Question: Chemical Reaction Engineering NOTE : -Show each step clearly in your derivations required in the solution of each problem. - DO NOT USE the final
Chemical Reaction Engineering
NOTE : -Show each step clearly in your derivations required in the solution of each problem. - DO NOT USE the final equations directly from your textbook. - R: 1.987cal/molK, 0.082 L.atm/mol.K, 8.314 J/mol.K
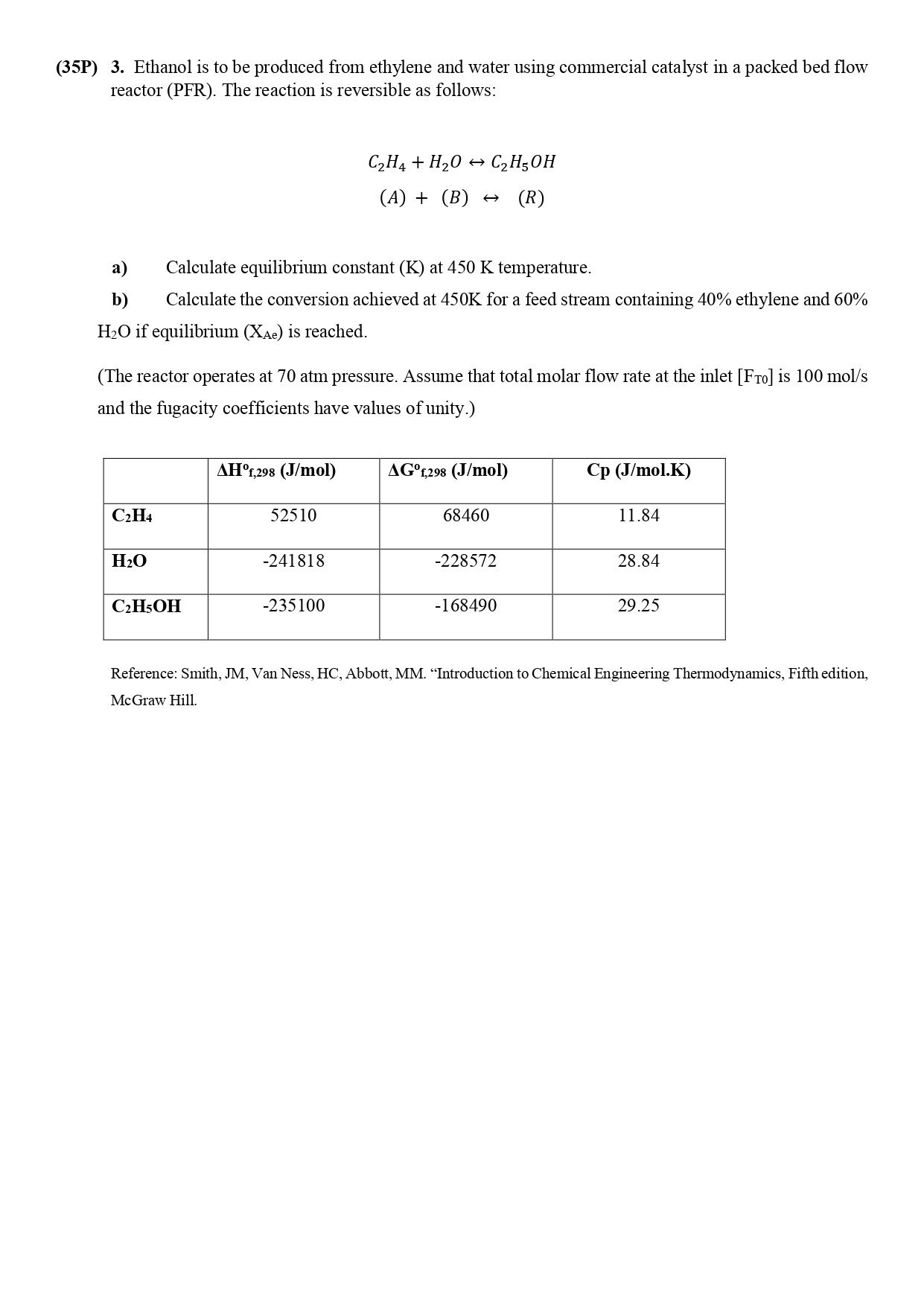
(35P) 3. Ethanol is to be produced from ethylene and water using commercial catalyst in a packed bed flow reactor (PFR). The reaction is reversible as follows: C2H4+H2OC2H5OH(A)+(B)(R) a) Calculate equilibrium constant (K) at 450K temperature. b) Calculate the conversion achieved at 450K for a feed stream containing 40% ethylene and 60% H2O if equilibrium (XAe) is reached. (The reactor operates at 70atm pressure. Assume that total molar flow rate at the inlet [FT0] is 100mol/s and the fugacity coefficients have values of unity.) Reference: Smith, JM, Van Ness, HC, Abbott, MM. "Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Fifth edition, McGraw Hill. (35P) 3. Ethanol is to be produced from ethylene and water using commercial catalyst in a packed bed flow reactor (PFR). The reaction is reversible as follows: C2H4+H2OC2H5OH(A)+(B)(R) a) Calculate equilibrium constant (K) at 450K temperature. b) Calculate the conversion achieved at 450K for a feed stream containing 40% ethylene and 60% H2O if equilibrium (XAe) is reached. (The reactor operates at 70atm pressure. Assume that total molar flow rate at the inlet [FT0] is 100mol/s and the fugacity coefficients have values of unity.) Reference: Smith, JM, Van Ness, HC, Abbott, MM. "Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Fifth edition, McGraw Hill
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


