Question: Consider a single-input, single-output linear system P yk+1 = >[aiyk-i + biuk-i] + Wk+1. i=0 The input ux and the output yx can be measured
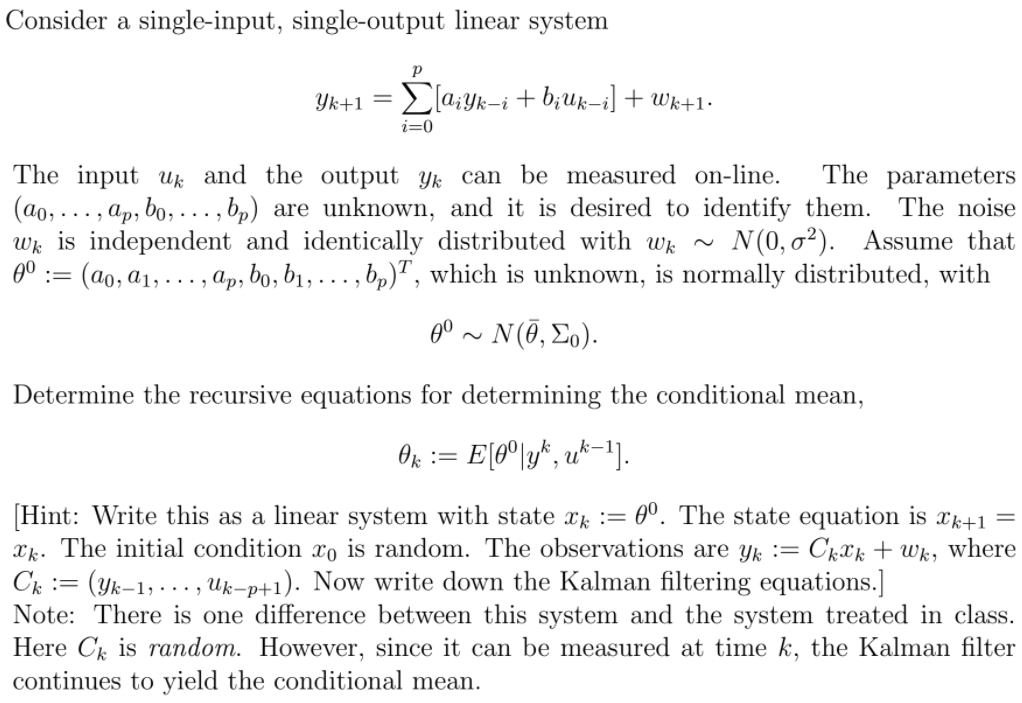
Consider a single-input, single-output linear system P yk+1 = >[aiyk-i + biuk-i] + Wk+1. i=0 The input ux and the output yx can be measured on-line. The parameters (do, . .., ap, bo, . .., bp) are unknown, and it is desired to identify them. The noise wx is independent and identically distributed with Wk ~ N(0, o?). Assume that 90 := (do, a1, . . ., ap, bo, b1, . .., bp) , which is unknown, is normally distributed, with 80 ~ N(0, Zo). Determine the recursive equations for determining the conditional mean, OK : = E[0lyk, uk-1]. Hint: Write this as a linear system with state Ck := 0. The state equation is Ck+1 = Xk. The initial condition To is random. The observations are yk := Ckk + Wk, where Ck := (yk-1, . .., Uk-p+1). Now write down the Kalman filtering equations.] Note: There is one difference between this system and the system treated in class. Here Ck is random. However, since it can be measured at time k, the Kalman filter continues to yield the conditional mean
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


