Question: Consider a composite solid of materials A and B, shown in the Figure 1. An electrical resistance heater embedded in solid B generates heat at
Consider a composite solid of materials A and B, shown in the Figure 1.
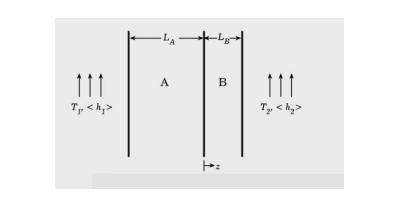
An electrical resistance heater embedded in solid B generates heat at a constant volumetric rate of q (W/m 3 ). The composite solid is cooled from both sides to avoid excessive heating. Figure 1: Composite solid of materials A and B component with heat generation embedded in solid B
(a) Obtain expressions for the steady temperature distributions in solids A and B. [ 5 Marks]
(b) Calculate the rate of heat loss from the surfaces located at z = L A and z = L B.. [ 5 Marks]
(c) For the following numerical values, T 1 = 5oC, T 2 = 25oC, k A = 180 W/mK h 1 = 500 W/m 2K, h 2 = 10 W/m 2K ,k B = 1.2 W/mK, L A = 36 cm, L B = 3 cm, Calculate the value of q to keep the surface temperature of the wall at z = L A constant at 15oC. [10 Marks]
(d) Obtain the temperature distribution in solid A when the thickness of solid B is very small, and draw the thermal resistance circuit . A practical application of this case is the use of a surface heater, i.e., a very thin plastic film containing electrical resistance, to clear condensation and ice from the rear window of your car or condensation from the mirror in your bathroom. [10 Marks]
LA 111 A B 111 T,
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


