Question: Complete the following exercise in Java An example main and the output is provided below to show how the code should work . Some important
Complete the following exercise in Java

An example main and the output is provided below to show how the code should work.
Some important things to keep in mind

Please provide the code, some test inputs and their outputs.
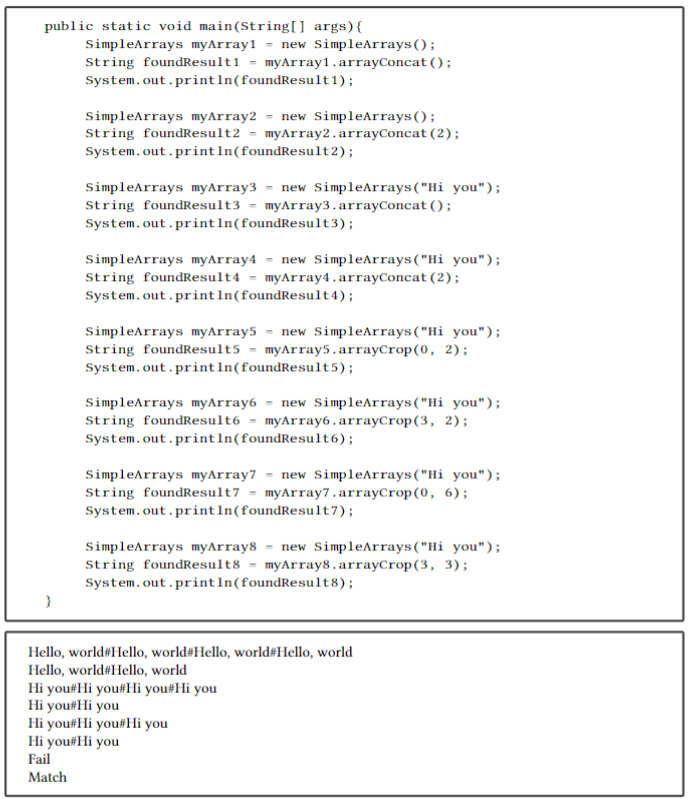
below. 1. Look at the documentation on java.util.Arrays. 2. Create a class 'SimpleArrays' which has the characteristics specified to the right! 3. You may include additional methods, but no methods beyond those specified need to be included. 4. You may use additional methods provided by java.util.Arrays, beyond those specified. public static void main(String[] args) { SimpleArrays myArray1 new SimpleArrays(); String foundResult1 - myArray1.arrayConcat(); System.out.println(foundResult 1); SimpleArrays myArray2 = new SimpleArrays(); String foundResult2 - myArray2.arrayConcat(2); System.out.println(foundResult2); SimpleArrays myArray3 = new SimpleArrays("Hi you"); String foundResult3 - myArray3. arrayConcat(); System.out.println(foundResult3); SimpleArrays myArray4 = new SimpleArrays ("Hi you"); String foundResult4 - myArray4.arrayConcat(2); System.out.println(foundResult 4); SimpleArrays myArray5 - new SimpleArrays("Hi you"); String foundResults - myArray5.arrayCrop(0, 2); System.out.println(foundResult5); SimpleArrays my Array6 = new SimpleArrays("Hi you"); String foundResult - myArray6.arrayCrop(3, 2); System.out.println(foundResult6); SimpleArrays myArray7 = new SimpleArrays("Hi you"); String foundResult7 - myArray7.arrayCrop(0, 6); System.out.println(foundResult7); SimpleArrays myArray8 = new SimpleArrays("Hi you"); String foundResult8 = myArray8.arrayCrop(3, 3); System.out.println(foundResults); Hello, world#Hello, world#Hello, world#Hello, world Hello, world#Hello, world Hi you#Hi you#Hi you#Hi you Hi you#Hi you Hi you#Hi you'Hi you Hi you#Hi you Fail Match Tip: arrayCrop() and arrayConcat() have some common behavior, which should not be implemented twice. Important: When you use dynamic array allocation for an array of objects, you only create references, not objects. Important: Remember to document your code
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


