Question: Process fluid is heated in a series of three stirred tank heaters of the same size. Steam TC Tup(s) where: Steam 2=const G.(s) Controller
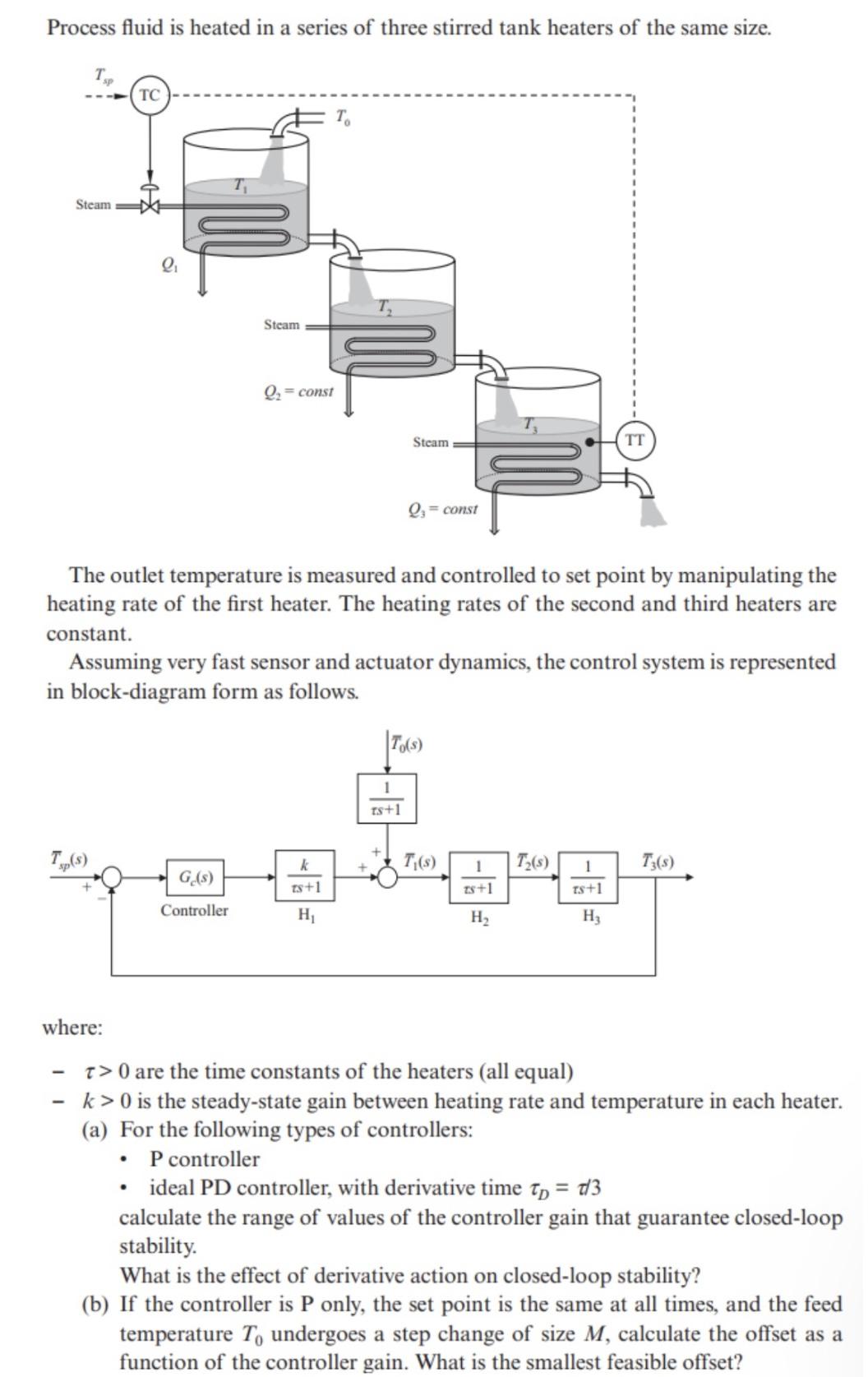
Process fluid is heated in a series of three stirred tank heaters of the same size. Steam TC Tup(s) where: Steam 2=const G.(s) Controller To The outlet temperature is measured and controlled to set point by manipulating the heating rate of the first heater. The heating rates of the second and third heaters are constant. Assuming very fast sensor and actuator dynamics, the control system is represented in block-diagram form as follows. k ts+1 H Steam Q=const 1 ts+1 To(s) TT T(s) 1 T(s) 1 zs+1 TS+1 H H3 T3(s) T> 0 are the time constants of the heaters (all equal) k>0 is the steady-state gain between heating rate and temperature in each heater. (a) For the following types of controllers: P controller ideal PD controller, with derivative time t = d/3 calculate the range of values of the controller gain that guarantee closed-loop stability. What is the effect of derivative action on closed-loop stability? (b) If the controller is P only, the set point is the same at all times, and the feed temperature To undergoes a step change of size M, calculate the offset as a function of the controller gain. What is the smallest feasible offset?
Step by Step Solution
3.52 Rating (149 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


