Question: Consider the following weighted undirected graph. 2 7 a C e 3 4 5 1 8 b d 9 6 Suppose Kruskal's algorithm is
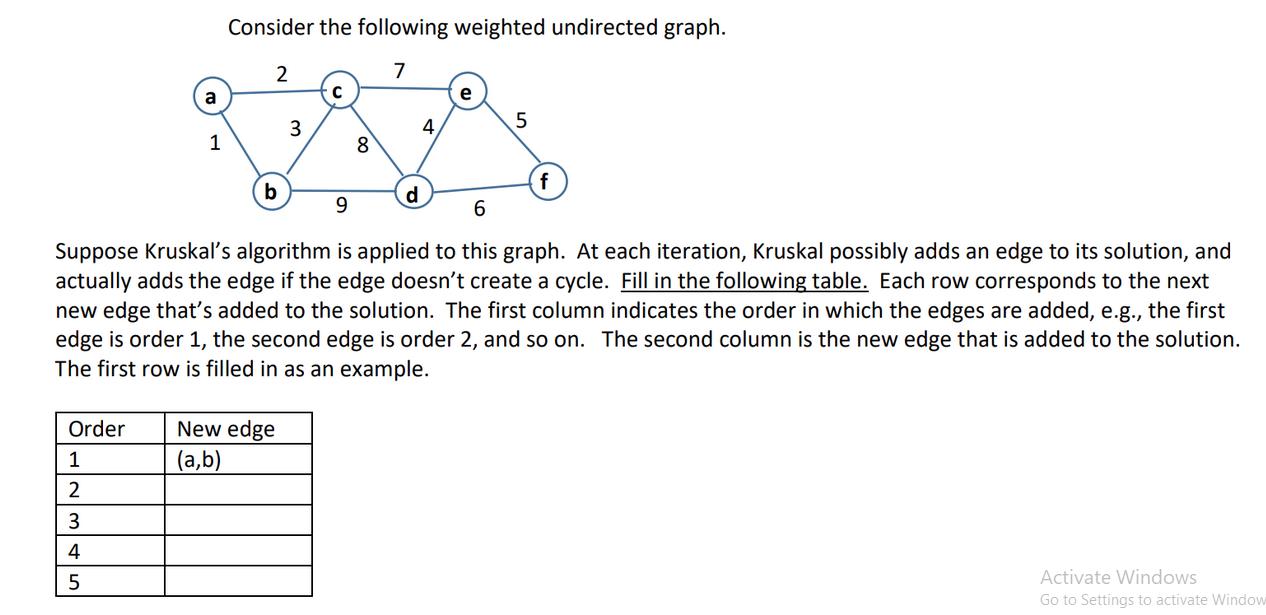
Consider the following weighted undirected graph. 2 7 a C e 3 4 5 1 8 b d 9 6 Suppose Kruskal's algorithm is applied to this graph. At each iteration, Kruskal possibly adds an edge to its solution, and actually adds the edge if the edge doesn't create a cycle. Fill in the following table. Each row corresponds to the next new edge that's added to the solution. The first column indicates the order in which the edges are added, e.g., the first edge is order 1, the second edge is order 2, and so on. The second column is the new edge that is added to the solution. The first row is filled in as an example. Order 1 New edge (a,b) 2 3 4 5 Activate Windows Go to Settings to activate Window
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (161 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The weights are as follows EdgeWeight Ca2 ab3 ae5 bd6 df8 ef9 Ce123 We... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


