Question: Chapter 9 Part 2 Example 11 How Lower-of-Cost-or-Market Works Step 1: Designated Market Value Replacement Net Realizable NRV less Designed Cost Value (Ceiling) Nonnul Profit
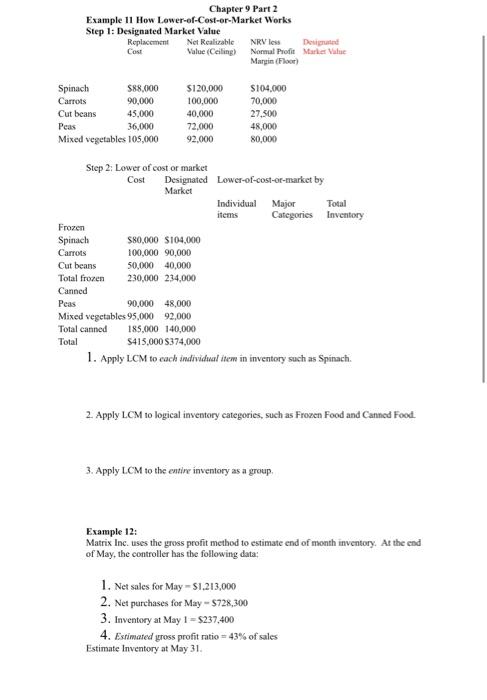

Chapter 9 Part 2 Example 11 How Lower-of-Cost-or-Market Works Step 1: Designated Market Value Replacement Net Realizable NRV less Designed Cost Value (Ceiling) Nonnul Profit Market Value Margin (Floor) 90,000 Spinach 588.000 Carrots Cut beans 45,000 Peas 36,000 Mixed vegetables 105,000 S120,000 100,000 40,000 72.000 92.000 $104.000 70,000 27.500 48,000 80,000 Major Step 2: Lower of cost or market Cost Designated Lower-of-cost-of-market by Market Individual Total items Categories Inventory Frozen Spinach $80,000 $104.000 Carrots 100,000 90,000 Cut beans 50,000 40,000 Total frozen 230,000 234,000 Canned Peas 90,000 48,000 Mixed vegetables 95,000 92,000 Total canned 185.000 140,000 Total 5415,000 374,000 1. Apply LCM to each individual item in inventory such as Spinach. 2. Apply LCM 10 logical inventory categories, such as Frozen Food and Catined Food 3. Apply LCM to the entire inventory as a group, Example 12: Matrix Inc. uses the gross profit method to estimate end of month inventory. At the end of May, the controller has the following data: 1. Net sales for May = 51.213,000 2. Net purchases for May -- $728,300 3. Inventory at May 1 - $237,400 4. Estimated gross profit ratio = 43% of sales Estimate Inventory at May 31. 4. Estimated gross profit ratio - 43% of sales Estimate Inventory at May 31. Example 13. Coastal Shores Inc. (CSI) was destroyed by Hurricane Fred on August 5, 2021. At January 1, CSI reported an inventory of $170,000. Sales from January 1, 2021, to August 5. 2021, totaled $480,000 and purchases totaled $195,000 during that time. CSI consistently marks up its products 60% over cost to arrive at a selling price. The estimated inventory loss due to Hurricane Fred would be: A. S131,175. B. 865,000. C. $17.143. D. None of the above is correct Example 14: Under the retail inventory method A. A company measures inventory on its balance sheet by converting retail prices to cost. B. A company measures inventory on its balance sheet at current selling prices C. A company measures inventory on its balance sheet on a LIFO basis. D. None of the above is correct. Example 15: Fuque Inc. uses the retail inventory method to estimate ending inventory for its monthly financial statements. The following data pertain to a single department for the month of October COST RETAIL Beg. Inventory, Oct. 1 52,000 $ 78,000 Purchases 272,000 423,000 Freight in 16,600 Purchase returns 5,600 8,000 Additional markups 9.000 Markup cancellations 2,000 Markdowns (net) 3,600 Normal spoilage 10,000 Sales 390,000 Prepare a schedule computing retail inventory using the following methods (1) Conventional (LCM) (2) Cost
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


