Question: Considering the below network diagram below, answer the following questions. 10.10.100.0 Net segment FAQ/2 Router A Router B 10.10.200.0 Net FA0/1 FA0/2 FA0/0 segment
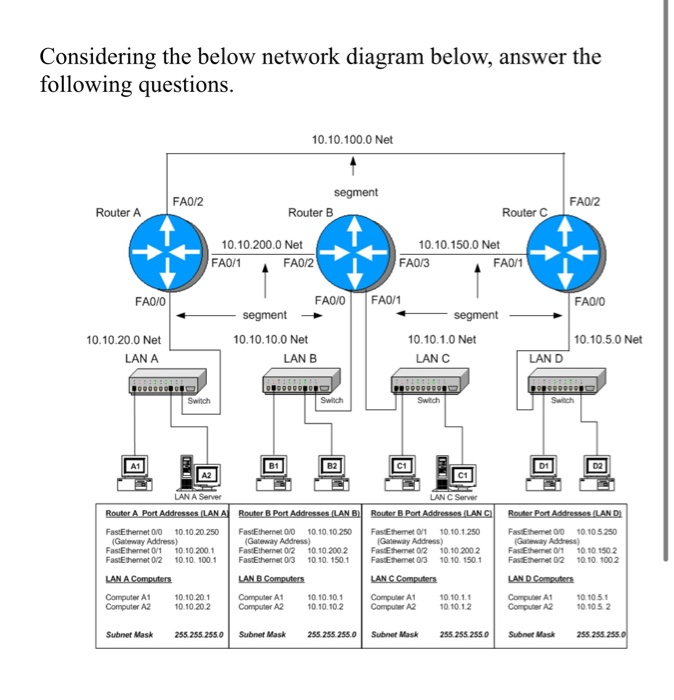
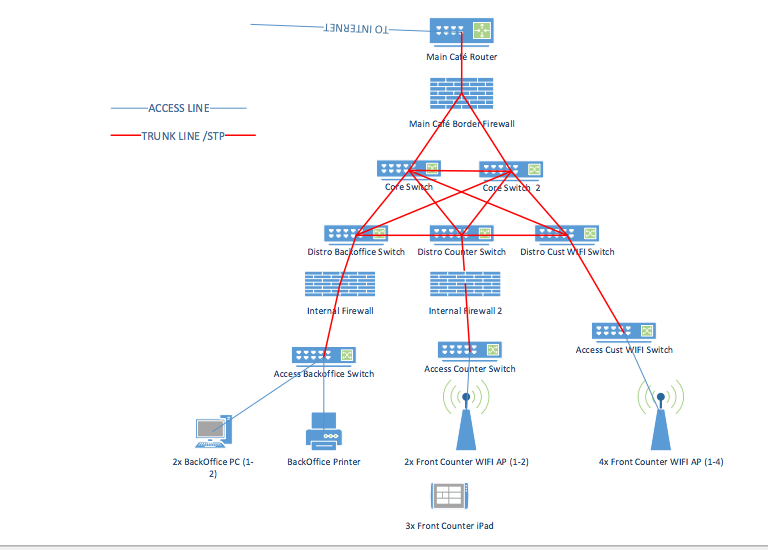
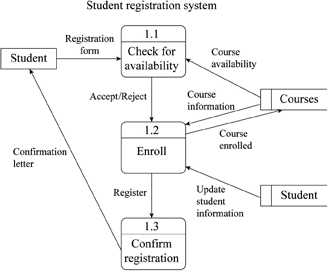
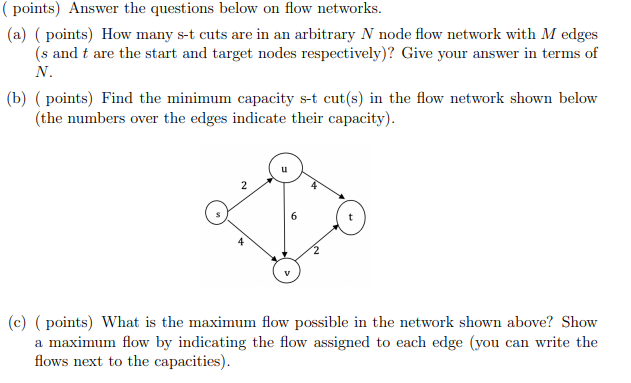
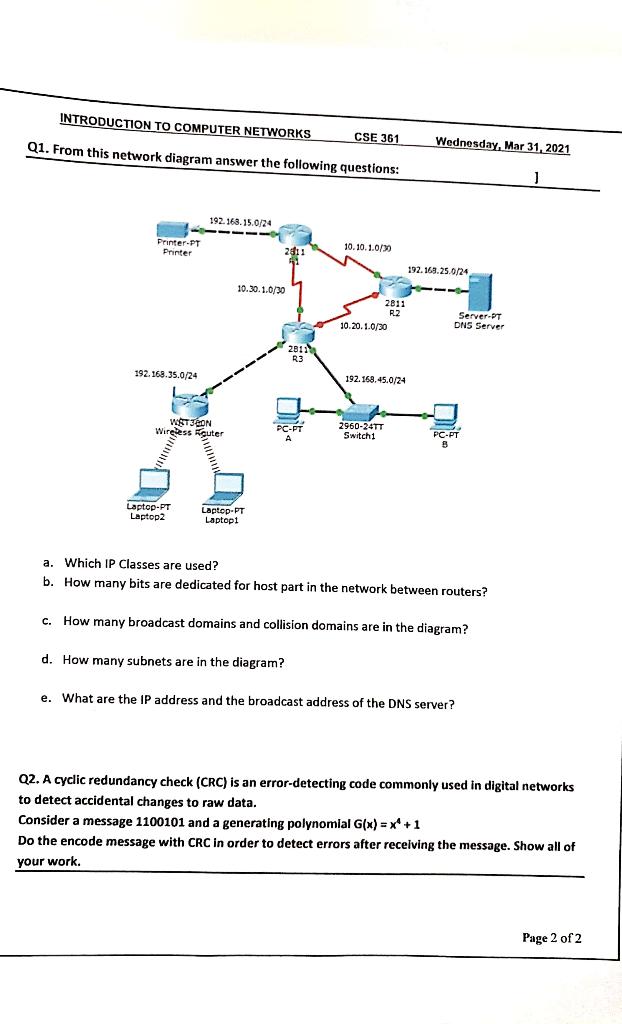
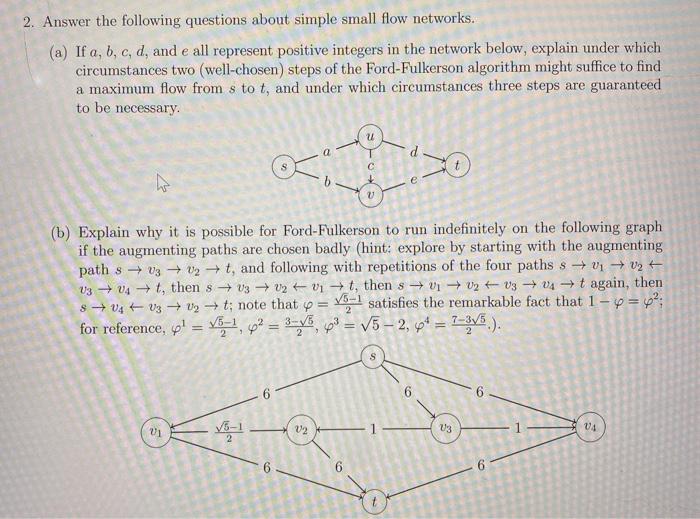
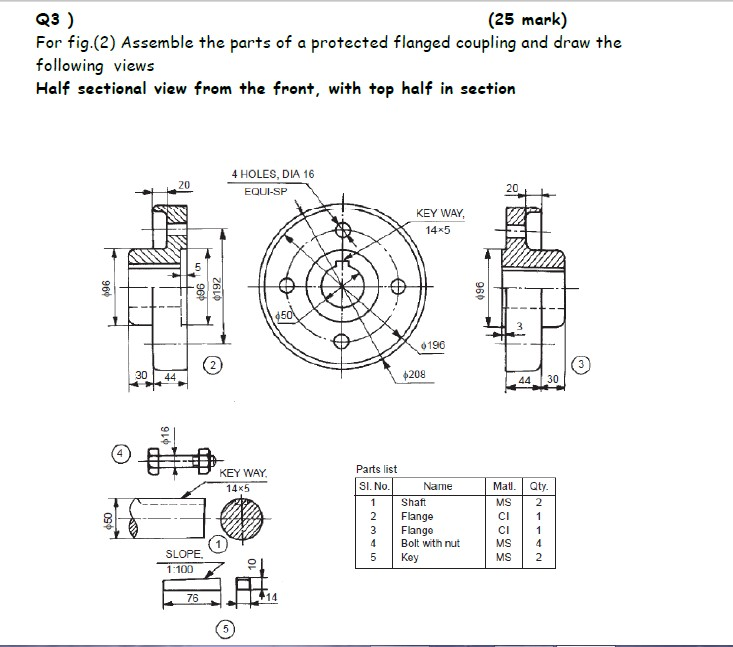
Considering the below network diagram below, answer the following questions. 10.10.100.0 Net segment FAQ/2 Router A Router B 10.10.200.0 Net FA0/1 FA0/2 FA0/0 segment 10.10.20.0 Net LAN A 10.10.10.0 Net LAN B A1 Switch A2 FA0/2 Router C 10.10.150.0 Net FA0/3 FA0/1 FA0/0 FA0/1 FADIO segment 10.10.1.0 Net 10.10.5.0 Net LAN C LAND Switch Switch D1 C1 Switch (Gateway Address) (Gateway Address) FastEthernet0/1 10.10.200.1 FastEthernet 0/2 10.10.200.2 FastEthernet0/2 10.10.100.1 FastEthernet0/3 10.10.150.1 LAN A Computers LAN B Computers LAN A Server LAN C Server Router A Port Addresses (LAN A Router B Port Addresses (LAN B) Router B Port Addresses (LAN C FastEthernet0/0 10.10.20.250 FastEthernet 0/0 10.10.10.250 FastEthernet0/1 10.10.1.250 (Gateway Address) FastEthernet 0/2 FastEthernet0/3 LAN C Computers 10.10.200.2 10.10.150.1 Router Port Addresses (LAND) FastEthernet0/0 10.10.5.250 (Gateway Address) FastEthernet0/1 10.10.150.2 FastEthernet02 LAN D Computers 10.10.100.2 Computer A1 Computer A2 10.10.20.1 10.10.20.2 Computer A1 Computer A2 10.10.10.1 10.10.10.2 Computer A1 Computer A2 10.10.1.1 10.10.1.2 Computer A1 Computer A2 10.10.5.1 10.10.5.2 Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 -ACCESS LINE- -TRUNK LINE/STP- Main Caf Router Main Caf Border Firewall Core