Question: Describe, with examples, how a project manager on a project you have observed did or did not exhibit desirable project manager behaviors as described inDesired
Describe, with examples, how a project manager on a project you have observed did or did not exhibit desirable project manager behaviors as described inDesired Project Manager Behaviors
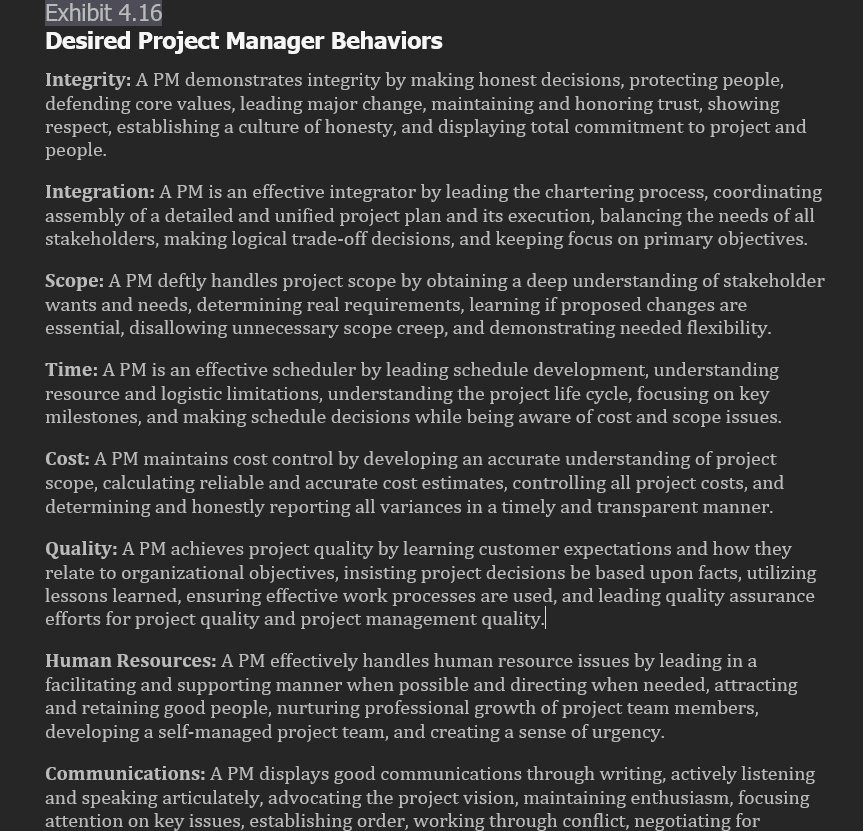
Integrity: A PM demonstrates integrity by making honest decisions, protecting people,
defending core values, leading major change, maintaining and honoring trust, showing
respect, establishing a culture of honesty, and displaying total commitment to project and
people.
Integration: A PM is an effective integrator by leading the chartering process, coordinating
assembly of a detailed and unified project plan and its execution, balancing the needs of all
stakeholders, making logical tradeoff decisions, and keeping focus on primary objectives.
Scope: A PM deftly handles project scope by obtaining a deep understanding of stakeholder
wants and needs, determining real requirements, learning if proposed changes are
essential, disallowing unnecessary scope creep, and demonstrating needed flexibility.
Time: A PM is an effective scheduler by leading schedule development, understanding
resource and logistic limitations understanding the project life cycle, focusing on key
milestones, and making schedule decisions while being aware of cost and scope issues.
Cost: A PM maintains cost control by developing an accurate understanding of project
scope, calculating reliable and accurate cost estimates, controlling all project costs, and
determining and honestly reporting all variances in a timely and transparent manner.
Quality: A PM achieves project quality by learning customer expectations and how they
relate to organizational objectives, insisting project decisions be based upon facts, utilizing
lessons learned, ensuring effective work processes are used, and leading quality assurance
efforts for project quality and project management quality.
Human Resources: A PM effectively handles human resource issues by leading in a
facilitating and supporting manner when possible and directing when needed, attracting
and retaining good people, nurturing professional growth of project team members,
developing a selfmanaged project team, and creating a sense of urgency.
Communications: A PM displays good communications through writing, actively listening
and speaking articulately, advocating the project vision, maintaining enthusiasm, focusing
attention on key issues, establishing order, working through conflict, negotiating forDesired Project Manager Behaviors
Integrity: A PM demonstrates integrity by making honest decisions, protecting people,
defending core values, leading major change, maintaining and honoring trust, showing
respect, establishing a culture of honesty, and displaying total commitment to project and
people.
Integration: A PM is an effective integrator by leading the chartering process, coordinating
assembly of a detailed and unified project plan and its execution, balancing the needs of all
stakeholders, making logical tradeoff decisions, and keeping focus on primary objectives.
Scope: A PM deftly handles project scope by obtaining a deep understanding of stakeholder
wants and needs, determining real requirements, learning if proposed changes are
essential, disallowing unnecessary scope creep, and demonstrating needed flexibility.
Time: A PM is an effective scheduler by leading schedule development, understanding
resource and logistic limitations understanding the project life cycle, focusing on key
milestones, and making schedule decisions while being aware of cost and scope issues.
Cost: A PM maintains cost control by developing an accurate understanding of project
scope, calculating reliable and accurate cost estimates, controlling all project costs, and
determining and honestly reporting all variances in a timely and transparent manner.
Quality: A PM achieves project quality by learning customer expectations and how they
relate to organizational objectives, insisting project decisions be based upon facts, utilizing
lessons learned, ensuring effective work processes are used, and leading quality assurance
efforts for project quality and project management quality.
Human Resources: A PM effectively handles human resource issues by leading in a
facilitating and supporting manner when possible and directing when needed, attracting
and retaining good people, nurturing professional growth of project team members,
developing a selfmanaged project team, and creating a sense of urgency.
Communications: A PM displays good communications through writing, actively listening
and speaking articulately, advocating the project vision, maintaining enthusiasm, focusing
attention on key issues, establishing order, working through conflict, negotiating for
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


