] Graph for the MgO(s)+HCl(aq) experiment [1 point] 1. Use the CRC handbook to find the standard enthalpy of formation of magnesium oxide, Hi, at 25.0C which equals the enthalpy of combustion of magnesium. [0.5 points] 2. For the reaction of magnesium with hydrochloric acid, calculate the heat of the solution (qsola) and thus, the heat of reaction (qmn) in Joules. [1 point] 3. Calculate the enthalpy of the reaction (equation 3-5) of magnesium with hydrochloric acid, H4 in kJ/mol. [1 point] 4. For the reaction of magnesium oxide with hydrochloric acid, calculate the heat of the solution (qsoln) and thus, the heat of reaction (qman2) in Joules. [1 point] 5. Calculate the enthalpy of the reaction (equation 3-6) of magnesium oxide with hydrochloric acid, H2, in kJ/mol. [1 point] 6. Apply Hess's Law to the experimental values of H1 and H2 and the literature value for the standard formation of liquid water, H3, to calculate the enthalpy of the combustion of magnesium, Hcomb(Mg). [1.5 points] 7. Calculate your % experimental error. [1 point] Accuracy: (grading use only) / [1 point] 8. Explain why your graphs of temperature versus time exhibit an increase in temperature. Also explain why the temperature reaches a maximum and then steadily decreases. [2 points] 9. The experimental procedure states that 1.5g of magnesium oxide are required. Will the calculated value for the enthalpy of reaction, H2, (Question 5) be affected if you used 1.6g of magnesium oxide instead? Explain why or why not. [ 2 points] 10. Explain why the reaction is performed inside a foam cup rather than in the usual glass beaker. How would your T and calculated H1 or H2 be affected if the reaction was performed in a beaker? [2 points]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