Switch Core Switch 2 Distro Backoffice Switch Distro Counter Switch Distro Cust WIFI Switch Internal Firewall Internal Firewall 2 Access Cust WIFI Switch Access Counter Switch Access Backoffice Switch 2x BackOffice PC (1- BackOffice Printer 2x Front Counter WIFI AP (1-2) 4x Front Counter WIFI AP (1-4) 2) 3x Front Counter iPad Student registration system 1.1 Registration form Check for Student availability Course availability Accept/Reject Course Courses Confirmation letter information 1.2 Course enrolled Enroll Register 1.3 Confirm registration Update Student student information (points) Answer the questions below on flow networks. (a) (points) How many s-t cuts are in an arbitrary N node flow network with M edges (s and t are the start and target nodes respectively)? Give your answer in terms of N. (b) (points) Find the minimum capacity s-t cut(s) in the flow network shown below (the numbers over the edges indicate their capacity). 2 4 (c) (points) What is the maximum flow possible in the network shown above? Show a maximum flow by indicating the flow assigned to each edge (you can write the flows next to the capacities). INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKS Q1. From this network diagram answer the following questions: CSE 361 Wednesday, Mar 31, 2021 ] 192.168.15.0/24 Printer-PT Printer 10.10.1.0/30 2811 192.168.25.0/24 10.30.1.0/30 2811 R2 10.20.1.0/30 2811 R3 192.168.35.0/24 192.168.45.0/24 WSTON Wireless guter Laptop-PT Laptop2 Laptop-PT Laptop1 Server-PT DNS Server PC-PT A 2960-24TT Switch1 PC-PT B a. Which IP Classes are used? b. How many bits are dedicated for host part in the network between routers? c. How many broadcast domains and collision domains are in the diagram? d. How many subnets are