Question: //Codes given //Prog340 import javax.swing.*; import java.io.*; import java.util.*; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; /** ProgramA simply reads a file containing rows of space-separated Strings, **


//Codes given
//Prog340
import javax.swing.*; import java.io.*; import java.util.*; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*;
/** ProgramA simply reads a file containing rows of space-separated Strings, ** your assignment is to print out those strings interpreted as a graph. **/
public class Prog340 extends JPanel implements ActionListener { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; // Keep Eclipse happy. File inputFile; File outputFile; PrintWriter output; JFileChooser fileChooser; Graph g; String[] comboBoxList; // For putting names in Combo Box
/** The main method instantiates a Prog340 class, which includes giving you a choice of things to do. ** The only one active now will be reading the graph file and having you parse it. ** ** @param args ** - Not used ** ** @throws FileNotFoundException ** - Thrown if the file selected is not found. Shouldn't happen with a FileChooser. **/
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { javax.swing.SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable() { public void run() { createAndShowGUI(); } }); } /** Create and show the GUI. ** For thread safety, this method should be invoked from the event-dispatching thread. **/ private static void createAndShowGUI() { // Create and set up the window JFrame frame = new JFrame("Prog340"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); // Create and set up the content pane. JComponent newContentPane = new Prog340(); newContentPane.setOpaque(true);; // content panes must be opaque frame.setContentPane(newContentPane);; // Display the window. frame.pack(); frame.setVisible(true); } /** The constructor creates a new ProgramA object, and sets up the input and output files. **/ public Prog340() { super( new BorderLayout() );
try { // I like the colorful FileChooser. UIManager.setLookAndFeel(UIManager.getSystemLookAndFeelClassName()); System.out.println( "Look and feel set."); } catch (Exception e) { // exit on exception. System.err.format("Exception: %s%n", e); System.exit(0); }
fileChooser = new JFileChooser(); fileChooser.setDialogTitle("Choose a file"); // Start looking for files at the currect directory, not home. fileChooser.setCurrentDirectory(new File(".")); inputFile = null; g = new Graph(); // Select the action comboBoxList = new String[5]; comboBoxList[0] = new String("prog340: Select file and read graph"); comboBoxList[1] = new String("Deliv A"); comboBoxList[2] = new String("Deliv B"); comboBoxList[3] = new String("Deliv C"); comboBoxList[4] = new String("exit");
JComboBox actionList = new JComboBox( comboBoxList ); actionList.setName("Action List"); actionList.setSelectedIndex(0); actionList.addActionListener( this ); add( actionList, BorderLayout.PAGE_START ); } // Listen to the Combo Box public void actionPerformed( ActionEvent e ) { JComboBox cb = (JComboBox)e.getSource(); int actionIndex = cb.getSelectedIndex(); switch( actionIndex ) { case 0: g = new Graph(); readGraphInfo( g ); break; case 1: DelivA dA = new DelivA( inputFile, g ); break; case 2: DelivB dB = new DelivB( inputFile, g ); break; case 3: DelivC dC = new DelivC( inputFile, g ); break; case 4: System.out.println( "Goodbye"); System.exit(0); default: System.out.println( "Invalid choice" ); System.exit(0); } } /** Read the file containing the Strings, line by line, then process each line as it is read. **/ public void readGraphInfo( Graph g ) {
try { if (fileChooser.showOpenDialog(null) == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) {
// Instantiate the selected input and output files. inputFile = fileChooser.getSelectedFile(); System.out.println( "Chosen file = " + inputFile + " "); } // read text file Scanner sc = new Scanner( inputFile ); // First line special: It contains "~", and "val", and the nodes with the edges. String firstLine = sc.nextLine(); String[] splitString = firstLine.split( " +" ); // Ignore first two fields of first line, Every other field is a node. for ( int i = 2; i
Node n = nodeList.get( nodeIndex ); n.setName( splitString[0] ); n.setVal( splitString[1] );
for ( int i = 2; i
} sc.close();
} catch (Exception x) { System.err.format("ExceptionOuter: %s%n", x); } }
}
//DelivA that needs to be edit.
