Question: Consider a three-period model, with t=0 representing the first date and t=3 the last date. There are two assets: the risk-free bank account and the
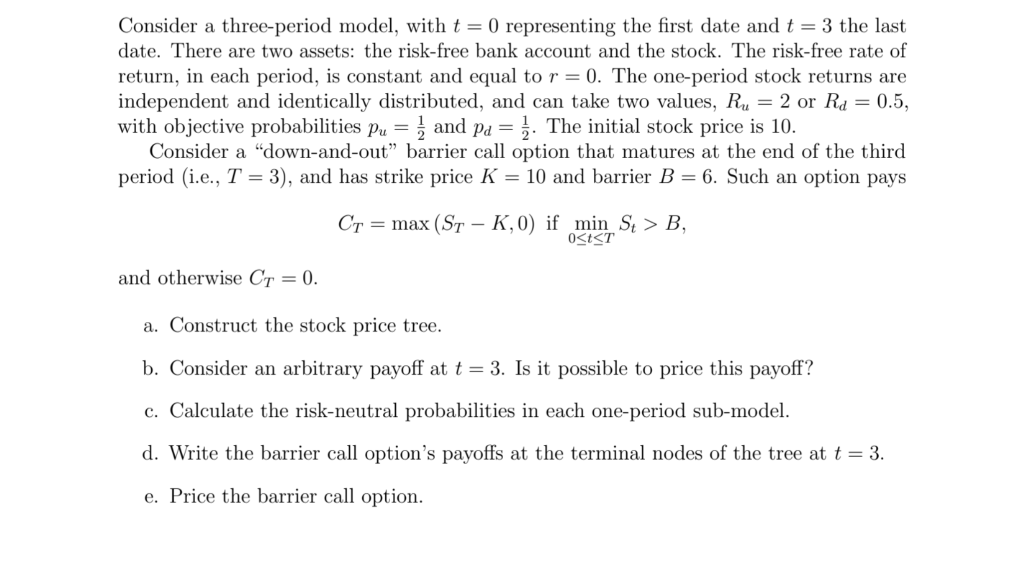
Consider a three-period model, with t=0 representing the first date and t=3 the last date. There are two assets: the risk-free bank account and the stock. The risk-free rate of return, in each period, is constant and equal to r=0. The one-period stock returns are independent and identically distributed, and can take two values, Ru=2 or Rd=0.5, with objective probabilities pu=21 and pd=21. The initial stock price is 10 . Consider a "down-and-out" barrier call option that matures at the end of the third period (i.e., T=3 ), and has strike price K=10 and barrier B=6. Such an option pays CT=max(STK,0)ifmin0tTSt>B, and otherwise CT=0 a. Construct the stock price tree. b. Consider an arbitrary payoff at t=3. Is it possible to price this payoff? c. Calculate the risk-neutral probabilities in each one-period sub-model. d. Write the barrier call option's payoffs at the terminal nodes of the tree at t=3. e. Price the barrier call option. Consider a three-period model, with t=0 representing the first date and t=3 the last date. There are two assets: the risk-free bank account and the stock. The risk-free rate of return, in each period, is constant and equal to r=0. The one-period stock returns are independent and identically distributed, and can take two values, Ru=2 or Rd=0.5, with objective probabilities pu=21 and pd=21. The initial stock price is 10 . Consider a "down-and-out" barrier call option that matures at the end of the third period (i.e., T=3 ), and has strike price K=10 and barrier B=6. Such an option pays CT=max(STK,0)ifmin0tTSt>B, and otherwise CT=0 a. Construct the stock price tree. b. Consider an arbitrary payoff at t=3. Is it possible to price this payoff? c. Calculate the risk-neutral probabilities in each one-period sub-model. d. Write the barrier call option's payoffs at the terminal nodes of the tree at t=3. e. Price the barrier call option
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