in the diagram? e. What are the IP address and the broadcast address of the DNS server? Q2. A cyclic redundancy check (CRC) is an error-detecting code commonly used in digital networks to detect accidental changes to raw data. Consider a message 1100101 and a generating polynomial G(x) = x+1 Do the encode message with CRC in order to detect errors after receiving the message. Show all of your work. Page 2 of 2 2. Answer the following questions about simple small flow networks. (a) If a, b, c, d, and e all represent positive integers in the network below, explain under which circumstances two (well-chosen) steps of the Ford-Fulkerson algorithm might suffice to find a maximum flow from s to t, and under which circumstances three steps are guaranteed to be necessary. V (b) Explain why it is possible for Ford-Fulkerson to run indefinitely on the following graph if the augmenting paths are chosen badly (hint: explore by starting with the augmenting paths3v2t, and following with repetitions of the four paths s 111 V3 V4t, then sv3 v2 vt, then svv2 v3 v4t again, then 8v4v3v2t; note that = satisfies the remarkable fact that 1-4=2; for reference, p= 1, 62 = 33, 63 = 5-2, 4 = 7-3/5). 2 2 2 5 6 U3 V2 6 6 V4 Q3) (25 mark) For fig.(2) Assemble the parts of a protected flanged coupling and draw the following views Half sectional view from the front, with top half in section 960 - 20 4 HOLES, DIA 16 EQUI-SP 30 44 $16 96 $192 SLOPE. 1:100 76 450 20 KEY WAY, 145 960 $208 196 3 44 30 Parts list KEY WAY, 145 Sl. No. Name Matl. Qty. 1 Shaft MS 2 2 Flange CI 1 3 Flange CI 1 4 Bolt with nut MS 4 5 Key MS 2 5 14 (3)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
It seems that the question ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