import java.io.*; import java.util.*;
// Class DelivA does the work for deliverable DelivA of the Prog340
public class DelivA {
File inputFile; File outputFile; PrintWriter output; Graph g; public DelivA( File in, Graph gr ) { inputFile = in; g = gr; // Get output file name. String inputFileName = inputFile.toString(); String baseFileName = inputFileName.substring( 0, inputFileName.length()-4 ); // Strip off ".txt" String outputFileName = baseFileName.concat( "_out.txt" ); outputFile = new File( outputFileName ); if ( outputFile.exists() ) { // For retests outputFile.delete(); } try { output = new PrintWriter(outputFile);
} catch (Exception x ) { System.err.format("Exception: %s%n", x); System.exit(0); } System.out.println( "DelivA: To be implemented"); output.println( "DelivA: To be implemented"); output.flush(); } }
Sample txt file (all whitespaces are spaced, not tabed)
A1.txt
![File outputFile; PrintWriter output; JFileChooser fileChooser; Graph g; String[] comboBoxList; // For](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f50033b9ff8_40366f50033b5a3a.jpg)
A4.txt
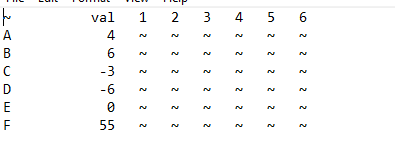
AB0.txt
ABD6.txt
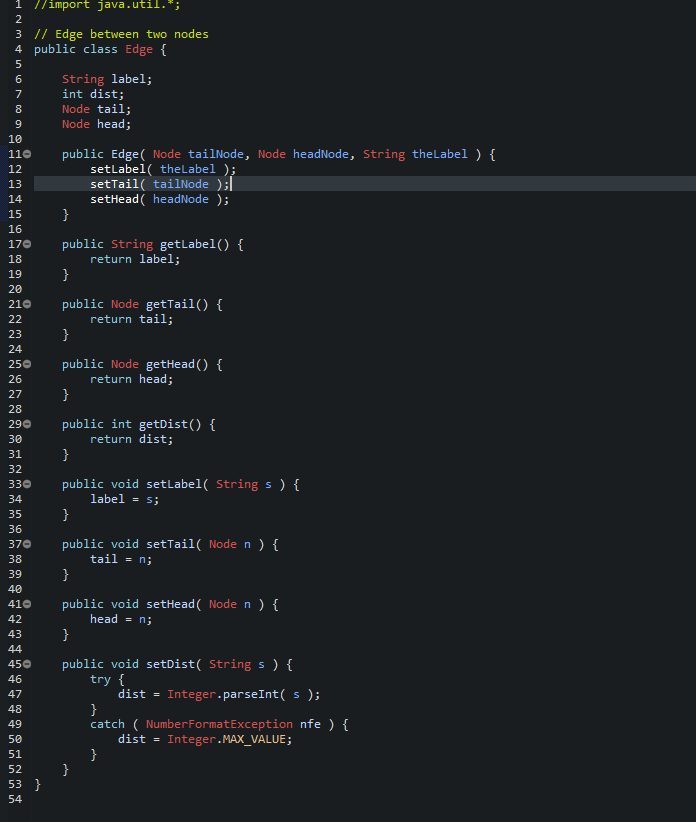
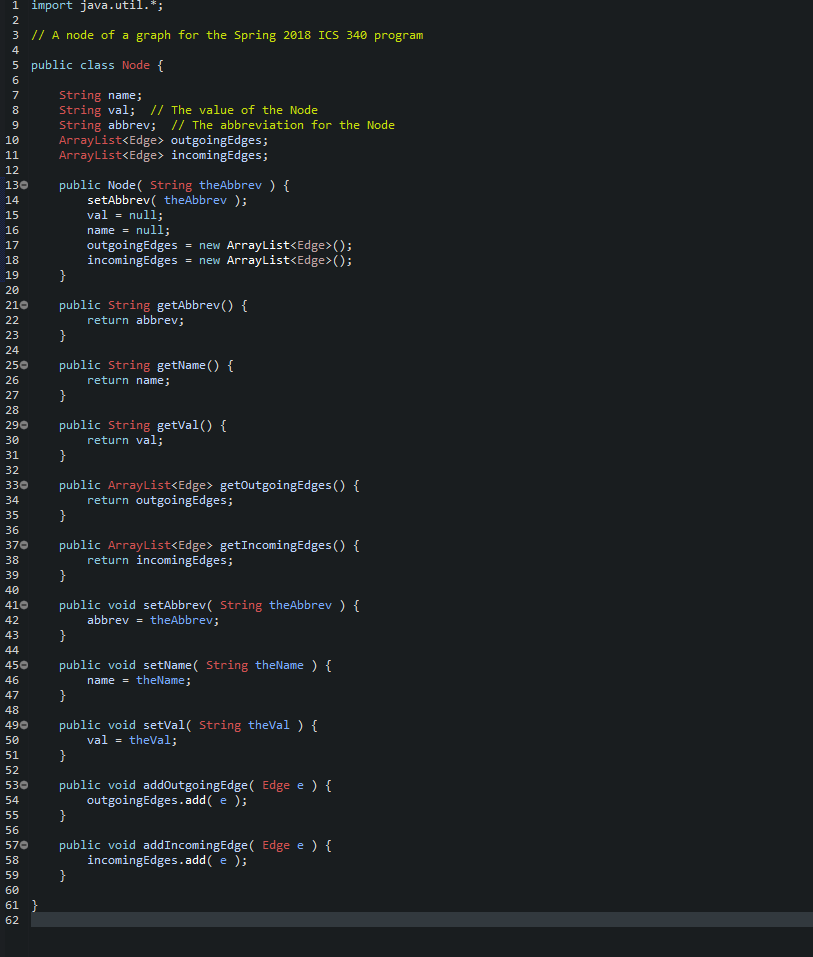
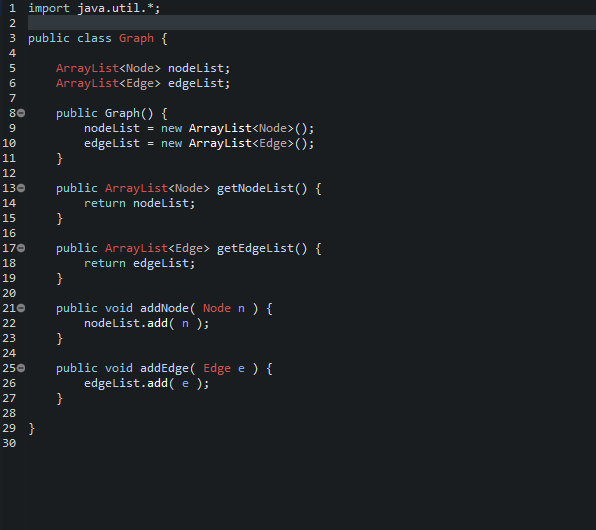
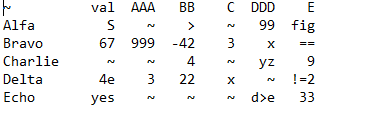
Start from a Working Program Some Java programs work on student computers but not on University lab (Windows) computers or grading computer. So this semester, you are given an initial codebase, Prog340, that seems to compile and run on all platforms. It opens a menu for you to select an action. It has a number of predefined menu items describing the various actions (which you will implement during the semester). When you start the program the first action you will want to take will be to read a file. The input files for all deliverables have the same, specified format. It allows you to continuously select actions as long as you wish o Including read another file. It allows you to exit the program. Each Deliverable will involve your modifying your existing program (DelivA involves modifying the initial program given to you). This minimizes any duplicate effort. But it means that if you screw up a deliverable, you may have screwed up another deliverable later in the course. Specification: Start with the given Java program prog340, which lets you select a file to read from your computer, reads the file, and interprets that file as the specification of a graph.? Then