Question: Consider a network shown in Figure above. A Poisson stream of packets has arrival rate lambda packets / sec and exponentially distributed packet lengths
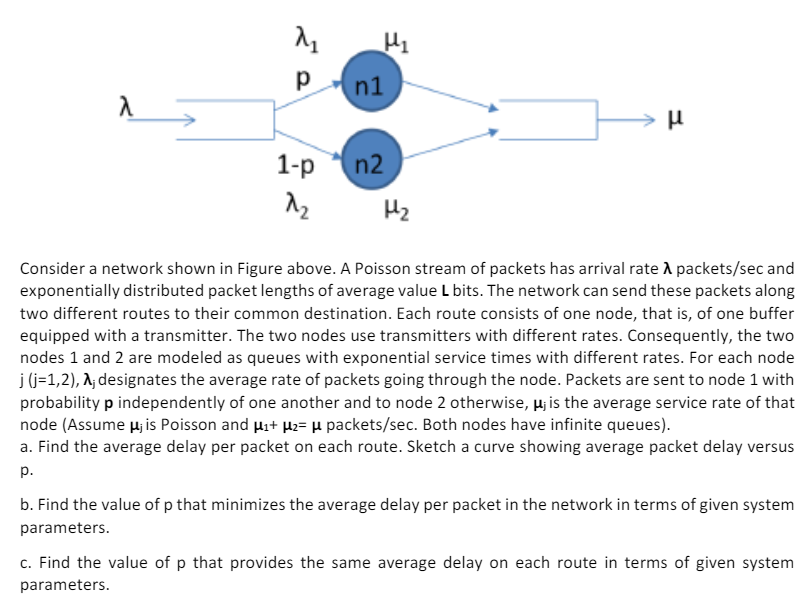
Consider a network shown in Figure above. A Poisson stream of packets has arrival rate lambda packetssec and
exponentially distributed packet lengths of average value L bits. The network can send these packets along
two different routes to their common destination. Each route consists of one node, that is of one buffer
equipped with a transmitter. The two nodes use transmitters with different rates. Consequently, the two
nodes and are modeled as queues with exponential service times with different rates. For each node
jjlambda j designates the average rate of packets going through the node. Packets are sent to node with
probability p independently of one another and to node otherwise, mu j is the average service rate of that
node Assume mu j is Poisson and mu mu mu packetssec Both nodes have infinite queues
a Find the average delay per packet on each route. Sketch a curve showing average packet delay versus
p
b Find the value of p that minimizes the average delay per packet in the network in terms of given system
parameters.
c Find the value of p that provides the same average delay on each route in terms of given system
parameters.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


