Question: Consider a dataset with 2 points in ID: (x = 0, y = -1) and (x2 = 2, y2 = 1). Map each point
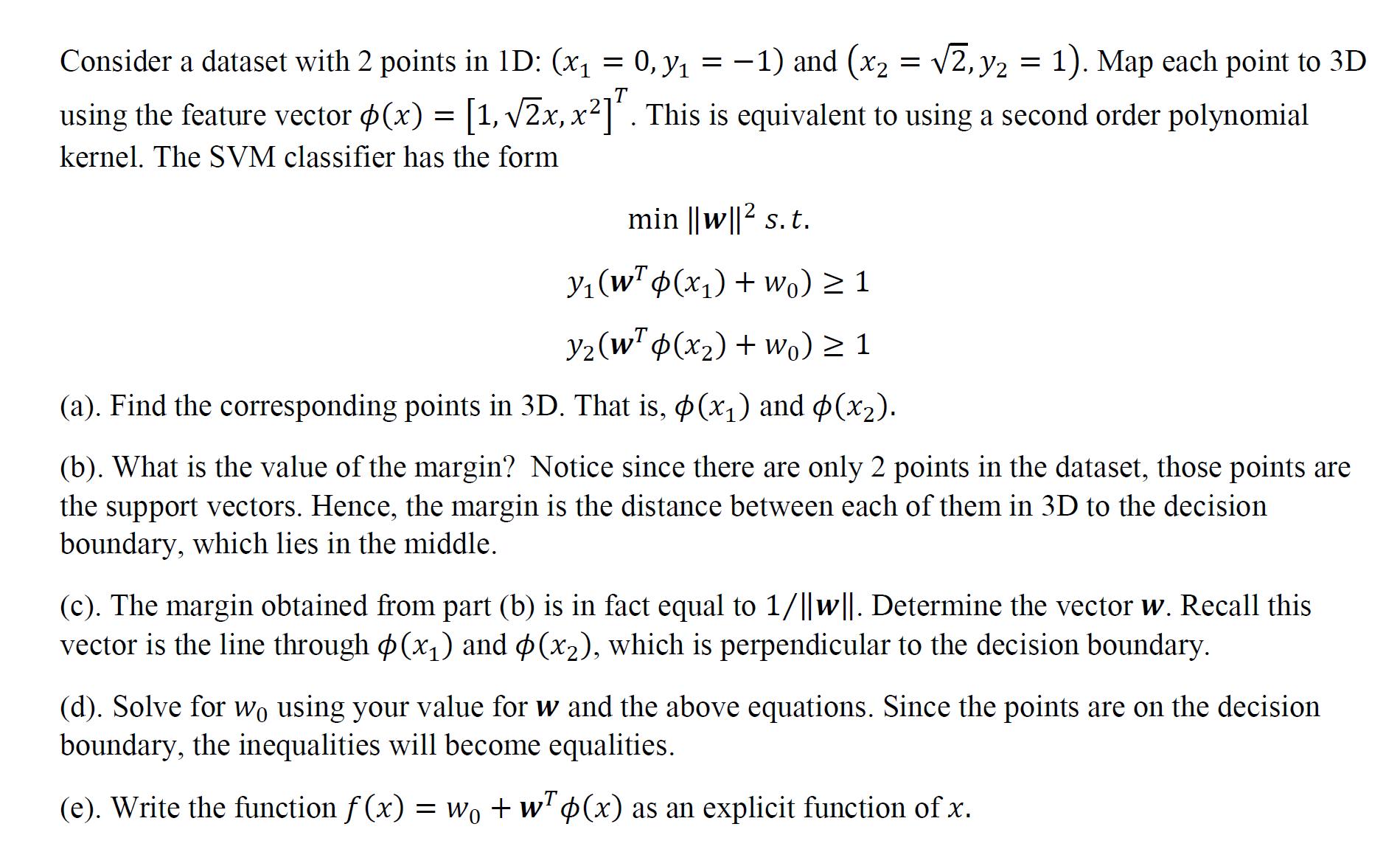
Consider a dataset with 2 points in ID: (x = 0, y = -1) and (x2 = 2, y2 = 1). Map each point to 3D using the feature vector (x) = [1, 2x, x]. This is equivalent to using a second order polynomial kernel. The SVM classifier has the form min ||w||2 s.t. Y(WT (x1) + Wo) 1 Y2(w (x2) + wo) 1 (a). Find the corresponding points in 3D. That is, (x) and (x2). (b). What is the value of the margin? Notice since there are only 2 points in the dataset, those points are the support vectors. Hence, the margin is the distance between each of them in 3D to the decision boundary, which lies in the middle. (c). The margin obtained from part (b) is in fact equal to 1/||w||. Determine the vector w. Recall this vector is the line through (x) and (x2), which is perpendicular to the decision boundary. (d). Solve for wo using your value for w and the above equations. Since the points are on the decision boundary, the inequalities will become equalities. (e). Write the function f(x) = w + w(x) as an explicit function of x.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