enhance it to do the following: 1. Write code necessary to print out, for each Edge, the name of the Node from which the Edge emanates, the name of the Node at which the Edge terminates, and the label of the Edge, in the format listed below. The prog340 handout describes the format of the input file for this and all program deliverables. As will always be the case in this class, the program must be written in Java and must run on the University Windows computer systems. Output: E fig Here is sample output for one graph. val AAA BB Alfa X > Bravo 67 999 -42 3 Charlie 4 Delta 4e 3 22 Echo yes DDD 99 X yz == 9 != 2 33 d>e The output for this file should be: Edge from Alpha to Bravo labeled >. Edge from Alpha to Delta labeled 99. Edge from Alpha to Echo labeled fig. Edge from Bravo to Alpha labeled 999. Edge from Bravo to Bravo labeled -42. Edge from Bravo to Charlie labeled 3. Edge from Bravo to Delta labeled x. Edge from Bravo to Echo labeled ==. Edge from Charlie to Bravo labeled 4. Edge from Charlie to Delta labeled yz. Edge from Charlie to Echo labeled 9. Edge from Delta to Alpha labeled 3. Edge from Delta to Bravo labeled 22. Edge from Delta to Charlie labeled x. Edge from Delta to Echo labeled !=2. Edge from Echo to Delta labeled d>e. Edge from Echo to Echo labeled 33. The order in which the Edges print out is not important. NA 19 1 //import java.util.*; 2 3 // Edge between two nodes 4 public class Edge { 5 6 String label; 7 int dist; 8 Node tail; 9 Node head; 10 110 public Edge Node tailNode, Node headNode, String theLabel ) { 12 setLabel( theLabel ); 13 setTail tailNode ); 14 setHead ( headNode ); 15 } 16 170 public String getLabel() { 18 return label; } 20 210 public Node getTail() { 22 return tail; 23 } 24 250 public Node getHead() { 26 return head; 27 } 28 290 public int getDist() { 30 return dist; 31 } 32 330 public void setLabel( String s ) { 34 label = s; 35 } 36 370 public void setTail( Node n ) { 38 tail = n; 39 } 40 410 public void setHead( Node n ) { 42 head = n; 43 } 44 450 public void setDist( String s ) { 46 try { 47 dist = Integer.parseInt(s); 48 } 49 catch (Number FormatException nfe ) { 50 dist = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 51 52 53 } 54 1 import java.util.*; 2 3 // A node of a graph for the Spring 2018 ICS 340 program 4 5 public class Node { 6 7 String name; 8 String val; // The value of the Node 9 String abbrev; // The abbreviation for the Node 10 ArrayList
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


